Quantities and units
advertisement

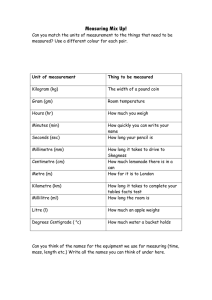
Over Betuwe College Physics Quantities and units Physics people are basically rather lazy people. They don’t feel like writing down names of things in full all the time. Imagine all those formulas in your tests every time. Example: Speed = distance: time Physicists over the whole world have made agreements about this. Everything in physics will be shortened to one or more letters. This counts for quantities as well as units. What is a (physical) Quantity: Firstly, the quantity is the letter that concerns the subject or what happens. The quantity is always in the formula. The quantity is a replacement for the word for what you are doing. A simple example of a quantity is speed (symbol v). (How fast does your moped go?) What is a Unit: The unit is behind the number and is the size of something. In the previous example the question was about the speed of the moped. A number thus appears in the answer. Behind the number is the unit. Example: My moped goes at 45 km/h. Km/h is then the unit. A quantity and a unit belong together. If you are asked what the distance is from Nijmegen to Amsterdam, then you don’t say 189 km/h, but 189 km. Important!!! With quantities and units you need to watch out for capital letters and small letters!! An example of the difference between capital letters and small letters is: T = Temperature t = time Over Betuwe College Physics Quantities and Units Quantity Width Symbol b Length Height Volume Capacity l h V V Temperature T Mass m Density (rho) Angle Tension Current Resistance Speed U I R v Distance Time Gravity Weight s t Fz Fg Magnetic force g Unit millimetre, centimetre decimetre, metre kilometre cubic … millilitre, litre Degrees Celsius Degrees Kelvin Gramme, Kilogramme Gramme per cubic centimetre Degrees Volt Ampere Ohm Metre per second or Kilometre per hour Metre or kilometre Second or hour Newton Newton Newton per kilogramme Symbol mm, cm, dm, m, km mm, cm, dm, m, km mm, cm, dm, m, km mm³, cm³, dm³, m³, km³ cm³ of mL, dm³ of L, m³ cm³ = mL en dm³ = L ºC ºK g, kg g/cm³ º V A (Ohm) m/s of km/h m of km s of h N N N / kg This year we are going to work, amongst other things, with the following formulae: Volume V=lbh Mass m=V Ohm’s Law U=IR Speed s=vt Force / Weight F = m 10 Over Betuwe College Physics METRIC SYSTEM SI-voorvoegsels (prefixes) 10n Prefix Symbol Name Decimal Equivalent 1024 yotta Y Septillion 1 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 1021 zetta Z Sextillion 1 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 1018 exa E Quintillion 1 000 000 000 000 000 000 1015 peta P Quadrillion 1 000 000 000 000 000 1012 tera T Trillion 1 000 000 000 000 109 giga G Billion 1 000 000 000 106 mega M Million 1 000 000 103 kilo Thousand 1 000 102 hecto h Hundred 100 deca da Ten 10 Tenth 0,1 10−2 centi c Hundredth 0,01 10−3 milli Thousandth 0,001 1 10 10−1 deci k d m 10−6 micro µ Miljoenste 0,000 001 10−9 nano n Billionth 0,000 000 001 10−12 pico p Trillionth 0,000 000 000 001 10−15 femto f Quadrillionth 0,000 000 000 000 001 10−18 atto Quintillionth 0,000 000 000 000 000 001 a 10−21 zepto z Sextillionth 0,000 000 000 000 000 000 001 10−24 yocto y Septillionth 0,000 000 000 000 000 000 000 001 Length km hm dam m dm cm mm Going down: point per step 1 place to the right Going up: point per step 1 place to the left e.g.: 1000 mm = 100 cm = 10 dm = 1m = 0.1 dam = 0.01 hm = 0.001 km kilometre hectometre decametre metre decimetre centimetre millimetre Over Betuwe College Physics km2 Surface hm 2 dam2 m 2 dm2 cm2 mm 2 Square kilometre Hectare or Square hectometre Square decametre Square metre Square decimetre Square centimetre Square millimetre Going down: point per step 2 places to the right Going up: point per step 2 places to the left e.g.: 1000000 mm2 = 10000 cm2 = 100 dm2 = 1m2 = 0.01 dam2 = 0.0001 hm2 = 0.000001 km2 km3 Volume hm dam 3 3 m3 dm3 cm mm 3 3 Going down: point per step 3 places to the right Going up: point per step 3 places to the left e.g.: 1000000000 mm3 = 1000000 cm3 = 1000 dm3 = 1m3 = 0.001 dam3 = 0.000001 hm3 = 0.000000001 km3 Cubic kilometre Cubic. hectometre Cubic decametre Cubic metre Cubic decimetre Cubic centimetre Cubic millimetre Over Betuwe College Capacity 1 m3 = 1 kL 1 dm3 = 1 L 1 cm3 = 1 mL Physics kL hL daL L dL cL mL Kilolitre Hectolitre Decalitre litre Decilitre Centilitre Millilitre Going down: point per step 1 place to the right Going up: point per step 1 place to the left e.g.: 1000 mL = 100 cL = 10 dL =1 L = 0.1 daL= 0.01 hL = 0.001 kL Mass kg g Kilogramme gramme mg Milligramme Going down: point per step 1 place to the right Going up: point per step 1 place to the left e.g.: 1000 mg = 1 g = 0.001 kg But also: ng µg mg nV µV mV kV MV GV nA µA mA kA MA GA nW µW mW kg Mg kW Gg MW GW