Pre Cell Theory Ideas

Pre Cell Theory Ideas
By Melissa Bajorek, eHow Contributor
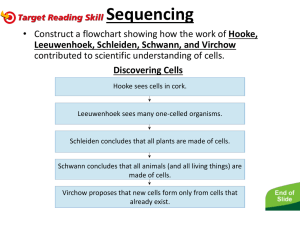
Robert Hooke was the first to use a microscope to describe cells, in 1665.
Cell theory is the concept that the cell is a basic unit of structure in living things.
Scientific development of cell began during the mid-17th century, along with advances in microscope technology and microscopy techniques. However, true cell theory wasn't formulated until the mid-1800s. Cell theory states that new cells are formed only from existing cells.
Atomist Theory
Leucippus, from the 5th century BCE, is usually credited with inventing atomism.
Prior to Hooke's work with cells and microscopy, many biologists firmly believed in atomist theory, a concept that dates back to the ancient Greek philosophers. Many important Greek theorists believed that the universe is made of physical, indivisible
"atoms" of substance. According to Stanford University, the Greeks developed a comprehensive philosophy explaining the origins of everything from the interaction of these "atoms." Atomists theory, to the Greeks, applied to topics of ethics, theology, philosophy and political science. The atomist theory remained strong for centuries, while other philosophical concepts changed.
Hooke, Malpighi and Grew
Around the time Robert Hooke described the first cork cell in 1665, Marcello Malpighi and Nehemiah Grew made detailed studies of plant cells using microscopes. Grew recorded observing plant cells reminded him of gas bubbles in rising bread, and thought cells may be created in a similar process. While these scientists were beginning to understand plant cells, proof of cells in animals wasn't found until much later. because the thin samples needed for viewing with a microscope are more difficult to prepare. In short, Hooke's contemporaries thought that plant cells may be born in a gassy, bubbling process; and that animals were composed of different types of fibers, as proven by the various types of tissues in an animal.
Leeuwenhoek
Leeuwenhoek was probably the first microscopist to see red blood cells.
Dutch scientist Antony van Leeuwenhoek was the first to publish observations of singlecelled organisms in 1676. He called them "little animalcules". It is commonly thought that Leeuwenhoek was the first to observe red blood cells. Leeuwenhoek researched single-celled organisms thoroughly, but a century passed before a connection was made between cellular structure of "animacules" and the existence of cells in plants and animals.
Globulism
In 1824, Henri Milne-Edwards, a French zoologist, suggested the basic structure of animal tissues was groupings of "globules." His globulist theory was short-lived, however, because of his insistence that all globules of all tissues must be one consistent size.
Dutrochet
Henri Dutrochet was the first to make the connection between plant cells and animal cells. He was also the first to suggest that the cells was a physiological building block, stating "...[E]verything is ultimately derived from the cell." Dutrochet also proposed that new cells arise from old ones.
Read more : http://www.ehow.com/list_7485059_pre-cell-theory-ideas.html