Chapter 2 Vocabulary
advertisement

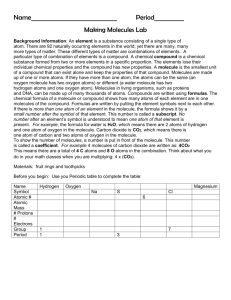
Chapter 2 Vocabulary 1. Atom- basic unit of matter. 2. Nucleus- the center of the atom which contains the protons and the neutrons; in cells, structure that contains the cells genetic material (DNA) and controls the cells activities. 3. Electron- negatively charged particle; located outside the atomic nucleus. 4. Element- substance consisting entirely of one type of atom. 5. Isotope- atom of an element that has a number of neutrons different from that of other atoms of the same element. 6. Compound- substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in definite proportions. 7. Ionic bond- bond formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another. 8. Ion- atom that has a positive or negative charge. 9. Covalent bond- bond formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms. 10. Molecule- smallest unit of most compounds. 11. Van der waals forces- a slight attraction that develops between the oppositely charged regions of nearby molecules. 12. cohesion- attraction between molecules of the same substance 13. adhesion- attraction between molecules of different substances; in plants, attraction between unlike molecules. 14. mixture- material composed of two or more elements or compounds that are physically mixed together but not chemically combined. 15. solution- mixture of two or more substances in which the molecules of the substances are evenly distributed. 16. solute- substance that is dissolved in a solvent to make a solution. 17. solvent- substance in which a solute is dissolved to form a solution. 18. suspension- mixture of water and non-dissolved materials. 19. pH scale- measurement system used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; ranges from 0-14. 20. acid- compound that forms hydrogen ions (H+) in solution. 21. base- compound that produces hydroxide ions (OH+) in solution. 22. buffer- weak acid or base that can react with strong acids or bases to help prevent sharp, sudden changes in pH. 23. monomer- small unit that can join together with other small units to form polymers. 24. polymer- large compound formed from combinations of many monomers. 25. carbohydrate- compound made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms; major source of energy for the human body. 26. monosaccharide- single sugar molecule 27. polysaccharide- large macromolecule formed from monosaccharides 28. lipid- macromolecule made mainly from carbon, and hydrogen atoms; includes, fats, oils, and waxes. 29. nucleic acid- macromolecule containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus. 30. nucleotide- monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. 31. ribonucleic acid (RNA) – single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose. 32. deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)- nucleic acid that contains the sugar deoxyribose. 33. protein- macromolecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen; needed by the body for growth and repair and to make up enzymes. 34. amino acid- compound with an amino group (-NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (-COOH) on the other end. 35. chemical reaction- process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals. 36. reactant- element or compound that enters into a chemical reaction. 37. product- element or compound produced by a chemical reaction. 38. activation energy- energy needed to get a reaction started 39. catalyst- substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction. 40. enzyme- protein that acts as a biological catalyst. 41. substrate- reactant of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction