1 What Is Energy
advertisement
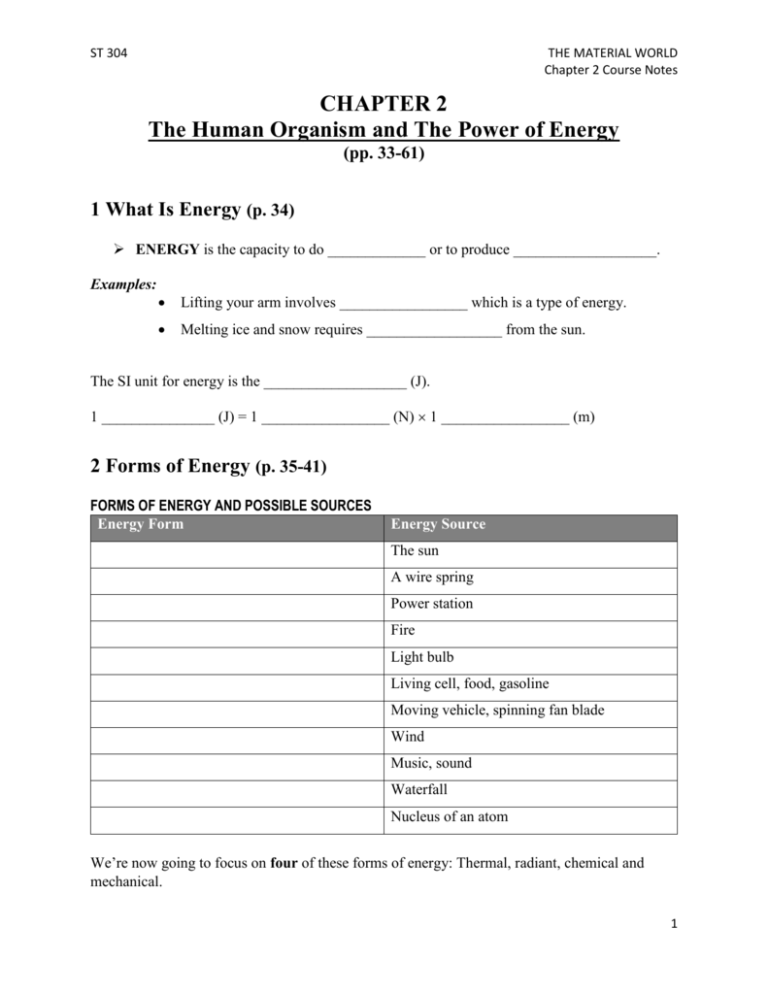
ST 304 THE MATERIAL WORLD Chapter 2 Course Notes CHAPTER 2 The Human Organism and The Power of Energy (pp. 33-61) 1 What Is Energy (p. 34) ENERGY is the capacity to do _____________ or to produce ___________________. Examples: Lifting your arm involves _________________ which is a type of energy. Melting ice and snow requires __________________ from the sun. The SI unit for energy is the ___________________ (J). 1 _______________ (J) = 1 _________________ (N) 1 _________________ (m) 2 Forms of Energy (p. 35-41) FORMS OF ENERGY AND POSSIBLE SOURCES Energy Form Energy Source The sun A wire spring Power station Fire Light bulb Living cell, food, gasoline Moving vehicle, spinning fan blade Wind Music, sound Waterfall Nucleus of an atom We’re now going to focus on four of these forms of energy: Thermal, radiant, chemical and mechanical. 1 ST 304 THE MATERIAL WORLD Chapter 2 Course Notes 2.1 THERMAL ENERGY (p. 36) THERMAL ENERGY is the energy that comes from the random _________________ of the ___________________ that make up a substance. The particles (atoms and molecules) in a substance are in constant random ________________ in all ____________________ and temperature is a measure of that _________________. Thermal energy is associated with: 1. The _______________________ of the substance 2. The _______________________ of the substance or _________________ of particles The greater the ______________________ of the substance, the greater its thermal energy. The greater the ______________________ of the substance, the greater its thermal energy. Examples of work or change that can be accomplished by thermal energy: __________________ snow by the heat of the sun Production of water vapour by a boiler of a steam ________________ to move a _________________ forward __________________ a hot-air balloon by heating the _________ inside the balloon with a burner 2 ST 304 THE MATERIAL WORLD Chapter 2 Course Notes 2.2 RADIANT ENERGY (p. 37) RADIANT ENERGY is the kind of energy that is __________________ in and _____________________ by _______________________________ waves. Examples of things that produce radiant energy: The _____________ A light_______________ ________________ Molten __________________ Radiant energy comes from the electromagnetic spectrum which consists of various types of electromagnetic _______________. The difference between the various types of electromagnetic waves is their _________________________ - the distance between two consecutive ________________ or __________________. Electromagnetic waves can transport ____________________ from one place to another. The shorter the wavelength, the ________________ energy the wave can transport. 3 ST 304 THE MATERIAL WORLD Chapter 2 Course Notes 2.3 CHEMICAL ENERGY (p. 38) CHEMICAL ENERGY is the energy stored in the ________________ of a ____________________. Chemical energy doesn’t release energy unless the ______________ holding the atoms together are ___________________. The more ________________ a molecule has, the ______________ energy it contains. Examples of work or change that is accomplished when chemical energy is released: Moving a car by burning _________________________ Producing light by burning a ____________________ Turning CO2 and H2O into glucose by __________________________ The energy to grow, move and think when the glucose in your food is “burned” in a process called ______________________ _______________________. 2.4 MECHANICAL ENERGY (p. 39-41) MECHANICAL ENERGY is the energy that results from the _________________ of an object, its _________________ and its ___________________ from the ground. The greater the ___________________ of the object, the ___________________ its ME. The greater the ___________________ of the object, the ___________________ its ME. The __________________ the object is off the ground, the ___________________ its ME. ____________ energy (movement of air) and ____________________ energy (movement of water) are forms of mechanical energy. Examples of work or change that is accomplished when chemical energy is released: the creation of a _________________ when an asteroid hits the Earth. the ___________________ of wind turbine blades by the wind the ___________________ of a turbine at a hydroelectric power plant by a waterfall 4 ST 304 THE MATERIAL WORLD Chapter 2 Course Notes 3 Energy Transformation and Transfer (p. 41-42) The TRANSFORMATION OF ENERGY is the _____________________ of energy from one form to _____________________. Examples: When a log of wood burns _____________________ energy is transformed into _____________________ and ____________________ energy. When you listen to music or watch videos on your iPhone, __________________ energy in the battery is transformed into __________________ energy and then to ________________ and __________________ energy. ENERGY TRANSFER is the _________________________ of energy from one ________________ to another. Examples: Heat emitted by the campfire is ____________________ to the air and people sitting around it. Electricity generated at a hydroelectric power plant in Northern Quebec is ____________________ along power lines to cities and towns in Southern Quebec. HEAT is the _____________________ of __________________ energy from a __________________ place to a _________________ place. 4 Physical Changes (p. 43-50) A PHYSICAL CHANGE does __________ affect the nature or ____________________ properties of matter. Examples: _________________________________ Dissolving sugar in your coffee _________________________________ 5 ST 304 THE MATERIAL WORLD Chapter 2 Course Notes 4.1 CHANGES OF STATE (p. 43-45) The matter around us exists in three states or ___________________: _______________, _________________, or _____________ and it can change from one state to another. A PHASE CHANGE is the _________________________ of matter from one state (or _______________) to another. ________________ state The particles of a _________ are _______ apart and _______ organized. There are _______ forces of attraction holding them together. The particles ______________ of a are The particles of a very ________________ ______________ and ______________ together but _______________ are together and there are not ___________________. ______________ forces The forces of holding them together are attraction holding them together. of attraction ___________________. ________________ state ________________ state Vaporization includes both ___________________ and _______________________. THE ROLE OF ENERGY IN PHASE CHANGES When we heat water to boil it, it ________________ energy which makes the water molecules move _________________ until they have enough ________________ to overcome the ________________ of attraction between them and turn into water ______________. Liquid water + __________________ water vapour 6 ST 304 THE MATERIAL WORLD Chapter 2 Course Notes When we freeze water (to make ice cubes), the temperature of the air inside the freezer is lower than that of the water, so heat passes from the ________________ to the cold ____________ which ______________ down its particles. As the water reaches its _________________ point, the particles ______________________ themselves into a rigid structure and become ice. Liquid water ice + ________________ Why do we sweat? Why do you feel cold when you get out of the water? The water or sweat on your skin __________________ heat from your skin until it _____________________. This causes the temperature of your skin to ____________________. Vaporization of liquid water absorbs _____________ J/g. Condensation of nitrogen gas releases ____________ J/g. 4.2 DISSOLUTION (p. 46-49) DISSOLUTION is the creation of a ____________________ by a ________________ dissolving in a ___________________. https://wsccbiology.wordpress.com/links/ During dissolution, the sugar molecules and the water molecules _____________ change – both substances remain the _____________. 7 ST 304 THE MATERIAL WORLD Chapter 2 Course Notes THE ROLE OF ENERGY IN DISSOLUTION Some substances, release or absorb energy when they are dissolved in a solvent. If a substance releases energy when it dissolves in water, then the temperature of the solution ______________________. (Ex. potassium hydroxide releases 1021.3 J/g) If a substance absorbs energy when it dissolves in water, then the temperature of the solution ______________________. (Ex. sodium chloride absorbs 66.7 J/g) APPLICATIONS: Heating and cooling pouches in first aid kits When we squeeze the pouch, we break an inner envelope that contains a substance that produces heat when it dissolves in the liquid surrounding it. 4.3 DEFORMATION (p. 49-50) DEFORMATION means changing the _________________ of a material. Examples: __________________ clay __________________ a spring ___________________a sheet of metal Some deformations are ______________________ and some are _______________________. THE ROLE OF ENERGY IN DEFORMATION Deformation always involves an energy __________________, an often more than one _________________________ of energy. Example: Mechanical energy of people jumping on a trampoline is ___________________ to the surface of the trampoline, where it is _________________________ into elastic energy. 8 ST 304 THE MATERIAL WORLD Chapter 2 Course Notes 5 CHEMICAL CHANGES (p. 50-52) ➢ A CHEMICAL CHANGE changes the ______________________ and __________________________ properties of matter. Examples of chemical changes: ● ________________________ bread ● fireworks ________________________ ● _______________________ soap ● ________________________ gasoline Chemical change = Chemical _______________________ During a chemical change, one or _______________ substances (____________________) react to make new substances (_____________________). During a chemical change, the bonds between the atoms of the reactants are _____________________. The products therefore have ________________________ characteristic properties from the reagents. Even if new substances are formed, the law of conservation of mass _____________________. During a chemical change, the number of atoms is ALWAYS _______________________. 9 ST 304 THE MATERIAL WORLD Chapter 2 Course Notes SIGNS OF CHEMICAL CHANGE ● The __________________ of gas ● The __________________ of heat ● The __________________ of light ● The __________________ of color ● The _______________________ of PRECIPITATE. Example (right): When sodium bicarbonate and vinegar are mixed, we can see a ____________ is released. 5.1 SYNTHESIS (p.53-55) ➢ SYNTHESIS is the _______________________ of a complex ____________________ from ___________________ or simpler ______________________. Example: 2 hydrogen atoms (H2) react with an oxygen molecule (O2) to create 2 _________________ molecules (H2O). This is called the ______________________ of _________________. THE ROLE OF ENERGY IN SYNTHESIS The synthesis of water is an explosive reaction that ___________________ a lot of energy. 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O + _______________ The formation of 2 molecules of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) from the reaction of a nitrogen molecule (N2) with 2 molecules of ___________________ (O2) ____________________ energy. N2 + 2 O2 + ________________ → 2 NO2 Synthesis is a ___________________ reaction that can either __________________ or _______________________ energy. 10 ST 304 THE MATERIAL WORLD Chapter 2 Course Notes Plants make glucose in a process called _____________________________. They do this by ________________________ energy from the ____________. During this process, plants transform ______________________ energy (from the sun) into ______________________ energy which is then stored in the _____________ of glucose molecules. Synthesis in living organisms always __________________ energy. The energy is transformed into _____________________ energy and __________________ in the bonds of the molecules that are produced. ENERGY INVOLVED IN THE SYNTHESIS OF VARIOUS SUBSTANCES SUBSTANCE ENERGY (J/g) Glucose (C6H12O6) Absorbs 7072 Carbon dioxide (CO2) Releases 8957 Water (H2O) Releases 13 444 5.2 DECOMPOSITION This process of decomposition is the _______________________ of synthesis. During decomposition, the bonds in a molecule are _______________________ and _________ or more __________________ molecules are formed. DECOMPOSITION is the transformation of _______________________ molecules into ____________________ molecules or into ___________________. 11 ST 304 THE MATERIAL WORLD Chapter 2 Course Notes THE ROLE OF ENERGY IN DECOMPOSITION During decomposition, the ______________________ energy in a molecule is usually ____________________ and transformed into other forms of _______________. In living organisms, decomposition always involves a ____________________ of energy. Example: When your body needs energy, it breaks down glycogen molecules into __________________. Certain decompositions ______________________ energy, like the _____________________ of water. Requires the input of electrical energy Decomposition is a chemical reaction that __________________ or _________________ energy. The amount of energy associated with the decomposition of molecule is __________________ to the energy required for its _______________________. Ex. If 2718 J/g is released by the synthesis of ammonia (NH3), then _____________ J/g is _____________________ in the decomposition of ammonia. 5.2 OXIDATION Oxidation is a ___________________ reaction involving _______________ or a substance that has similar properties to __________________ (ex. Sulfur, chlorine, fluoride). 12 ST 304 THE MATERIAL WORLD Chapter 2 Course Notes The best known oxidation process is the formation of ________________ (Fe2O3). 4 Fe + 3 O2 2 Fe2O3 + energy __________________________ is the oxidation or deterioration of metal. The _____________________ of fruit is another example of oxidation. THE ROLE OF ENERGY IN OXIDATION Oxidation generally involves a __________________ of energy. Examples: ______________________ or burning is an example of rapid oxidation in which a lot of energy is released in the form of fire (_____________ and _______________) ______________________ respiration in which _________________ oxidizes to produce carbon dioxide, water and __________________. 5.3 PRECIPITATION PRECIPITATION is the formation of an insoluble ________________ following the mixing of two solutions. The _________________ that forms falls to the Precipitation requires very little energy. bottom of the solution (“precipitates out”). END OF CHAPTER 2 NOTES 13








