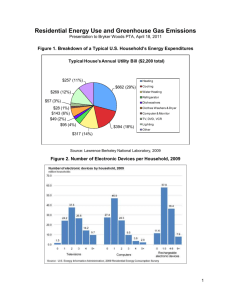
Modeling Options Matrix
advertisement

Option Analysis Component Input Output Emissions modeling Scenario-specific emission rates Option 2: RIA-level Assessment of ambient PM2.5, O3, NO2, SO2 impacts Option 3: Option 2 extended to cover ambient HAPs and Lead impacts Description/ Model Description/ Model Description/ Model 1.One model year of choice1 2. Two scenarios (baseline and alternative). 1.One model year of choice2 2. Two scenarios (baseline and alternative). 1. Wood Burning Tool 2. For EGUs, publicly available emissions rate estimates (e.g., EPA’s National Emissions Inventory) will be used. 1. Wood Burning Tool 2. For EGUs, publicly available emissions rate estimates (e.g., EPA’s National Emissions Inventory) will be used. Resolution of output: County, Annual Resolution of output: County, Annual 1. SMOKE (Pre-processing model to convert annual emissions into monthly gridded emissions for CMAQ.) 1. SMOKE (Pre-processing model to convert annual emissions into monthly gridded emissions for CMAQ.) 2. CMAQ (Full Model Air Shed Movement All Pollutants, converting emissions of : SOx, VOC, PM2.5, PM10, NOx, HAPS into ambient concentrations of air pollutants) 2. CMAQ (Full Model Air Shed Movement All Pollutants, converting emissions of : SOx, VOC, PM2.5, PM10, NOx, HAPS into ambient concentrations of air pollutants) 1.One model year (2017) 2. Two scenarios (baseline and alternative). Costing Assumptions Scenario-specific levels of polluting activity (e.g., wood burning, electric power use from particular EGUs in particular counties) Option 1: Screening-Level Assessment of ambient PM2.5 impacts Scenario-specific emissions of air pollutants (SOx, VOC, PM2.5, PM10, NOx, HAPS) from sources of interest (e.g., woodstoves, power plants) 1. Wood Burning Tool 2. For EGUs, publicly available emissions rate estimates (e.g., EPA’s National Emissions Inventory) will be used. Resolution of output: County, Annual Scenario-specific emissions of air pollutants from affected sources (e.g., woodstoves, power plants) Dispersion modeling Meteorology data Emissions of SOx, VOC, PM2.5, PM10, NOx, HAPS from all other sources for the modeling year (area, point, EGU, mobile, fire, and biogenetic sources.) 1 2 Ambient air pollution levels for each pollutant listed for the Option. COBRA. Resolution of output: County, Annual Resolution of output: CMAQ grid, hourly Limited to the years for which EPA’s emissions baselines are available (http://www.epa.gov/ttnchie1/emch/) Limited to the years for which EPA’s emissions baselines are available (http://www.epa.gov/ttnchie1/emch/) Resolution of output: CMAQ grid, hourly BenMAP for input manipulation and population projections Changes in ambient air pollution levels Resolution of output: CMAQ grid, Annual Health Effects Assessment Health impact functions Changes in health outcomes for each pollutant listed for the Option. COBRA. The model embeds a standard suite of functions and data used by EPA for PM2.5 benefits assessments. Health Effects Valuation Monetized benefits for each pollutant listed for the Option. COBRA. The model embeds a standard suite of functions and data used by EPA for PM2.5 benefits assessments. Impacts on Criteria Non-Attainment Counties (Annual standard)3 Impacts on Criteria Non-Attainment Counties (Hourly standard)5 3 County-level annual ambient concentrations Non-Attainment Record of Decision for each county for the hourly standard Projected change in attainment status if alternative scenario is implemented (no change is assumed for baseline scenario) Projected change in attainment status if alternative scenario is implemented (no Standard EPA configurations exist Extensive research of public health literature to develop health impact functions. BenMAP database Additional research may be needed BenMAP for input manipulations and income growth adjustment factors BenMAP for input manipulations and income growth adjustment factors. Possibly, additional software development. Resolution of output: CMAQ grid, Annual Resolution of output: County, Annual Unit values Non-Attainment Record of Decision for each county for the daily standard Spreadsheet-based comparisons, assuming that predicted annual average PM2.5 concentrations will characterize measurements at the FRM monitor. Resolution of output: CMAQ grid, Annual Standard EPA configurations exist Extensive research of economics literature to develop unit values. MATS4 software for PM2.5. Methods will need to be developed and programmed for NO2. Will be carried out only for Option 2 pollutants. MATS software for PM2.5 and O3. Methods will need to be developed and programmed for NO2, SO2, CO, PM10. Will be carried out only for Option 2 pollutants and Lead.6 Methods will need to be developed and programmed for Lead. Only relevant for NO2 and PM2.5: http://www.epa.gov/air/criteria.html Modeled Attainment Test Software: http://www.epa.gov/scram001/guidance/guide/MATS-2-3-1_manual.pdf 5 Only relevant for NO2, SO2, PM2.5, PM10, CO, O3: http://www.epa.gov/air/criteria.html 6 Lead standard is rolling 3-month average: http://www.epa.gov/air/criteria.html 4 Resolution of output: CMAQ grid, Annual Resolution of output: County, Annual Endpoint incidence rates Changes in health outcomes BenMAP for input manipulation and population projections. Possibly, additional software development. County-level hourly ambient concentrations change is assumed for baseline scenario) Completion Time 3 calendar months from project initiation 8 calendar months from project initiation NA, but likely much longer compared to Option 2 Cost $20,000-$40,000 $60,000-$200,000 NA, but likely much higher compared to Option 2 CMAQ Community Multiscale Air Quality model http://www.epa.gov/sciencematters/december2011/cmaq.htm Wood Burning Tool http://www.epa.gov/ttnchie1/conference/ei17/session2/huntley_pres.pdf Criteria Pollutants NOx, SOx, Particulates, CO, O3, Lead Air Toxics HAPS 187 pollutants including Mercury, same as HAPs Hazardous Air Pollutants, same as Air Toxics COBRA http://www.epa.gov/statelocalclimate/resources/cobra.html CMAQ does not model for all 188 HAPS. Only the ones below. Gas Phase Hazardous Air Pollutants (HAPs) P-Xylene 2,4-Toluene Diisocyanate Ethylene Oxide Hexamethylene 1,6-Diisocyanate Benzene Hydrazine Chloroform Maleic Anhydride 1,1,2,2-Tetrachloride Ethane M-Xylene 1,2-Dibromomethane Naphthalene Acetaldehyde Emissions Tracer O-Xylene Propylene Dichloride Quinoline Acrolein Emissions Tracer Toluene 1,3-Dichloride Propene Total Acetaldehyde Formaldehyde Emissions Tracer Total Acrolein Perchloroethylene Total Formaldehyde 1, 3-Butadiene Trichloroethylene Methylene Chloride Triethylamine Acrylonitrile Vinyl Chloride 1,2-Dichloromethane Elemental Mercury Carbon Tetrachloride Oxidized Mercury Compounds 1,4-Dichlorobenzene Table 1. Gas-Phase Hazardous Air Pollutants represented in the current CMAQ Multi-pollutant model. Aerosol Phase Hazardous Air Pollutants (HAPs) Beryllium Compounds Mercury Compounds Nickel Compounds Cadmium Compounds Chromium (III) Compounds Diesel Emissions Tracer Chromium (VI) Compounds Lead Compounds Manganese Compounds