Basic Concentration Problems Molarity = 1.00 L = 1000 mL Identify
advertisement
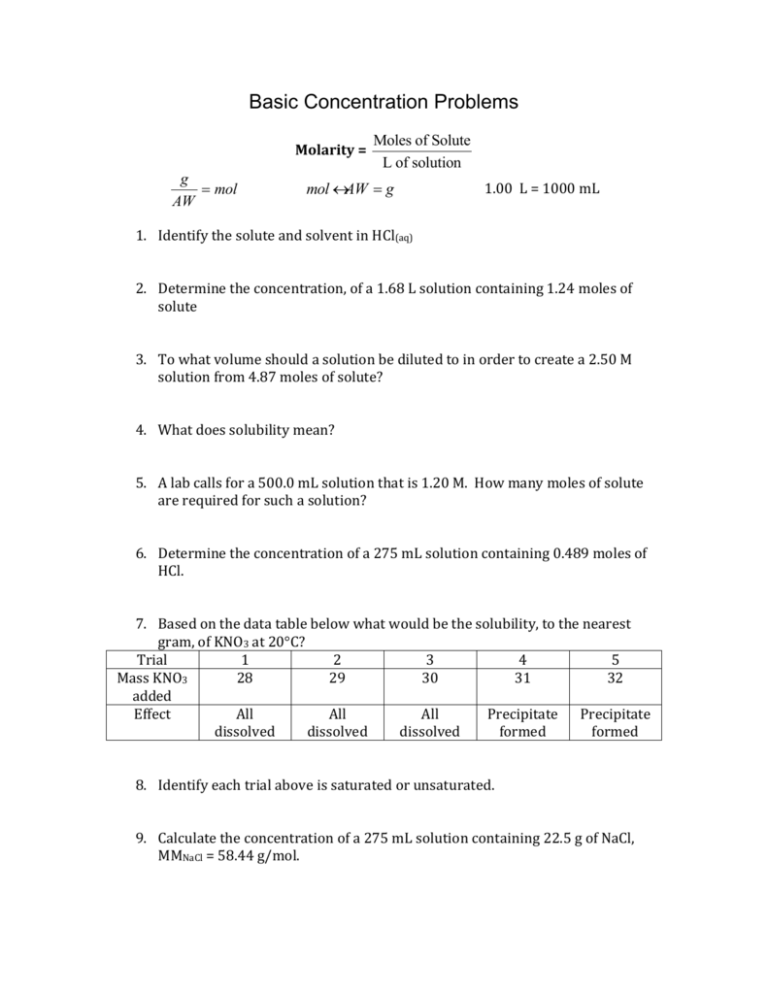
Basic Concentration Problems Molarity = g = mol AW Moles of Solute L of solution mol ´ AW = g 1.00 L = 1000 mL 1. Identify the solute and solvent in HCl(aq) 2. Determine the concentration, of a 1.68 L solution containing 1.24 moles of solute 3. To what volume should a solution be diluted to in order to create a 2.50 M solution from 4.87 moles of solute? 4. What does solubility mean? 5. A lab calls for a 500.0 mL solution that is 1.20 M. How many moles of solute are required for such a solution? 6. Determine the concentration of a 275 mL solution containing 0.489 moles of HCl. 7. Based on the data table below what would be the solubility, to the nearest gram, of KNO3 at 20°C? Trial 1 2 3 4 5 Mass KNO3 28 29 30 31 32 added Effect All All All Precipitate Precipitate dissolved dissolved dissolved formed formed 8. Identify each trial above is saturated or unsaturated. 9. Calculate the concentration of a 275 mL solution containing 22.5 g of NaCl, MMNaCl = 58.44 g/mol. 10. How many grams of MgCl2 will be required to create a 0.500 M, 250.0 mL solution, MMMgCl2 = 95.211 g/mol? 11. What is the volume, in mL, of a solution containing 12.5 g of KNO3 that is 1.0 M, MMKNO3 = 101.102 g/mol? 12. Name two ways to make a saturated solution unsaturated. 13. How much NaOH, MMNaOH = 39.997 g/mol, should be weighed out to make a 3.00 M, 1.75 L solution? 14. Which solution is guaranteed to have more solute present, a concentrated solution or a saturated solution? 15. You need a 1.00 M solution of HCl. All you have is 50.0 mL of 6.00 M HCl. How much water should be added to the 6.00 M solution to dilute it down to 1.00 M? Basic Concentration Solutions 1. Identify the solute and solvent in HCl(aq) Solute = HCl Solvent = H2O 2. Determine the concentration, molarity, of a 1.68 L solution containing 1.24 moles of solute 1.24 / 1.68 = 0.738 M 3. To what volume should a solution be diluted to in order to create a 2.50 M solution from 4.87 moles of solute? 2.50 = 4.87 / V 4.87 / 2.50 = 1.95 L 4. What does solubility mean? How much solute can be dissolved in the solvent at a given temp 5. A lab calls for a 500.0 mL solution that is 1.20 M. How many moles of solute are required for such a solution? 500.0 mL = 0.5000 L 1.20 = n / 5.000 1.20 (5.000) = 0.600 moles 6. Determine the concentration of a 275 mL solution containing 0.489 moles of HCl. M = 0.489 / 0.275 = 1.78 M 7. Based on the data table below what would be the solubility, to the nearest gram, of KNO3 at 20°C? Trial 1 2 3 4 5 Mass KNO3 28 29 30 31 32 added Effect All All All Precipitate Precipitate dissolved dissolved dissolved formed formed 30 g 8. Identify weather each trial above is saturated or unsaturated. 1 and 2 are unsaturated 3-5 are saturated 9. Calculate the concentration of a 275 mL solution containing 22.5 g of NaCl, MMNaCl = 58.44 g/mol. 22.5 g / 58.44 = 0.385 moles 0.385 / 0.275 = 1.40 M 10. How many grams of MgCl2 will be required to create a 0.500 M, 250.0 mL solution, MMMgCl2 = 95.211 g/mol? 0.5 (0.2500) = 0.125 moles (95.211) = 11.9 g of MgCl2 11. What is the volume, in mL, of a solution containing 12.5 g of KNO3 that is 1.0 M, MMKNO3 = 101.102 g/mol? 12.5 g / 101.102 = 0.124 moles 1.0 = 0.124 / V V = 0.124 L 12. Name two ways to make a saturated solution unsaturated. Heat up the solution or add more solvent 13. How much NaOH, MMNaOH = 39.997 g/mol, should be weighed out to make a 3.00 M, 1.75 L solution? 3.00 = n / 1.75 n = 5.25 moles (39.997) = 210 g NaOH (sig figs) 14. Which solution is guaranteed to have more solute present, a concentrated solution or a saturated solution? A saturated solution 15. You need a 1.00 M solution of HCl. All you have is 50.0 mL of 6.00 M HCl. How much water should be added to the 6.00 M solution to dilute it down to 1.00 M? MV = MV 1.00 V = 6.00 (0.0500) V = 0.30 L or 300 mL Must add 250 mL







