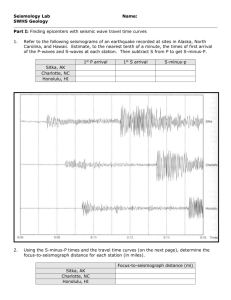
Student guided notes
advertisement

Crustal Movement Notes I. II. Continental Drift a. 1912 Alfred Wagner proposed that Europe and Africa fit together like puzzle pieces. i. Continental Drift 1. Continents floated in oceans ii. Pangea – Large super continent from 350 million years ago that split up to form todays continents. iii. Evidence 1. ___________________________ 2. ___________________________ 3. ___________________________ 4. ___________________________ b. Evidence from the oceans (Start of problems for CD) i. Sonar – Saw underwater volcanoes and mountain ranges called ridges. 1. ___________________________________________________________ ii. Magnetic reversals 1. ___________________________________________________________ 2. Every 10,000 years a reversal occurs Plate Tectonics a. ________________________________________________________________________ b. Convection currents in the mantle move plates. i. Hot magma rises while cooler magma sinks. Plate Boundary Notes I. II. III. IV. V. Plate Boundaries a. _____________________________________________ b. Average rate of movement I 3 cm/year or speed you finger nails grow. Convergent a. _________________________________________________________ b. Subduction zone – ________________________________________________________ c. Trench – Deep troughs were crust is being pushed down and disappearing. d. Volcanoes ___, Earthquakes ____, Tsunamis _____ Divergent a. Two (2) plates moving apart from each other. b. Mid-ocean ridge or rift c. Volcanoes ___, Earthquakes _____, Tsunamis_____ Transform a. ________________________________________ b. Volcanoes ___, Earthquakes ___, Tsunamis ___ Hot spots a. ________________________________________________________________________ b. Random but does show direction of movement. Earthquake Notes I. II. Earthquake a. Movement or vibration of the crust from crustal movement i. Epicenter-______________________________________ ii. Focus-__________________________________________ iii. Fault-___________________________________________ iv. Seismic waves-____________________________________ b. Seismic waves i. P-Waves (Primary) 1. ________________________________ 2. ___________________________________ ii. S-Waves (Secondary) 1. ________________________________ 2. ____________________________________ iii. Others 1. Love (L-waves) and Ray (R-waves) c. Scales i. Richter – _____________________________________________________ ii. Mercalli – _____________________________________________________ How to locate an earthquake epicenter a. S-P time b. Use ESRT c. Draw circle around city d. Repeat at least three times. Earthquake location Notes I. II. III. IV. V. VI. VII. VIII. Steps to find an epicenter: a. Arrival times b. Difference c. ESRT 11 d. Draw circle e. Repeat 2 more times ESRT page 11 a. Each line on time (y-axis) equals? ___________ b. Each line on distance (x-axis) equals? ___________ Step 1 a. Find the P and S arrive times Step 2 a. Subtract P and S waves. b. Using time you must out in hr:min:sec (00:00:00) and use 24 time scale. c. 00:08:00 00:04:00 ??? Step 3 a. Using the ESRT pg 11 b. Find a piece of scrap paper and mark off 0 and the time you just found on the y axis mark on your scrap paper. c. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ d. Follow line on graph down to bottom of chart and there is your distance. Step 4 a. Using the map and the scale set a drawing compass to the distance you calculated from the ESRT pg 11 chart. b. ________________________________________________________________________ Step 5 a. ________________________________________________________________________ P-wave travel time a. ________________________________________________________________________ b. Use the epicenter distance and on the ESRT pg 11 go up to the P curve. c. Read off the time and that’s it! IX. Practice (don’t use a calculator, it doesn’t work!!) 12:00:00 11:34:30 01:21:10 -11:55:30 -11:30:50 -01:18:18 Station Arrival Arrival S-P time Distance (City) P-wave S-wave +/- (00:00:30) +/- (200km) A 11:55:30 12:00:00 B 11:30:50 11:34:30 C 01:18:18 01:21:10 P-wave travel time Tsunamis I. II. III. IV. V. Tsunami a. _______________________________!!!! b. _______________________________ c. Large wave that uses the whole water column to transfer energy. Size a. _____________________________________________ b. _______________________________________________ Causes a. ______________________________________________ b. __________________________________________________ Issues with tsunamis (hazards) a. Flooding b. Waves are very fast c. Knock over buildings d. Destroy roads e. Destroys everything it touches Predictions a. Bouys in the ocean move up or down normally, but when they move extreme it sets off an alarm. b. Also if there is an earthquake centered underwater there might be a tsunami.