ADHD IQ Test Profiles
advertisement

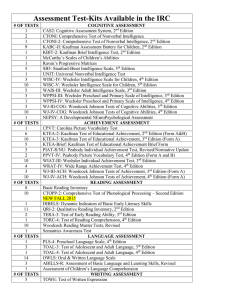
IQ Test Profiles Frequently Associated with ADHD Intelligence Test (Author) Differential Ability Scales (DAS; Elliott, 1990) ADHD Profile (Study Notes/Authors) Cognitive Assessment System (CAS; Naglieri & Das, 1997) Relative to general education students, significantly lower Planning Scale scores (Note: subjects, students referred for ADHD evaluation; Naglieri, Salter, & Edwards, 2004). Relative to normal controls, low scores on the Sequential and Quantitative Reasoning, and Recall of Digits subtests (Note: subjects, 63% combined type; Gibney, McIntosh, Dean, & Dunham, 2002). Relative weakness on the Hand Movements subtest (Note: test used, Kaufman Assessment Battery for KABC; Barkley, 2006). Children (KABC-II; Kaufman & Kaufman, 2004) Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale-Fifth Relative to normal controls, significantly lower Working Memory factor scores (Note: subjects, combined type; Blashko, 2006). Edition (SB-V; Roid, 2003) Universal Nonverbal Intelligence Test (UNIT; Bracken & McCallum, 1998) Memory Quotient score on average 10 points lower than Reasoning Quotient score (Pendley, Myers, & Brown, 2004). Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC-IV; Wechsler, 2003) Relative to Full Scale IQ, 84% have significant Processing Speed + Freedom from Distractibility weakness (Notes: subjects, inattentive subtype; test used, WISC III; Calhoun & Mayes, 2005). Woodcock-Johnson Test of Cognitive Abilities (WJ-III Cog; Woodcock, McGrew, & Mather, 2001) Relative to children without ADHD, significantly lower Processing Speed scores (Note: subjects, all but one combined type; Penny, Waschbusch, Carrey, & Drabman, 2005). References: Barkley, R. A. (2006). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A handbook for diagnosis and treatment (3rd ed.). New York: Guilford Press. Blashko, P. C. (2006). Performance of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder – combined subtype on the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale, Fifth Edition. Dissertation Abstracts International. Section A: Humanities and social Sciences, 67, 1220. Bracken, B. A., & McCallum, R. S. (1998). Universal Nonverbal Intelligence Test: Examiner’s Manual. Rolling Meadows: Riverside. Calhoun, S. L., & Mayes, S. D. (2005). Processing speed in children with clinical disorders. Psychology in the Schools, 42, 333-343. Elliott, C. D. (1990). Differential Ability Scales: Introductory and technical handbook. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation. Gibney, L. A., McIntosh, D. E., Dean, R. S., & Dunham, M. (2002). Diagnosing attention disorders with measures of nerocognitive functioning. International Journal of Neuroscience, 112, 539-564. Kaufman, A. S., & Kaufman, N L. (2004). Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children (2nd ed.). Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Services Naglieri, J. A., & Das, J. P. (1997). Cognitive Assessment System. Rolling Meadows: Riverside. Naglieri, J. A., Salter, C. J., & Edwards, G. H. (2004). Assessment of children with attention and reading difficulties using the PASS theory and Cognitive Assessment System. Journal of Psychoeductional Assessment, 22, 93-105. Pendley, J. D., Myers, C. L., & Brown, R. D. (2004). The Universal Nonverbal Intelligence Test with children with attentiondeficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Psychoeduational Assessment, 22, 124-135. Penny, A. M., Waschbusch, D. A., Carrey, N., & Drabman, R. S. (2005). Applying a psychoeducational perspective to ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders, 8, 208-220. Roid, G. H. (2003). Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scales (5th ed.). Rolling Meadows, IL: Riverside. Wechsler, D. (2003). Wechsler Individual Achievement Test (2nd ed.). San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation. Woodcock, R. W., McGrew, K. S., & Mather, N. (2001). Woodcock-Johnson III: Tests of Cognitive Abilities. Rolling Meadows, IL: Riverside.