Word Text Document - Association of Travel Instruction
advertisement

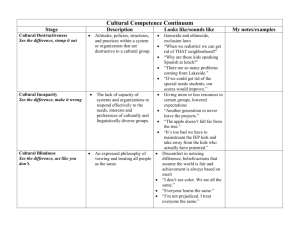
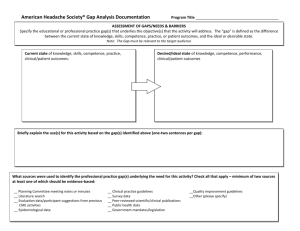
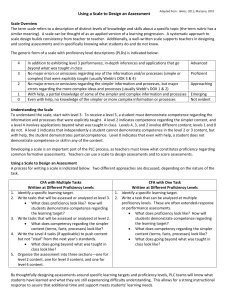
Slide 1: Cultural Competency and Travel Training • Kristen Salkas, RTA Chicago, IL • Anthony Johnson, PTMA Montgomery County, PA Slide 2: Our Guiding Light We hope to have an open and nonjudgmental discussion on issues surrounding culture when it comes to training people from diverse backgrounds. Slide 3: What is culture? Any of the following can make up one’s culture: • Race • Ethnicity • Sexual Orientation • Nationality • Language • Gender • Age • Disability • Location Slide 4: What cultures do you encounter during travel training? Slide 5: Cultural Competence Kristen Salkas Slide 6: Cultural Competence • The ability to interact with people from different cultural backgrounds Slide 7: Camphina-Bacote, 2002 • Cultural Competence is a process • People from the same cultural group are more different from each other than alike • Competence is essential for providing any service effectively! Slide 8: Camphina-Bacote, 2002 Slide 9: Balcazar, Suarez-Balcazar & Taylor-Ritzler, 2009 • Developing a conceptual framework for cultural competency • Meta-analysis Slide 10: Balcazar, Suarez-Balcazar & Taylor-Ritzler, 2009 • There are three components to cultural competence: 1. Critical Awareness (being aware of a cultural need of a client) 2. Skills Development (developing the skills to successfully interact with the client in a culturally-competent way) 3. Organizational Support (receiving what you need from your organization and other organizations that the client might work with as well) Slide 11: Next steps… • Travel Training as a practice has no standards for cultural competence! • What can your program improve upon? Slide 12: Language Anthony Johnson & Kristen Salkas Slide 13: Language • Language is a vital part of culture • Cultural competence requires proficiency in a language that someone can understand completely • Appropriate language is a good place to start in becoming more culturally competent Slide 14: Appropriate Language • Comprehensible for client’s level of proficiency • In the client’s native language • Disability language/culture Slide 15: Appropriate Language • • Comprehensible for client’s level of proficiency • ESL learners • Clients with ID In the client’s native language • Translated • • Interpreted Disability language/culture • Deaf culture and ASL • Screen reader compatibility • Using pictures instead of words Slide 16: Anthony’s and Kristen’s Experiences Slide 17: Looking Toward the Future… Anthony Johnson Slide 18: Transit Troubles • Shanghai: the city’s Municipal Transportation Authority voted against adding English to its bus stop signs • Philadelphia: SEPTA removes gender-identifying stickers from passes • Greenville, SC: plans to remove a pedestrian bridge would cut off lower-income community from bus routes • Dayton, OH: local town created onerous requirements such as heated and cooled bus shelters if Greater Dayton RTA wanted to expand bus service Slide 19: One Country, Many Approaches • Contra Costa County, CA: Bilingual buddies are paired with riders; bilingual materials at key locations • Washington, DC: METRO station announcements made in English/Spanish • Detroit: SMART’s Community Partnership Program includes a bilingual scheduler/drivers Slide 20: One Country, Many Approaches • San Francisco: MUNI pays for trip to first class • Atlanta: MARTA offers materials in alternate formats • Los Angeles: Occidental College Spanish 211 students translate community materials as class activity Slide 21: One Country, Many Approaches • Fort Collins: Trainers provide on-site services for community groups • Anchorage: How-to-ride DVDs w/ Spanish, Tagalog and Korean subtitles