Sample Plan of Study
advertisement
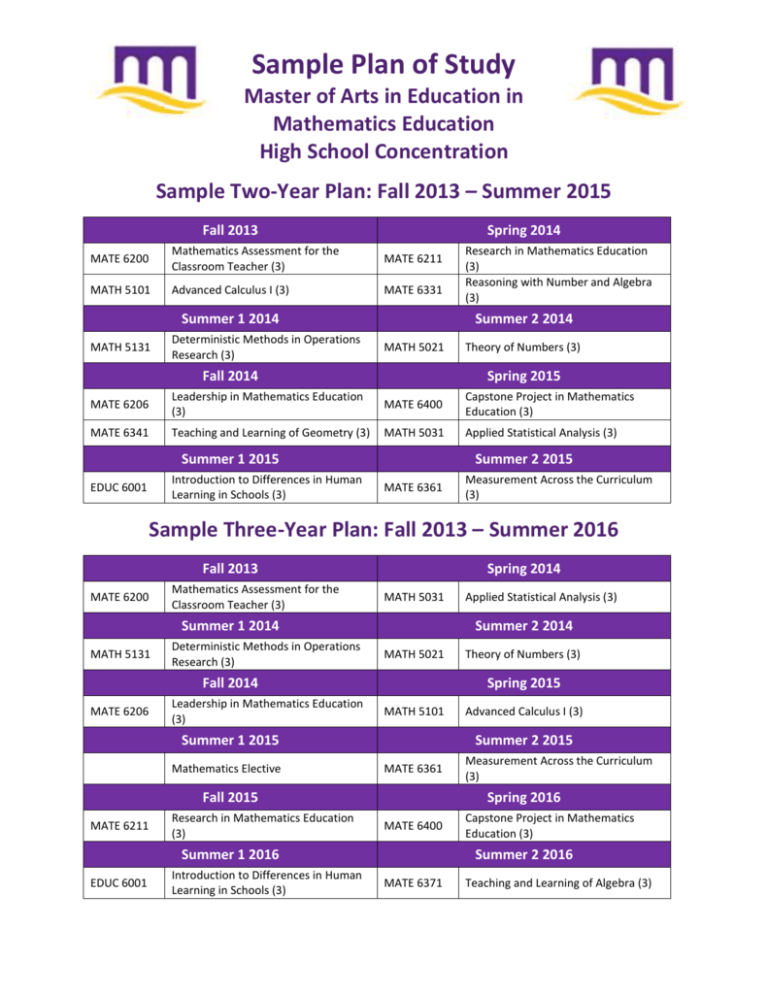
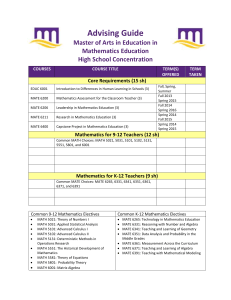
Sample Plan of Study Master of Arts in Education in Mathematics Education High School Concentration Sample Two-Year Plan: Fall 2013 – Summer 2015 Fall 2013 Spring 2014 MATE 6200 Mathematics Assessment for the Classroom Teacher (3) MATE 6211 MATH 5101 Advanced Calculus I (3) MATE 6331 Summer 1 2014 MATH 5131 Deterministic Methods in Operations Research (3) Research in Mathematics Education (3) Reasoning with Number and Algebra (3) Summer 2 2014 MATH 5021 Fall 2014 Theory of Numbers (3) Spring 2015 MATE 6206 Leadership in Mathematics Education (3) MATE 6400 Capstone Project in Mathematics Education (3) MATE 6341 Teaching and Learning of Geometry (3) MATH 5031 Applied Statistical Analysis (3) Summer 1 2015 Introduction to Differences in Human Learning in Schools (3) EDUC 6001 Summer 2 2015 MATE 6361 Measurement Across the Curriculum (3) Sample Three-Year Plan: Fall 2013 – Summer 2016 Fall 2013 MATE 6200 Mathematics Assessment for the Classroom Teacher (3) Spring 2014 MATH 5031 Summer 1 2014 MATH 5131 Deterministic Methods in Operations Research (3) Summer 2 2014 MATH 5021 Fall 2014 MATE 6206 Leadership in Mathematics Education (3) MATH 5101 Research in Mathematics Education (3) MATE 6361 Introduction to Differences in Human Learning in Schools (3) Measurement Across the Curriculum (3) Spring 2016 MATE 6400 Summer 1 2016 EDUC 6001 Advanced Calculus I (3) Summer 2 2015 Fall 2015 MATE 6211 Theory of Numbers (3) Spring 2015 Summer 1 2015 Mathematics Elective Applied Statistical Analysis (3) Capstone Project in Mathematics Education (3) Summer 2 2016 MATE 6371 Teaching and Learning of Algebra (3) Course Catalog Descriptions Education Core Courses EDUC 6001. Introduction to Differences in Human Learning in Schools (3) Examines race, ethnicity, socioeconomic class, gender, sexual preference, and exceptionality relative to historical, philosophical, social, cultural, political, and legal issues in schools. MATE 6200. Mathematics Assessment for the Classroom Teacher (3) Formerly MATH 6200 P: Consent of instructor. Theory, methods, and techniques of assessment for improving mathematics learning. Requires assessment and intervention project adapted to local classroom setting. MATE 6206. Leadership in Mathematics Education (3) Formerly MATH 6206 P: Admission to MAEd program; consent of instructor. Mathematics content and information necessary for service as leader in public school mathematics education. MATE 6211. Research in Mathematics Education (3) Formerly MATH 6211 Readings, reports, and syntheses of research literature on teaching and learning K-12 mathematics. Projects based on this literature. MATE 6400. Capstone Project in Mathematics Education (3) Research project, portfolio modeled on the National Board Professional Teaching Standards, or equivalent project. 9-12 Mathematics Electives MATH 5021. Theory of Numbers I (3) P: MATH 3263 or consent of instructor. Topics in elementary and algebraic number theory such as properties of integers, Diophantine equations, congruences, quadratic and other residues, and algebraic integers. MATH 5031. Applied Statistical Analysis (3) (WI) May not count toward mathematics hours required for the mathematics concentration of the MA. P: MATH 2228, 3584; or equivalent; or consent of instructor. Topics include analysis of variance and covariance, experimental design, multiple and partial regression and correlation, nonparametric statistics, and use of computer statistical package. MATH 5101. Advanced Calculus I (3) P: MATH 2173 or consent of instructor. Axioms of real number system, completeness, sequences, infinite series, power series, continuity, uniform continuity, differentiation, Riemann integral, Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. MATH 5102. Advanced Calculus II (3) P: MATH 3256, 5101; or consent of instructor. Mathematical analysis of functions of several real variables. Limits, continuity, differentiation, and integration of multivariable functions. MATH 5131. Deterministic Methods in Operations Research (3) P: MATH 2173; 3307 or 5801. Mathematical models; linear programming; simplex method, with applications to optimization; duality theorem; project planning and control problems; and elementary game theory. MATH 5581. Theory of Equations (3) P: MATH 2173 or consent of instructor. Topics include operations with complex numbers, De Moivre’s Theorem, properties of polynomial functions, roots of general cubic and quartic equations, methods of determining roots of equations of higher degree, and methods of approximating roots. MATH 5801. Probability Theory (3) P: MATH 2173 or 3307. Axioms of probability, random variables and expectations, discrete and continuous distributions, moment generating functions, functions of random variables, Central Limit Theorem, and applications. MATH 6001. Matrix Algebra (3) P: MATH 3256 or consent of instructor. Properties of vectors and matrices and their applications. K-12 Mathematics Electives MATE 6265. Technology in Mathematics Education (3) Technology applications in grades 6-12 based on national recommendations, research, and issues pertaining to equity and access. MATE 6331. Reasoning with Number and Algebra (3) Rational numbers, proportional reasoning, and linear relations as tools to explore mathematical relationships in grades 6-8. MATE 6341. Teaching and Learning of Geometry (3) Analysis of middle school student work using the van Hiele model to examine relationships of shape, size, symmetry, and transformations in 2- and 3-dimensional space. MATE 6351. Data Analysis and Probability in the Middle Grades (3) Data analysis, probability concepts, and pedagogical issues for middle grade teachers. MATE 6361. Measurement Across the Curriculum (3) Key issues in teaching and learning measurement as it supports other mathematical strands. MATE 6371. Teaching and Learning of Algebra (3) Current mathematical learning theory and research as it pertains to algebra taught from a problem-solving, student-centered perspective. MATE 6391. Teaching with Mathematical Modeling (3) Historical and contemporary models applied to real-world situations to demonstrate the power and limitations of modeling.