Is it Physical or Chemical?
advertisement

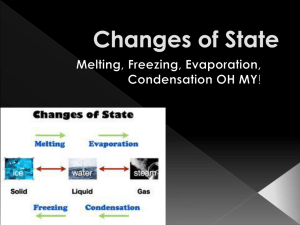
Name:_______________________________________ Matter Study Guide Due: ______________________ Chapt. 3.1 (pg. 89-91), Chapt. 3.4 (pgs. 105-109), chapt. 4.1 (Pgs 125, 127,129) Melting: _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Evaporation: _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Freezing: _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Condensation: _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Sublimation: _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Solid: _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Liquid: _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Gas: _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Law of conservation of mass: Matter: Physical Properties: Chemical Properties: Chemistry: Is it Physical or Chemical? State if each scenario is a Physical property/change or a Chemical property/change. (refer to the chart for “WHY?”). EXAMPLE (scenario) PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL? WHY? Melting a snowman An Iron fence changing into a green color when exposed to oxygen. Watching wood burning at a campfire and turning to ask. Your IPhone being dropped and shattering into many pieces. STATES OF MATTER Solid Liquid Gas Shape: Shape: Shape: Volume: Volume: Volume: Description of arrangement of particles: Description of arrangement of particles: Description of arrangement of particles: How Particles move: How Particles move: How Particles move: How Matter CHANGES states MELTING (Adding or taking away) Energy (Faster or Slower) Speed of particles (close together/farther apart) Arrangement of particles Speed of particles Arrangement of particles Speed of particles Arrangement of particles Speed of p articles Arrangement of particles EVAPORATION Energy FREEZING Energy CONDENSATION Energy GAS Melting SOLID LIQUID Freezing Label the diagram to the left with the correct change of state. Law of Conservation of Mass (pg. 109) Calcium + Chlorine = Calcium Chloride 10 grams + 30 grams = ??? Based on the Law of Conservation of Mass, what must the mass of Calcium Chloride be? The mass of a block of wood is 25 grams. It is placed in a fire and turns to ash. The mass of the ash is 15 grams. Did you just destroy the other 10 grams and prove the Law of Conservation of Mass to be false? Or can you explain what actually happened? ____________________________________________