ICMap_PECS - ESEProgramEvaluation
advertisement
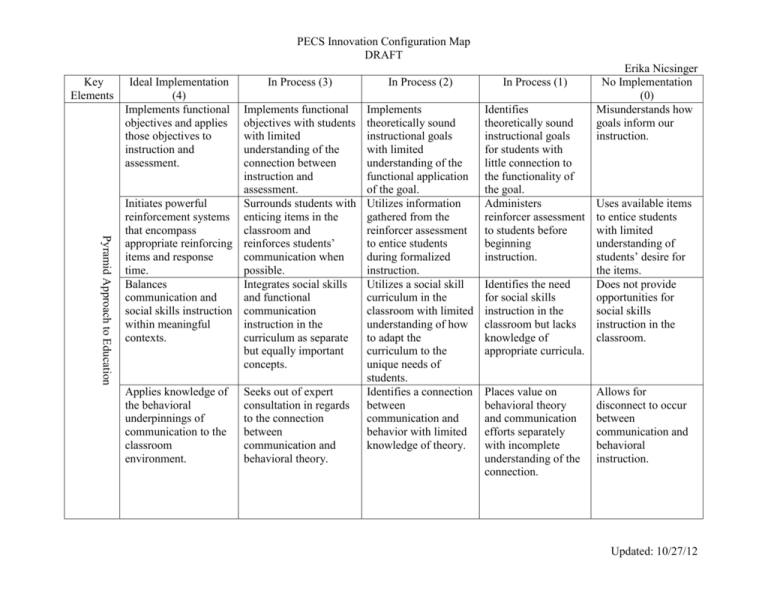
PECS Innovation Configuration Map DRAFT Key Elements Ideal Implementation (4) Implements functional objectives and applies those objectives to instruction and assessment. In Process (3) Pyramid Approach to Education Implements functional objectives with students with limited understanding of the connection between instruction and assessment. Initiates powerful Surrounds students with reinforcement systems enticing items in the that encompass classroom and appropriate reinforcing reinforces students’ items and response communication when time. possible. Balances Integrates social skills communication and and functional social skills instruction communication within meaningful instruction in the contexts. curriculum as separate but equally important concepts. Applies knowledge of the behavioral underpinnings of communication to the classroom environment. Seeks out of expert consultation in regards to the connection between communication and behavioral theory. In Process (2) In Process (1) Implements theoretically sound instructional goals with limited understanding of the functional application of the goal. Utilizes information gathered from the reinforcer assessment to entice students during formalized instruction. Utilizes a social skill curriculum in the classroom with limited understanding of how to adapt the curriculum to the unique needs of students. Identifies a connection between communication and behavior with limited knowledge of theory. Identifies theoretically sound instructional goals for students with little connection to the functionality of the goal. Administers reinforcer assessment to students before beginning instruction. Identifies the need for social skills instruction in the classroom but lacks knowledge of appropriate curricula. Places value on behavioral theory and communication efforts separately with incomplete understanding of the connection. Erika Nicsinger No Implementation (0) Misunderstands how goals inform our instruction. Uses available items to entice students with limited understanding of students’ desire for the items. Does not provide opportunities for social skills instruction in the classroom. Allows for disconnect to occur between communication and behavioral instruction. Updated: 10/27/12 PECS Innovation Configuration Map DRAFT Collaborates with experts to understand communication and its intricacies. Understands how augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) systems work in tandem with speech development. Functional Communication Seeks consultation with experts in the area of communication. Identifies the value of communication and experts in the area. Demonstrates an emerging understanding of the connection between AAC and speech development and a desire for further knowledge. Seamlessly integrates Attempts to promote critical communication communication outside skill instruction of the daily routine. naturally within the learning environment. Fosters a positive Reinforces students’ environment spontaneous conductive to communication within spontaneous the natural context of communication. instruction. Accepts that AAC and speech can coexist with a limited understanding of the rationale behind the connection. Provides instruction in the area of communication as part of daily prescribed routine. Allows for students to communicate as they desired with limited regard for reinforcing communication. Views communication as one-dimensional and static. Misunderstands the connection between AAC and speech and sees one as inhibiting the other. Erika Nicsinger Misunderstands communication. Lacks an awareness of the connection between speech development and AAC systems. Identifies that communication is a skills that is required to survive. Misidentifies communication skills that are required to survive. Provides framework within which students may communicate during daily prescribed routine. Stifles spontaneous communication during natural settings. Updated: 10/27/12 PECS Innovation Configuration Map DRAFT Environment reflects an understanding of the theoretical underpinnings of operational communication and applies that knowledge to instruction. Understands the rationale and function of each communicative phase. Environment promotes operational communication throughout the day as part of planned and deliberate efforts. Phase Implementation Seeks out guidance to aid in understanding the rationale and function of each communicative phase. Identifies the key Implements components of each communicative phases implementation phase with fidelity within the and generalizes the formalized instructional information to all areas setting, but with limited of instruction. adherence to protocol during informal opportunities. Frames classroom Identifies ways in environment with a which PECS mindset towards requirements can be meeting established integrated through implementation goals formal and informal as outlined in the instruction. PECS manual. Environment encourages operational communication during direct-instruction opportunities. Environment allows for operational communication to occur naturally with little or no assistance from staff. Demonstrates a desire to understand the theory beneath each communicative phase. Erika Nicsinger Environment stifles operational communication. Identifies that the various communicative phases are based in theory. Attempts to implement Misunderstands how communicative phases to implement the with fidelity within the communicative instructional setting. phases correctly. Administers the phases without understanding the theoretical underpinnings. Implements communicative phases with a lack of regard for fidelity of the program. Adheres to established PECS requirements for each student. Does not meet established PECS requirements (50+ opportunities, 2+ conversation partners and 2+ settings each day). Attempts to meet established criteria for implementation during instructional opportunities. Updated: 10/27/12 PECS Innovation Configuration Map DRAFT Data Collection Teaching Communication Across the Day Uses baseline data to inform instruction and improves instruction throughout the process. Utilizes collected data to identify ways in which instruction can be improved in order to meet the diverse needs of students. Provides meaningful opportunities for language instruction embedded within PECS instruction. Promotes and maintains communication instruction within functional routines as part of daily living activities. Understands the rationale behind gathering baseline data before implementing the PECS program. Shows evidence of initial data analysis prior to data submission. Gathers baseline data information, such as a reinforcer assessment and phase level. Misunderstands the role of baseline data in the instructional process. Erika Nicsinger Begins PECS instruction without attention to baseline data. Balances classroom data collection requirements with instructional requirements. Submits complete and accurate data collection forms each week. Data collection forms are not completed or are completed incorrectly. Appeals to expert knowledge to fully understand the connection between communication and language development. Demonstrates a limited understanding of the connection between communication and language development. Provides communication instruction within functional contexts. Identifies that a connection exists between communication and language development. Ignores the connection between PECS communication and language development. Uses communication instruction as part of the natural, functional environment. Disconnects communication instruction from functional, daily living skills. Identifies personal bias towards studentcentered instruction. Ignores students’ interests with preference for teaching towards the norm. Strictly adheres to lesson plans without attention towards “teachable moments”. Prompts diverse team members, such as OT or PT, to utilize communication instruction as part of their specific therapeutic interventions. Encourages students to Identifies students’ direct the interests and plans to communication use that knowledge instruction by teaching mindfully in the to the students’ planning process. interests. Updated: 10/27/12