Name: Period: ______ Date: CHAPTER 13: GEOLOGIC TIME
advertisement

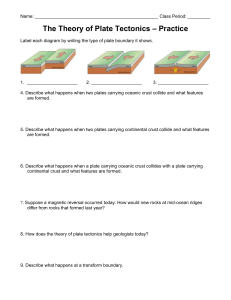
Name:________________________________ Period: ______ Date:______________ CHAPTER 13: GEOLOGIC TIME REVIEW WORKSHEET Vocab to Know: 2 bonus points for creating vocab flash cards for the following terms: Uplift Subduction zone Weathering Volcanic arcs Erosion Rift valley Erosion Half-life Divergent zones Theory of plate tectonics Transform fault Mantle Plumes Continental Crust Upwelling Oceanic crust Convection Continental drift Hot spots Convergent zones Endemic Answer the following questions: The Galapagos Islands are thought to have been created by a plate crossing over a hotspot which created the volcanic island chain over time. 1. The Galapagos Islands are found on the ________________ plate which is traveling towards _______________________. 2. Find the islands of San Cristobal and Fernandina on the map of the Galapagos Islands. Knowing the direction of plate movement, which of the islands would you think is the younger and which is the older? Why? The table below shows the ages and distances for islands and seamounts in the Galapagos. Seamount or Island Espanola San Cristobal Floreana Santa Cruz Santiago Isabela Fernandina Distance (km) 202 194 126 94 56 18 0 Age (Myr) 3.2 2.4 1.0 1.0 0.7 0.7 0.7 3. A. Plot the distances of the islands shown as a function of time. B. From your data points make a “best fit” line and determine the slope of the line. 4. How fast is this plate moving? Show your work. Give your answer in centimeters per year. (Hint: Slope calculation here.) 5. During which time period was the plate moving the fastest? 6. How long will it take before the Galapagos Islands to go down the trench off of South America's west coast? The Galapagos Islands are about 677 miles off the coast of South America. (1 mile = 1.61 km) 7. What geologic process is responsible for tectonic plate movement? Draw a labeled diagram showing how this works. 8. Complete the table below describing the 3 main plate boundary types: 1 2 3 Plate boundary type: Description of what is happening at this plate boundary. Labeled drawing of plate boundary. Actual location where you can find this type of boundary: Geologic structure(s) formed at this plate boundary 9. Draw and label a cross section of the Earth, identify the inner core, outer core, mantle continental crust and oceanic crust. 10. Describe the process(es) by which mountains can be formed, such as the Rocky Mountains in Colorado. Be sure to use some of those vocab terms! 11. On the graph paper below, draw a mountain profile (you choose the starting height!) Label the axes Elevation (y axis) and Distance (x axis). A. Using a different color, draw what the mountain profile would look like in one erosional half life. Make sure to label the elevation! B. Using a third color, draw what the mountain profile would have looked like in one erosional half life in the past. Make sure to label the elevation! Practice Dimensional Analysis Problems: Show all your work using dimensional analysis – don’t forget units!!! 12. The average student is in class 330 min/day. How many hours/year is the average student in class? 13. Light can travel 300,000,000 meters per second (m/s). Calculate how fast this is in miles per hour (mi/hr). There are 1.61 km in 1 mile. 14. A unit of length called the “furlong” is used in horse racing. The units of length called the “chain” and the “link” are used in surveying. There are 8 furlongs in 1 mile (mi), 10 chains in 1 furlong, and 100 links in 1 chain. What is the length of 1 link in inches? ***Also Review the “BUILDING BRIDGES” lesson and make sure you know how to use the fossil record to identify endemic species and infer plate movements.***