Things to study for chemistry test #1
advertisement

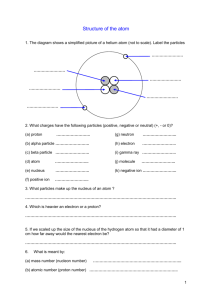
Chemistry Lab Methods: Review for Test 1 Name: _________________ Period: ____ Date: _____ Sample Questions Labs 1. Rutherford’s gold foil experiment resulted in a change in the atomic structure model of the time – from the “Plum Pudding” model to the “Rutherford” model. What were the two main changes to the model? 2. Which of the sub-atomic particles were transferred when the rulers in the Electrical Charge lab were rubbed with wool or plastic? 3. What would you predict would happen if both rulers were rubbed with wool – and then held close together? 4. Which of the two particles – iodine or starch – moved through the dialysis tubing in the Another Look at Size lab? 5. What evidence did you have that the substance really did move through the tubing? 6. Other than being small enough to fit through the “holes” in the tubing, what else was happening to allow the particles to move from one side to the other? Atomic Structure 1. Atoms are made up of what three sub-atomic particles? 2. In a neutral atom, there are the same number of which two sub-atomic particles? 3. The nucleus of an atom contains which two sub-atomic particles? 4. Which of the sub-atomic particles travel in orbits? What is the charge of these particles? 5. The mass number of an isotope equals the total number of which two sub-atomic particles? 6. If an atom gains an electron, what charge does it become? 7. What is a negatively-charged ion called? What is a positively-charged ion called? Periodic Table 1. What element characteristics were used to arrange the table? 2. An element is defined by which of the three subatomic particles? 3. What are the columns called and how are the elements in each column similar to each other? 4. What are the horizontal rows called and how many are there in the Periodic Table? 5. To which family does each of the following columns of elements belong? (Give the family name) a. Farthest column to the right _____________ b. Column with Fluorine at the top ____________ Chemistry Lab Methods: Review for Test 1 Name: _________________ Period: ____ Date: _____ 6. Fill in the following table for a NEUTRAL atom: Element Symbol # protons # electrons Atomic Mass Gold Ga 17 7. Fill in the following table: Mass Number: most common Element isotope Carbon Bromine Potassium 8. # protons # neutrons Isotope Name Fill in the following table: Element # Valence Electrons # Electrons atom will gain or lose Charge of ion likely to form Symbol for ion 9. How many electrons do elements in column 1 tend to lose to form an ion? 10. Which element has fewer protons than helium? 11. What element would you get if you added 6 protons to a neutral carbon atom? 12. What element would you get if you added 3 electrons to a nitrogen atom? Other topics to review Scientific Law & Theory – definitions and key similarities and differences Observations & Interpretations – definitions and differences Measurements – how to measure with a meter stick and with a graduated cylinder Graphing – critical components of a good graph Definitions - on the Vocabulary Wall Unit Conversions – VERY comfortable with “level 1” problems. Ok with “level 2”. Density – equation and calculations Atomic Structure – be able to draw a model of an atom or ion Labs – overview of procedure and results Star Stuff video – all elements come from stars; Big Bang created cloud of hydrogen Chemistry Lab Methods: Review for Test 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. Name: _________________ Period: ____ Date: _____ This is the ion that is named first when naming ionic compounds. This is the name for SO4 This is the chemical formula for sodium hydroxide This is the chemical formula for beryllium nitride This is the name for Li2SO4 This is the chemical formula for silver nitrate This is what we call a bond that shares electrons This is how an ionic bond is formed This is the kind of bond likely to form between two non metals The type of bond formed by Na and Cl This is the type of bond that forms KNO3 The type of bond that c and o are likely to form with each other Compounds containing this type of bond are likely to conduct electricity C11H22011 in solution is likely to conduct electricity (true/false) This is the name for the negatively charged ion in an ionic bond This is the reason dry ionically bonded substances do not conduct electricity This is why the iodine entered only one side of the dialysis tubing in the charged particles lab Chemistry Lab Methods: Review for Test 1 Name: _________________ Period: ____ Date: _____ Things to study for chemistry test #1 Rutherford’s experiment Structure of atoms (be able to draw/calculate the number of protons, neutrons, electrons) Protons, neutrons, electrons (know where they are located/their charge/how many each atom has) Metals, nonmetals, metalloids, noble gases, ect. Labs- electrical charge lab, Rutherford, grouping by chemical behavior, Another look at size, conductivity, know what conducts and why (must be ionic, must be in solution, must contain mobile ions), charged particles in solution Ionic and covalent bonds (how they’re formed, their properties, what elements are likely to form which) Ionic compounds versus molecules (formed with covalent bonds) Naming ionic compounds Writing compounds using names Atoms or elements versus compound Valence electrons Organization of the periodic table Families and groups Charges of atoms Ch 17 and 23 in your textbook Metric conversion Metric system Scientific method Parts of a graph Graphing Length Volume Elements Compounds Density calculations Mass Temperature Labs- mass and volume of water, Measurement review Density of water 3 step method Measurement