z6o005152814so1 - American Psychological Association
advertisement

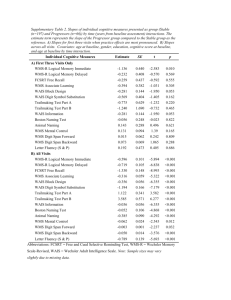
Supplemental Materials A Meta-Analysis on the Impact of Psychiatric Disorders and Maltreatment on Cognition by M. Masson et al., 2015, Neuropsychology http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/neu0000228 Studies Sample characteristics (M+PD/Control): Sample size; % Male; Education (years) Age (years) Onset of maltreatment (years) Diagnosis PTSD Bremner et al. (1995) 21/20; 71.4/80; 13.5/14 18 and older 28.6% before the age of 5 years De Bellis et al. (1999) 44/61; 56.8/59; Not reported 7-18 4.5 (for 77.3% of the maltreated subjects) Freeman & Beck (2000) 20/20; 0/0; Not reported 7-18 Not reported PTSD De Bellis et al. (2002) 28/66; 50/47; Not reported 7-18 3.9 PTSD Beers & De Bellis (2002) 14/15; 57.1/53.3 Not reported 7-18 Not reported PTSD PTSD Neuropsychological test Cognitive domains Effect size (g) SRT verbal continuous long-term retrieval, SRT verbal delayed recall, SRT verbal long term retrieval, SRT verbal long term storage, SRT verbal recall, SRT visual continuous long-term retrieval, SRT visual delayed recall, SRT visual long term retrieval, SRT visual long term storage, SRT visual recall, WAIS-R FSIQ, WAIS-R PIQ, WAIS-R VIQ, WMS figural memory delayed, WMS figural memory immediate, WMS figural memory retention, WMS logical memory delayed, WMS logical memory immediate, WMS logical memory retention WISC-R estimated FSIQ, WISC-R estimated PIQ, WISC-R estimated VIQ Verbal memory, Visual memory, Intelligence -0.337 Intelligence -0.961 K-BIT FSIQ, K-BIT PIQ, K-BIT VIQ Intelligence -0.584 WISC FSIQ, WISC PIQ, WISC VIQ Intelligence -0.309 Cowa animal naming, Cowa total words, CVLT discriminability, CVLT LDFR, CVLT list B, CVLT SDFR, CVLT trials 1-5, ROCF copy, ROCF recall, Stroop color, Stroop color word, Stroop interference, Stroop word, TMT A, TMT Executive Functions, Verbal memory, Visuo-spatial/problem solving, Visual memory, Processing speed, Working memory, Intelligence, -0.595 18 and older 7 PTSD 18 and older At least 5 years PTSD B, WCST category, WCST perseverative responses, WISC-III object assembly, WISC-III bloc design, WISC-III Codes, WISC-III Digit span, WISC-III similarities, WISC-III Vocabulary WAIS-R FSIQ, WAIS-R PIQ, WAIS-R VIQ, WMS figural memory delayed, WMS figural memory immediate, WMS figural memory retention, WMS logical memory delayed, WMS logical memory immediate, WMS logical memory retention WMS auditory delayed, WMS visual delayed, WMS visual immediate, WMS working memory, WMS-III auditory immediate Bremner et al. (2004) 18/15; 0/0; 15/17 Pederson et al. (2004) 17/17; 0/0; 13.7/15.4 Porter et al. (2005) 24/24; 20.83/20.83 Not reported Irle et al. (2005) 30/25; 0/0; 11/11 18 and older Not reported BPD De Bellis & Kuchibhatla (2006) 58/98; 51.7/51; Not reported 7-18 Not reported PTSD WISC FSIQ, WISC PIQ, WISC VIQ GrassiOliveira et al. (2008) 17/15; 0/0; 9.47/9 18 and older Not reported MDD WMS-R DVR, WMS-R IVR, WMS-R retention De Bellis et al. (2009) 22/45; 61.5/62; 7-18 Not reported PTSD 7-18 33% before the age 5, 21% at age 5, 46% after the age of 5 PTSD WISC-III PIQ, WISC-III VIQ WAIS-R bloc design, WAIS-R PIQ, WAIS-R VIQ, WMS-R attention concentration, WMS-R delayed recall*, WMS-R digit span backward, WMS-R digit span forward, WMS-R verbal memory, WMS-R visual memory, WMS-R visual span backward, WMS-R visual span forward CPT-II omission, CPT-II variability, NEPSY auditory attention, NEPSY memory for faces, NEPSY memory for Intelligence, Visual memory, Verbal memory -0.554 Verbal memory, Visual memory, Working memory -0.058 Intelligence -0.914 Visuo-spatial/problem solving, Intelligence, Attention, Working memory, Verbal memory, Visual memory -0.633 Intelligence -0.675 Verbal memory -0.961 Attention, Visual memory, Verbal memory, Executive -0.709 Not reported names, NEPSY narrative memory, NEPSY tower, NEPSY visual attention, PPVT-III, WISC-III/WPPSI-R Functions, Intelligence * "WMS-R delayed recall" was only included in the global analysis of effect size whereas not in analysis by cognitive domain because this data group both visual and verbal memory Table 1S: Characteristics of the studies included in the meta-analysis (k=12) Studies included in the meta-analysis Beers, S. R., & De Bellis, M. D. (2002). Neuropsychological function in children with maltreatment-related posttraumatic stress disorder. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 159(3), 483-486. Bremner, J. D., Randall, P., Scott, T. M., Capelli, S., Delaney, R., McCarthy, G., & Charney, D. S. (1995). Deficits in short-term memory in adult survivors of childhood abuse. Psychiatry Research, 59(1-2), 97-107. Bremner, J. D., Vermetten, E., Afzal, N., & Vythilingam, M. (2004). Deficits in verbal declarative memory function in women with childhood sexual abuse-related posttraumatic stress disorder. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 192(10), 643-649. De Bellis, M. D., Hooper, S. R., Spratt, E. G., & Woolley, D. P. (2009). Neuropsychological findings in childhood neglect and their relationships to pediatric PTSD. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 15(6), 868-878. De Bellis, M. D., Keshavan, M. S., Clark, D. B., Casey, B. J., Giedd, J. N., Boring, A. M., et al. (1999). A.E. Bennett Research Award. Developmental traumatology. Part II: Brain development. Biological Psychiatry, 45(10), 1271-1284. De Bellis, M. D., Keshavan, M. S., Shifflett, H., Iyengar, S., Beers, S. R., Hall, J., & Moritz, G. (2002). Brain structures in pediatric maltreatmentrelated posttraumatic stress disorder: a sociodemographically matched study. Biological Psychiatry, 52(11), 1066-1078. De Bellis, M. D., & Kuchibhatla, M. (2006). Cerebellar Volumes in Pediatric Maltreatment-Related Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 60(7), 697-703. Freeman, J. B., & Beck, J. G. (2000). Cognitive interference for trauma cues in sexually abused adolescent girls with posttraumatic stress disorder. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 29(2), 245-256. Grassi-Oliveira, R., Stein, L. M., Lopes, R. P., Teixeira, A. L., & Bauer, M. E. (2008). Low plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor and childhood physical neglect are associated with verbal memory impairment in major depression--a preliminary report. Biological Psychiatry, 64(4), 281-285. Irle, E., Lange, C., & Sachsse, U. (2005). Reduced size and abnormal asymmetry of parietal cortex in women with borderline personality disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 57(2), 173-182. Pederson, C. L., Maurer, S. H., Kaminski, P. L., Zander, K. A., Peters, C. M., Stokes-Crowe, L. A., & Osborn, R. E. (2004). Hippocampal volume and memory performance in a community-based sample of women with posttraumatic stress disorder secondary to child abuse. Journal of Traumatic Stress, 17(1), 37-40. Porter, C., Lawson, J. S., & Bigler, E. D. (2005). Neurobehavioral sequelae of child sexual abuse. Child Neuropsychology, 11(2), 203-220. Regression of Âge on Hedges's g 0,00 -0,10 Hedges's g -0,20 -0,30 -0,40 -0,50 -0,60 -0,70 -0,80 -0,90 -1,00 5,02 8,64 12,26 15,88 19,50 23,12 26,74 30,36 33,98 37,60 Âge Figure 1S: Scatterplot of age for cognitive disorders in M+PD 41,22