Externality Factor Markets Public Goods Practice Exam
advertisement

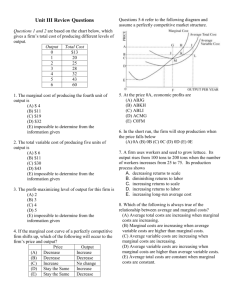
1. A public good is A) consumed by only one person who does not have to pay for it B) consumed by everyone simultaneously, even if they do not pay for it C) consumed by only one person who has to pay for it D) consumed by everyone simultaneously, as long as they pay for it 2. Competitive markets will generally produce A) too much of a public good B) the efficient amount of a public good C) the efficient amount of a public good in the short run, but not in the long run D) too little of the public good 3. Which of the following are associated with public goods? I. Free riders II. Adding demand curves vertically to find the demand curve for society III. Nonrivalry in consumption IV. Nonexcludability A) I and II only B) I and IV only C) II and III only D) I, III, and IV only E) I, II, III, and IV 4. If there is an external cost from making paper, an unregulated competitive market produces A) less than the efficient quantity B) the efficient quantity C) a quantity that could be greater than, the same as, or less than the efficient amount D) more than the efficient quantity 5. An externality is a cost or a benefit from an economic transaction that falls on A) people who did not participate in the transaction B) consumers of the good but not producers C) producers of the good but not consumers D) both consumers and producers of the good 6. An example of an activity that generates an external cost is A) planting flowers along an interstate highway B) dumping soapsuds into a trout stream C) eating an apple D) national defense services 7. If a market for a good is producing a negative externality, A. at the market output the marginal costs to society exceed the private marginal costs of production. B. at the market output the marginal benefits to society exceed the private marginal costs of production. C. at the market output the marginal costs to society exceed the total benefits to society. D. at the market output the private marginal costs of production exceed the marginal costs to society. E. at the market output the marginal benefits to society exceed the marginal costs to society. 8. Loony Spoons corporation sells silverware in a competitive market at a constant price of $2 per piece. A competitive labor market sets the wage at $5 per hour. The table above indicates the total product per hour using various numbers of workers. How many workers should Loony Spoons hire per hour? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 9. The table above shows how hiring increasing amounts of labor to a fixed amount of capital affects the hourly output of Molly’s lemonade stand. Based on this table of production data, which of the following can be said? A. Diminishing marginal returns begins with the first worker hired. B. Marginal cost begins to rise at the 6th worker hired. C. Total product is maximized at the 3rd worker hired. D. Average product begins to decline with the first worker hired. E. Diminishing marginal returns begins with the 4th worker hired. 10. The demand for labor falls if A. labor productivity falls. B. price of the good produced by labor rises. C. the price of a complementary input falls. D. demand for the good produced by labor rises. E. a minimum wage is removed from the labor market. 11. A monopsony employer hires labor up to the point where A. Wage = Marginal Factor Cost. B. Marginal Factor Cost = Marginal Product of Labor. C. Marginal Factor Cost = Marginal Revenue Product of Labor. D. Wage = Marginal Revenue Product of Labor. E. Wage = Price of the good produced by the labor. 12. The price of labor is $5 and the price of capital is $10 per unit. Using the table below, what is the least cost combination of labor and capital that should be hired to produce 18 units of output? A. B. C. D. E. 1 Labor and 2 Capital 4 Labor and 8 Capital 2 Labor and 1 Capital 5 Labor and 5 Capital 3 Labor and 2 Capital 13. Suppose the state requires hairdressers and manicurists to pass a series of exams to be certified cosmetologists. How does this policy change the supply of cosmetologists, the equilibrium wage, and the price of a manicure? 14. The local market for bankers is currently in equilibrium. Which of the following increases the local wage paid to bankers? A. Internet banking at home is becoming more popular. B. More college students are majoring in finance and economics, majors that make them attractive as bank employees. C. The price of banking software, a complementary resource to bankers, rises. D. Several banks in the local market merge and consolidate many operations. E. The price of automatic teller machines, a substitute for bankers, decreases and the output effect is greater than the substitution effect. 15. The U.S. government collects tax revenue, buys military equipment from many private firms, and uses this equipment to provide national defense to all Americans. This is a good example of A. a natural monopoly. B. an excise tax on military equipment. C. a regressive tax. D. a public good. E. dead weight loss. Questions 16–17 refer to the table below, which describes employment and production of a firm that hires labor and produces output in competitive markets. The competitive price of the product is $.50. 16. Which unit of labor has marginal revenue product equal to $1.50? A. 1st B. 2nd C. 3rd D. 4th E. 5th 17. If the wage paid to all units of labor is $4.50, how many units of labor are hired? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 E. 5 18. The price of labor is $2 and the price of capital is $1. The marginal product of labor is 200 and the marginal product of capital is 50. What should the firm do? A) Increase capital and decrease labor so that the marginal product of capital falls and the marginal product of labor rises. B) Increase capital and decrease labor so that the marginal product of capital rises and the marginal product of labor falls. C) Decrease capital and increase labor so that the marginal product of capital rises and the marginal product of labor falls. D) Decrease capital and increase labor so that the marginal product of capital falls and the marginal product of labor rises. E) Increase both capital and labor until the ratio of marginal products per dollar are equal. 19. A firm’s demand for labor is known as a derived demand because A) the firm gains utility from hiring more labor B) the wage rate paid to workers depends on the demand for labor C) the amount of labor demanded depends on the amount of capital invested D) the amount of labor demanded depends on the demand for the firm’s product E) the firm will benefit from hiring additional labor 20. If the price of a good produced by a competitive firm increases, then A) the marginal product of labor will increase B) the average product of labor will increase C) the marginal revenue product of labor will increase D) the short-run demand for labor will decrease E) the supply of labor will increase 21. With the presence of a positive externality, which of the following would correct the externality? A) a government subsidy B) a government tax C) a higher price D) a lower level of output E) a government-created task force 22. Which of the following is true? A) A marginal social cost = marginal private cost + marginal social benefits B) Value of externality = marginal social costs C) Value of externality = marginal private costs D) Marginal social cost = marginal private cost + negative externality E) Marginal social cost = marginal private cost + positive externality 23. Which of the following is an example of an economic rent? A) A superstar basketball player’s $50 million earnings. B) A social security retirement income. C) A welfare payment from social services. D) A check to a college student from a parent or guardian. E) A cashier at a restaurant receiving the same $8 an hour that other cashiers receive. 24. Jeffrey spends all of his income on warm-up suits and running shoes, and the price of a pair of shoes is four times the price of a warm up suit. In order to maximize total utility, Jeffrey should A) buy four times as many warm-up suits as pairs of running shoes B) buy four times as many pairs of running shoes as warm-up suits C) buy both items until the marginal utility of a pair of running shoes is four times the marginal utility of a warm-up suit D) buy both items until the marginal utility of a warm-up suit is four times the marginal utility of a pair of running shoes E) buy equal amounts of warm-up suits and running shoes 25. Jane is maximizing total utility while consuming food and clothing. Her marginal utility from food is 50, and her marginal utility from clothing is 25. If clothing is priced at $10 per unit, the price of food per unit must be A) $2 B) $2.50 C) $5 D) $20 E) $25 26. Consumption of a pure public good A) depletes the supply of the good for others B) increases the supply of the good C) denies the opportunity to consume the good to others D) excludes others from consuming the good somewhat E) neither depletes the good nor excludes others from consuming it 27. Suppose that farmers decide individually whether or not to get their own cattle vaccinated against anthrax. Which of the following results? A) There is market failure because the equilibrium quantity of vaccine is too low. B) There is market failure because the equilibrium price of vaccine is too low. C) There is market failure because both the equilibrium price and quantity of vaccine are too high. D) There is no market failure because the market will tend toward equilibrium. E) There is no market failure, although both the equilibrium price and quantity of vaccine are too high. 28. The pursuit of self-interest in a “commons” where everyone has access to a valuable resource will cause A) the common good of society to be realized B) careful conservation of the resource C) overuse of the resource D) individuals to make sure they bear the full costs of their actions E) a reduction in pollution levels 29. Suppose that Silvia’s Dance Studio uses both labor and capital to teach dance lessons. Given her current mix of labor and capital, the cost efficiency of labor is 5 dance lessons per dollar and the cost efficiency of capital is 1 dance lesson per dollar. Silvia should: A) Hire less labor and more capital. B) Hire less capital and more labor. C) Use all capital to produce dance lessons. D) Use all labor to produce dance lessons. Free Response Questions 1. 2. Answer Key 1. B 2. D 3. E 4. D 5. A 6. B 7. A 8. C 9. E 10. A 11. C 12. C 13. A 14. E 15. D 16. E 17. B 18. C 19. D 20. C 21. A 22. D 23. A 24. C 25. D 26. E 27. A 28. C 29. B Free Response: 1. 2.