tpj12717-sup-0001
advertisement

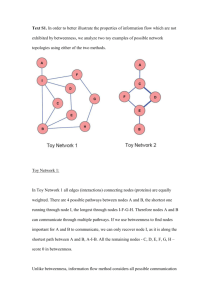
Glossary Network term Correlation-based network (CN) Clique Community Community detecting algorithm (CDA) Modularity score Fast-greedy community algorithm (FCA) (Clauset et al. 2004). Geodesic distance Walktrap community algorithm (WCA) (Pons and Latapy 2005) Edge betweenness community algorithm (EBCA) (Newman and Girvan 2004) Definition CNs are obtained by applying (Pearson) correlations on the data profiles from considered components. In biological CNs, nodes correspond to the biological components, and edges are established based on correlations between the corresponding data profiles. A clique is a maximal complete subnetwork, in which each pair of nodes is connected by an edge. A community is a collection of densely or strongly connected nodes relatively to their relation with the rest of the network. Communities are detected by community detecting algorithms. A CDA detects communities in a network derived on principles observed in the physical, biological, applied mathematical, computational, and social sciences. A modularity score quantifies the strength of the division of a network into communities based on the CDA applied. The FCA applies a hierarchical bottom-up approach, in which initially each node is separated into a different community. Iteratively, communities are logically merged until an optimal modularity score is achieved. The geodesic distance between two nodes is the length of the shortest path (i.e. geodesic) between them. The WCA is based on the idea of short random walks, where nodes are merged into communities based on the similarity of their corresponding random walks. The EBCA, also known as the GirvanNewman algorithm, is based on the edgebetweenness centrality property, which is given by the number of geodesic distances between any two nodes that contain a given edge. The EBCA applies a hierarchical decomposition process, in which edges are removed based on their betweenness score. Communities are build on the idea that edges connecting different communities are more Weighted node degree (WND) Global clustering coefficient (GCC) Assortativity coefficient (AC) likely to be contained as multiple shortest paths. The WND quantifies the weight of all edges incident on a node. In case of a CN the weight of an edge corresponds to the absolute correlation coefficient. The GCC is defined as the ratio of all closed triplets over all triplets possible in a network. It assesses how close the network is from being a fully connected network. The AC is the correlation between the node of degree k and the average of neighbor degree over all nodes of degree k. It tells in a concise fashion how nodes are preferentially connected to each other.