Identify the theory of communication
advertisement

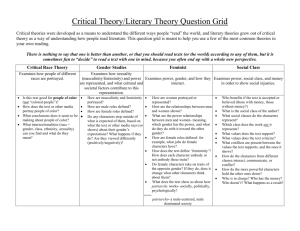
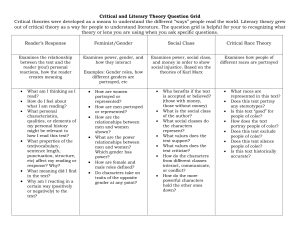
Theories of organizations, relationships, and media COMM 518 Dr. Swanson Analyzing the Organization *SWOT analysis Internal environment Performance Niche Structure Ethical base Internal impediments Public perception Visibility Reputation External environment Supporters Competitors Opponents External impediments Checklist 2A, 2B, 2C Tollefson’s list of relevant theories Classical Theory of Organizations [examines productivity, precision, and efficiency of an organization using a machine metaphor] Critical Theory of Communication approach to organizations [critiques how social reality is created and recreated in organizations] Cultural Approach to Organizations [examines how members of an organization create a sense of shared reality] Human Relations Theory of Organizations [examines employees’ relationships and other factors affecting happiness and satisfaction] Information Systems/ Weick’s Theory of Organizing (Sense-Making [explains how we make sense out of confusing information] Leadership Theories [numerous theories examine issues of leadership] Organizational Socialization [stages in employees’ socialization within an organization] Structuration Theory [we create the organization as we act within it; the theory creates awareness of rules and resources we use within groups] Systems Theory [examines an organization as a self-contained system whose major goal is survival] Uncertainty Reduction Theory [assumes that when strangers meet their primary concern is reducing uncertainty and increasing predictability; examines ways we reduce uncertainty] Unobtrusive and Concertive Control Theory [examines how individual create identifications within an organization, and how identification relates to control and discipline] See also Tollefson’s category X (public relations theory/ relationships). Analyzing the Relationships Tollefson’s list of relevant theories Publics Publics, markets, audiences Characteristics of publics Key publics Intercessory publics Opinion leaders Affinity-Seeking Strategies [strategies used to get others to like us or see us in a favorable way] Attraction Theories include the following: Interpersonal Goal-Oriented Theory of Attraction [examines attraction in later stages of relationship development] Reinforcement Theory [we are attracted to persons who reward us] Similarity and Interpersonal Attraction [we are attracted to persons whom we perceive to be similar to us] Attribution Theory [the ways we infer the causes of behavior in others and ourselves] Communication Accommodation Theory [examines underlying motives and how we accommodate others] Communication Privacy Management Theory (Boundary Management) [how we negotiate disclosures, secrets, and boundaries in interpersonal relationships] Coordinated Management of Meaning [examines social processes of persons in conversation; the ways we communicate are often more important than the content] Expectancy Violations Theory [examines expectancy, violations, and communicator rewards] Interpersonal Deception Theory [strategies used by liars to deceive others] Relational Dialectics Theory [examines the tension and struggles of Stages of development Stereotypes The benefit statement Checklist 3A, 3B interpersonal relationships, such as connectedness-separateness, certaintyuncertainty, openness-closedness] Social Exchange Theory [relationships are evaluated in terms of rewards received] Social Identity Theory [each person has different ‘selves’ that act on different levels with different group situations] Social Penetration Theory [compares human personality to an onion to suggest multiple levels that can be accessed through self-disclosure] Speech Act Theory [examines basic units of language used to express meaning, focusing on functions of speech acts] Symbolic Interactionalism [examines the construction of social reality through language] Turning Point Theory [events associated with changes in relationships] Uncertainty Reduction Theory [assumes that when strangers meet their primary concern is reducing uncertainty and increasing predictability; examines ways we reduce uncertainty] Social Order Theory [social order is manifested through predictable or coordinated actions; it is dependent on culture and sustained through trust, division of labor, regulation of power, and legitimization of social activity among humans] Also consider Tollefson’s categories II (intercultural), III (gender), IV (small group) and X (public relations theory/ cognition and behavior). I could argue there’s relevance/ crossover with the theories in V (persuasion) and VI (rhetoric). Analyzing the Media Tollefson’s list of relevant theories Goals and objectives Message strategy Information Persuasion Dialogue Proactive strategies Reactive strategies Message structure Message content Organizational media News media Advertising media Social media Cultivation Analysis [mass media exposure cultivates/grows attitudes in persons] Agenda Setting [Mass media don’t tell us what to think, but what to think about] Uses and Gratifications [examines reasons persons have for using the mass media and/or the pleasures they derive] Spiral of Silence [persons are pressured by society to not express views that deviate from socially accepted views] Technological Determinism [technologies shape human existence; “the medium is the message”] Semiotics [examines how signs convey meanings and perpetuate dominant interpretations] Cultural Studies [critiques power relationships and seeks changes] Mass Communication and Para-social Interaction [audience views persons in the mass media as members of their peer group or acquaintances] Media Dependency Theory [the more the mass media fulfills individual needs, the more important the mass media] Checklist 7B, 7C I could argue there’s relevance/ crossover with the theories in Tollefson’s category V (persuasion) and VI (rhetoric). Source: Smith, R. D. (2009). Strategic planning for public relations. (3 ed.). New York: Routledge.