Development of Feudalism notes 2
advertisement
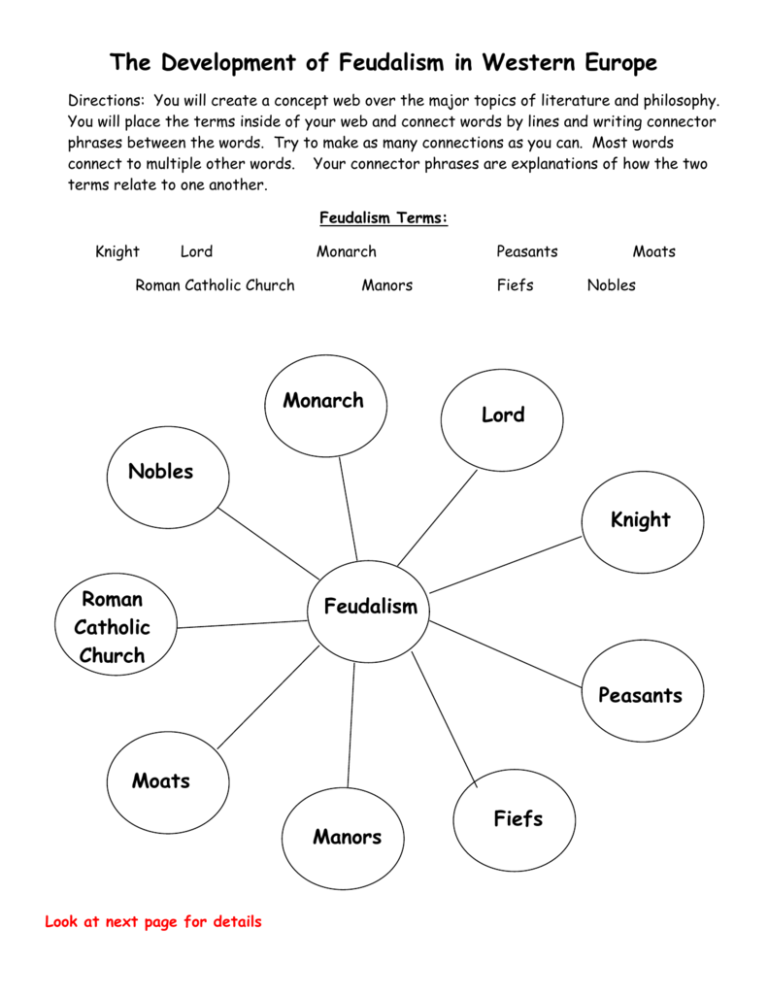
The Development of Feudalism in Western Europe Directions: You will create a concept web over the major topics of literature and philosophy. You will place the terms inside of your web and connect words by lines and writing connector phrases between the words. Try to make as many connections as you can. Most words connect to multiple other words. Your connector phrases are explanations of how the two terms relate to one another. Feudalism Terms: Knight Lord Monarch Roman Catholic Church Manors Monarch Peasants Fiefs Moats Nobles Lord Nobles Knight Roman Catholic Church Feudalism Peasants Moats Manors Look at next page for details Fiefs Feudalism Monarch – The monarchs were the top of the feudal society and were very strong. Lord – In the feudal system, people pledged their loyalty to a lord. Knight – Knights were warriors under this system. Peasants – Most people during the Middle Ages were peasants, and they were the lower class under this system. Fiefs – These were land grants under this system. Manors – These were large estates under this system. Moats – These were developed to protect the manors during this time. Roman Catholic Church – The church owned a great deal of land under this system. Nobles – Upper society during this time period and afterwards Monarch Nobles – Vassals or nobles were relied upon by the monarchs to provide enough knights and soldiers. Lords – Monarchs were feudal lords. When a monarch gave a fief to a lord, the lord became his vassals. Nobles and Peasants Complete the Venn diagram to compare and contrast the lives of nobles and peasants on a feudal manor. In the overlapping parts of the ovals, write or draw three ways these groups were similar. In each of the other parts of the ovals, draw or write three ways they were different. Nobles Most privileged life Member of nobility Given manor(s) to run Lived in grander structures Had to manage and defend his land and people who worked it Appt official to ensure work was being done Acted as judges – power to fine and punish Held posts in king’s gov’t Sent knights into warfare Leisure activity: hunting, hawking, feasting, dancing, board games, and reading Peasants Most lived on manors Diseases affected both groups Medieval times Bathed once a week Answered to monarch Legally classified as free or unfree Worked the land of the nobles or some other skilled work Paid taxes to the lord Had to give portions of their grain to the lord Lived in small houses with 1-2 rooms with little furniture or other possessions Answer the following questions: 1. What were Charlemagne’s greatest accomplishments? How was he helped by the Catholic Church? Charlemagne unified nearly all the Christian lands of Europe into a single empire. Pope Leo III helped him by giving him the blessing of the church (the church was a central part of society) and crowning him Holy Roman Emperor in 800 CE. 2. Why was there a need for order after the death of Charlemagne in 814? The rulers who came after Charlemagne failed to defend the empire against invasions. In addition, Europe was threatened by Muslims, Magyars, and Vikings in the 9th and 10th Centuries. Letter writing: Pretend you are a knight in medieval Europe. You would like to let future generations of your family know what life was like on a feudal manor. Write a letter to them below. Be sure to mention these things: The main groups of people who live on your manor What each person or group does for the others What works well in the feudal system and why What doesn’t work well in the feudal system and why Label and What responsibilities did monarchs have in the feudal system? - Kept order and supplied protection to their vassals. answer the questions. Monarch Why is William the Conqueror considered an important monarch? - After his victory at the Battle of Hastings in 1066, William brought the idea of feudalism to England. lords What responsibilities did lords have in the feudal system? - For managing and defending their manors and acting as judges - Fought for their own lords in times of war and supplied soldiers - Also appointed leaders What was the role of noblewomen in the feudal system? - Responsible for raising and training their children and sometimes the children of other noble families. They were also responsible for overseeing their households. What responsibilities did knights have in the feudal system? - Mounted soldiers in feudal system and were expected to be loyal to their church and lord, to be fair, and to protect the helpless What was the code of chivalry? What stages did a boy go through to become a knight? Knights -code of chivalry – set of rules of behavior that all knights were expected to live by - Training for knighthood – page, squire, knight Peasants (serfs) What responsibilities did peasants have in the feudal system? - Most worked at raising crops and tending livestock - Some worked as carpenters, shoemakers, and smiths - Paid taxes to the lords How were the lives of male and female peasants different? -In addition to working in the fields, peasant women had to care for their families and homes. Think about which individuals or groups in our society are most similar to the various social clases in European Feudal society. List those modern groups/individuals next to each level of feudal society, and draw symbols to respresent them. Then list some of their similarities and differences. Social Classes in Feudal Europe Monarch Individuals/ Groups Similarities and Differences between these in Our Society two groups President/Gov’t S- rulers/leaders D- President answers to other branches S- manage the land, appt officials to ensure things Governors/ are done Congress D- no “nobility” in USA, don’t life on manors, no protection (like moats) around homes, don’t act as judges Lords Army S- trained to protect (fight); some USA consider it a way of life D – USA doesn’t have to go through so many steps, don’t help women in every way possible, don’t have to perform in tournaments American citizens S – work land or jobs, pay taxes to gov’t D – USA all free; houses varies in size, free to many whom we wanted, can move up or down the social classes Knights Peasants Feudalism Notes This nickname was given to the Middle Ages. Dark Ages The period known as “The Middle Ages” is characterized by trade, land ownership, strong central govt. or no religion? Explain your selection. The Feudal system and the control of the church (which held a large amount of land) Who would most likely have said, “If you give me your loyalty, I will give you land and protection.”? A vassal or a lord What was a knight’s most important training? There is debate for the correct answer here—so think of what their main purpose was in the Feudalism activity. Although they were trained in chivalry, their most important training was for fighting. Serf were peasants who were not allowed to marry without permission from the lord/can’t leave the land. What do these medieval items have in common? They were all used in military strategy or where examples of military technology. o Stone Wall o Moat o Knight’s armor In the feudal system an individual’s social status was generally determined by what? birth What does the word feudalism mean? The economic and political system that developed in Europe during the Middle Ages Which city was added to the empire by Charlemagne by 814? Rome On which river is Tours located? Loire Which island was added by Charlemagne by 814? Corsica What physical feature did Charlemagne cross to enter Italy? The Alps