4.2 synthesis and decomposition reactions and 5.3 elements and
advertisement

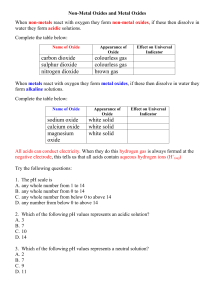
4.2 Synthesis and Decomposition Reactions 5.3 Elements and their Oxides Synthesis Two reactants combine to form a larger more complex product A + B --> AB a) Metals + Non-metal --> ionic compound Mg (s) + Cl2 (g) --> MgCl2 (s) * Purple Haze Demo: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N5h5ohd8298 What has happened? Aluminum + iodine --> aluminum iodide solid (water is the catalyst) Oxide - a compound of any element combined with oxygen (usually from air) Special case: Metal + oxygen --> Metal oxide Ex. sodium + oxygen -->sodium oxide (aka basic oxide why???) Demo: Sodium oxide + water --> sodium hydroxide (place sodium into water under a blast shield then test the products with red litmus and pH paper) NOTE: anytime a metal oxide is placed in water, a BASE is made! b) Non-metal + Non-metal --> molecular compound involving hydrogen H2 (g) + F2 (g) --> HF (g) easy to predict the products not involving hydrogen are difficult to predict and require chemical tests to verify the product produced (ex. carbon + oxygen can make CO or CO2 depending on amt of O) Special Case: Non metal + oxygen --> non-metal oxide Ex. C + O2 --> CO2 (aka acidic oxide why?) Carbon dioxide + water --> Carbonic acid sulfur trioxide + water --> sulfuric acid nitrogen dioxide + water --> nitric acid NOTE: anytime a non-metal oxide is placed in water, an ACID is made! Decomposition A larger more complex compound breaks down to form two or more simpler products They usually need energy to get started (requires heat, electricity or a catalyst) AB --> A + B a) ionic compound --> element + element 2 KCl --> 2 K(s) + Cl2 (g) DEMO: Hoffman apparatus - electricity split water into hydrogen and oxygen gas (do gas tests) DEMO: Elephant toothpaste: 30% hydrogen peroxide (50mL) + 2g KI (catalyst) --> oxygen gas and water (do on top of a piece of aluminum foil in a 500 mL erlenmyer flask . test water with cobalt chloride paper --> pink, test oxygen with glowing splint --> relights) ****very hot, leave to cool***** DEMO: Genie in a Bottle: 30% hydrogen peroxide (20 ml) + MnO2 (catalyst) --> oxygen + water (complete the reaction in a 500 mL erlenmyer flask on top of a piece of aluminum foil) ****very hot, leave to cool**** b) compounds with polyatomic ions or molecular compounds are difficult to predict 2 KClO3 --> 2 KCl + 3 O2 (chlorates will release oxygen and make a metal chloride) CaCO3 --> CaO + CO2 (carbonates will release carbon dioxide and a metal oxide) DEMO: magnesium carbonate heated in a test tube over a Bunsen burner (2 min) test for carbon dioxide (flaming splint dies out) Homework: p. 161 #1-9 p. 204 #1-7