CHAPTER 11 Cardiovascular Drugs Quiz Yourself 1. Beta
advertisement

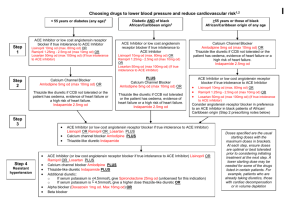
CHAPTER 11 Cardiovascular Drugs Quiz Yourself 1. Beta-blocker drugs block all beta1 and beta2 receptors. Cardioselective beta-blocker drugs are more selective in their action and block only beta1 receptors in the heart and beta2 receptors in the blood vessels (but not in the bronchi). 2. [Only need to give one example of a drug from each category.] diuretic drugs (discussed in Chapter 7) beta-blocker drugs carteolol (Cartrol) nadolol (Corgard) penbutolol (Levatol) pindolol (Visken) propranolol (Inderal) timolol (Blocadren) cardioselective beta-blocker drugs acebutolol (Sectral) atenolol (Tenormin) betaxolol (Kerlone) bisoprolol (Zebeta) metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol-XL) nebivolol (Bystolic) alpha/beta-blocker drugs carvedilol (Coreg) labetolol (Normodyne, Trandate) alpha-blocker drugs doxazosin (Cardura) prazosin (Minipress) mecamylamine (Inversine) terazosin (Hytrin) calcium channel blocker drugs amlodipine (Norvasc) clevidipine (Cleviprex) diltiazem (Cardizem) felodipine (Plendil) isradipine (DynaCirc) nicardipine (Cardene) nifedipine (Adalat CC, Procardia) nisoldipine (Sular) verapamil (Calan, Covera-HS) ACE inhibitor drugs benazepril (Lotensin) captopril (Capoten) enalapril (Vasotec) enalaprilat fosinopril (Monopril) lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril) moexipril (Univasc) perindopril (Aceon) quinapril (Accupril) ramipril (Altace) trandolapril (Mavik) angiotensin II blocker drugs candesartan (Atacand) eprosartan (Teveten) irbesartan (Avapro) losartan (Cozaar) olmesartan (Benicar) telmisartan (Micardis) valsartan (Diovan) renin inhibitor drugs aliskiren (Tekturna) aldosterone receptor inhibitor drugs eplerenone (Inspra) peripheral vasodilator drugs hydralazine (Apresoline) minoxidil 3. Bile acid sequestrant drugs are given orally; they bind with bile, forming an insoluble complex that is excreted in the feces, taking the cholesterol with it. Because the bile is not reabsorbed, the liver must draw cholesterol from the blood to produce a new supply of bile. This lowers the level of cholesterol in the blood. 4. Digitalis drugs exert two therapeutic effects on the heart; they have a positive inotropic effect that causes the heart to contract more forcefully, and they have a negative chronotropic effect that causes the heart to beat more slowly. 5. Vincent van Gogh’s painting, The Starry Night, could show evidence that the painter suffered from digitalis toxicity. It is known that he had mania and epilepsy; he may have been treated with digitalis for lack of a more specific drug available at that time. His depiction of yellow-green halos around the stars in this painting is a common visual side effect of patients with toxic levels of digitalis. Because digitalis was given in its crude form at that time, overdoses were common, as doses could not be calculated accurately and digitalis is well known for its low therapeutic index. 6. Symptoms of digitalis toxicity can be treated in one of three ways: (1) Decrease the dose of the digitalis drug, (2) give the digitalis drug less frequently or, in severe cases, (3) administer an antidote drug to reverse the toxic effects of the digitalis drug. 7. The suffix –olol is common to generic betablocker drugs. The suffix –pril is common to generic ACE inhibitor drugs. The suffix –sartan is common to generic angiotensin II blocker drugs. The suffix –azosin is common to generic alpha-blocker drugs. The suffix –statin is common to HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor drugs. 8. Nitroglycerin can be administered by these five routes: sublingually as a tablet, translingually as a spray, inhaled as vapors through the nose, orally as a sustainedrelease capsule or tablet, transdermally as a patch, or topically as an ointment (measured in inches), or intravenously. 9. Nitrate drugs, beta-blocker drugs, and calcium channel blocker drugs. 10. Digoxin immune Fab. 11. lidocaine (Xylocaine) 12. a. Cardioselective beta-blocker drug used to treat hypertension and angina pectoris b. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor drug used to treat hypercholesterolemia c. Anticholinergic drug used to treat bradycardia d. Combination calcium channel blocker drug and HMG-CoA reducase inhibitor drug used to treat hypertension and hypercholesterolemia e. Digitalis drug used to treat congestive heart failure and atrial fibrillation f. Calcium channel blocker drug used to treat hypertension and angina pectoris g. Antiarrhythmic drug used to treat cardiac asystole h. Antiarrhythmic drug used to treat ventricular fibrillation i. Angiotensin II receptor blocker drug used to treat hypertension j. Cardioselective beta-blocker drug used to treat hypertension k. Nitrate drug used to treat angina pectoris l. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor drug used to treat hypercholesterolemia m. ACE inhibitor drug used to treat hypertension n. Combination drug used to treat hypercholesterolemia 13. angiotensin-converting enzyme; congestive heart failure; digoxin; fragment, antibody binding; hypertension Clinical Application Questions 1. a. Lower the level of cholesterol in your blood b. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor drugs or “statin” drugs 2. a. congestive heart failure b. No c. Furosemide, a diuretic drug, will help the body excrete the excess fluid of peripheral and pulmonary edema in the urine. Furosimide 20 milligrams, intravenous, twice a day. d. Digoxin. e. It makes the heart pump more slowly but more strongly. f. 0.25 milligrams on even days g. Nitroglycerin ointment [instead of Nitro paste] one inch every 6 hours. h. Isosorbide 2.5 milligrams sublingual, three times a day. i. A digoxin level 3. a. propranolol b. Beta-blocker drug c. 20 mg d. Inderal e. Hypertension, ventricular arrhythmias caused by digitalis toxicity, tachycardia, and atrial flutter and fibrillation 4. a. Lipitor b. atorvastatin c. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor drug d. 10 mg 5. a. Procardia XL b. nifedipine c. calcium channel blocker drug d. 90 mg 6. Each prescription was filled by a different pharmacist (different pharmacist’s initials), each was assigned a different prescription number (Rx #), the prescription bottle on the left includes the words “by mouth,” the prescription bottle on the left is for 50 mg while the one on the right is for 100 mg, each has a different number of refills good until a different date. 7. a. amiodarone, Zoloft, Cardizem CD, Toprol-XL, Mavik, iron sulfate b. The trade names for amiodarone are Cordarone and Pacerone. Zoloft, Cardizem, Toprol-XL, and Mavik are trade name drugs. [Do not need to do this for iron sulfate.] c. Zoloft and iron sulfate d. Amiodarone is used to treat ventricular tachycardia. Cardizem is used to treat hypertension and tachycardia. Toprol-XL is used to treat hypertension. Mavik is used to treat hypertension. e. Amiodarone 200 milligrams twice a day for one week and then once a day thereafter Zoloft 25 milligrams once a day Cardizem CD 360 milligrams once a day Toprol-XL 100 milligrams once a day Mavik 2 milligrams once a day Iron sulfate 325 milligrams once a day