Social Emotional Learning in HS - AppB
advertisement
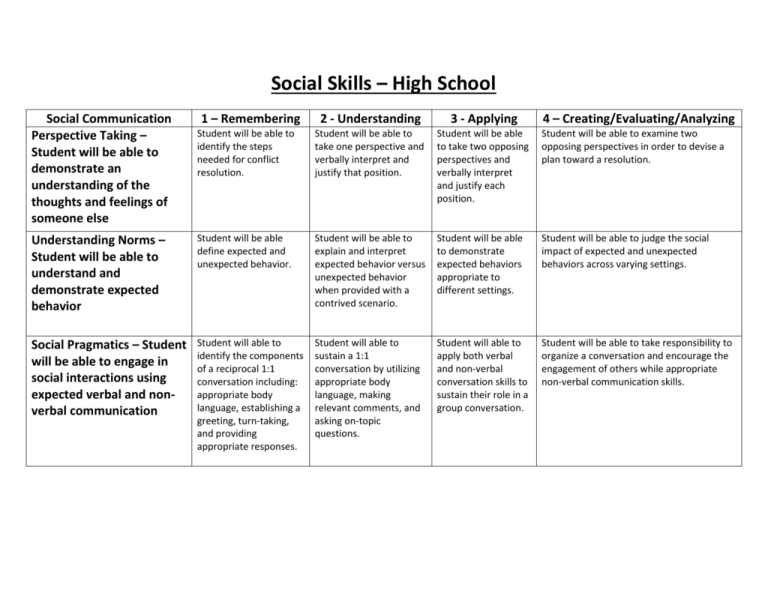
Social Skills – High School Social Communication Perspective Taking – Student will be able to demonstrate an understanding of the thoughts and feelings of someone else 1 – Remembering 2 - Understanding 3 - Applying 4 – Creating/Evaluating/Analyzing Student will be able to identify the steps needed for conflict resolution. Student will be able to take one perspective and verbally interpret and justify that position. Student will be able to take two opposing perspectives and verbally interpret and justify each position. Student will be able to examine two opposing perspectives in order to devise a plan toward a resolution. Understanding Norms – Student will be able to understand and demonstrate expected behavior Student will be able define expected and unexpected behavior. Student will be able to explain and interpret expected behavior versus unexpected behavior when provided with a contrived scenario. Student will be able to demonstrate expected behaviors appropriate to different settings. Student will be able to judge the social impact of expected and unexpected behaviors across varying settings. Social Pragmatics – Student will be able to engage in social interactions using expected verbal and nonverbal communication Student will able to identify the components of a reciprocal 1:1 conversation including: appropriate body language, establishing a greeting, turn-taking, and providing appropriate responses. Student will able to sustain a 1:1 conversation by utilizing appropriate body language, making relevant comments, and asking on-topic questions. Student will able to apply both verbal and non-verbal conversation skills to sustain their role in a group conversation. Student will be able to take responsibility to organize a conversation and encourage the engagement of others while appropriate non-verbal communication skills. Self-Advocacy Identify Needs— Student can verbally identify own needs and demonstrate selfawareness 1 – Remembering 2 - Understanding 3 - Applying 4 – Creating/Evaluating/Analyzing Student can identify and share his or her personal interests and preferences in three contexts: academic, interpersonal and leisure Student can identify and explain ways in which his interests and preferences are influenced by personal history, family/culture and personal beliefs Student can apply knowledge of personal preferences, influences and personal strengths and weaknesses to a discussion about a real life situation Student can self-identify a challenging life situation and create and present a personal needs assessment for that situation that considers personal preference and belief, strengths/weaknesses and personal responsibility Identify Resources— Student will be able to identify and access the person(s) and/or appropriate resource or strategies to execute and/or implement their plan Student can identify individuals in their life who are potential resources and supports, and state what potential support/areas of expertise are offered by each individual (e.g., a sister offers emotional support, while a guidance counselor offers career and educational expertise) Student demonstrates understanding of personal rights and can explain how these rights guarantee access to supports and resources across at least 2 areas of life (e.g., people with disabilities have the right to receive an appropriate education; people have the right to be free from harm and harassment, etc.) Student can identify an area of personal need, and apply their knowledge of personal and community resources to explain which resources are needed, available and how they would be accessed Student can take responsibility for personally seeking out and accessing needed resources for an identified problem, and afterward evaluating the effectiveness of the accessed resources in discussion with counselor and/or small group. Communicate NeedStudent will be able to express their needs and evaluate options and take expected action/ develop a plan to address the need. Student will be able to create an “I” statement to express a problem/ need. Student will be able to explain the 5 important components of selfadvocacy. Student will be able to develop a plan to communicate an identified need using the 5 components of self-advocacy. Student will be able to execute and evaluate the developed plan to communicate their need. Self-Regulation Self-Awareness: Student will be able to identify internal feelings and emotions and their physiological responses. 1 – Remembering 2 - Understanding 3 - Applying 4 – Creating/Evaluating/Analyzing SWBAT identify/ explain the connection between mind/ body/ thoughts/ behavior (using a CBT model). SWBAT demonstrate understanding of their triggers for a range of emotions (e.g. using if/then statements, behavior mapping) SWBAT apply the mind/ body connection to their own emotions by identifying triggers for their own emotions/ behaviors. SWBAT analyze and predict the ways in which past experiences may impact the way they react to new emotional situations. Self-Management: Student will be able to evaluate and use expected coping strategies. Student can identify/define what a coping strategy is. Student can explain what a coping strategy is and give an example of when they would use one. Student will be able to make a chart outlining their preferred coping strategies and when they will use them. Student is able to judge a situation and decide which coping strategy they will use. Problem Solving: Student will develop an action plan in response to triggers or conflicts. Student can list strategies they have used in response to triggers or conflicts. Student will discuss how each of their strategies helped in response to triggers or conflicts. Student can use their outlined strategies in response to triggers or conflicts. Student will produce an action plan with outlined strategies in response to triggers or conflicts.