World War 2 Mini Quiz - Cabarrus County Schools
advertisement

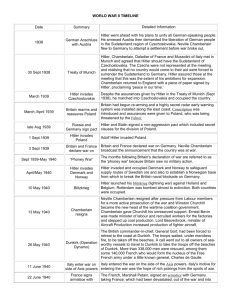
Quiz #3 World War II 1. Which of the following is an example of genocide? a. When an individual hates an entire race of people. b. When an entire ethnic group is wiped out. c. When ethnic discrimination is legalized by the government. d. When a person is denied a job based on their ethnicity. 2. What was the Final Solution? a. The Nazis’ plan to murder all European Jews. b. A Jewish revolt in the Warsaw ghetto. c. A law that denied Jews citizenship. d. America’s war plan against Germany. 3. According to the political cartoon to the right… a. England represents the gap in the bridge. b. the League of Nations remains weak without the United States included. c. the League of Nations includes the countries of Germany and the Soviet Union. d. none of the above. 4. What caused Neville Chamberlain to appease Adolf Hitler? a. His belief that Britain would eventually defeat Hitler. b. His desire to avoid another world war. c. His belief that Britain would be crushed by Hitler’s army. d. His personal friendship with Hitler. 5. What is being portrayed in the political cartoon to the right? a. The Non-Aggression agreement between Hitler and Stalin of 1938. b. The Lend-Lease Act between Roosevelt and Churchill of 1940. c. The Munich Agreement between Chamberlain and Hitler of 1938. d. The Iron Pact between Hitler and Mussolini of 1938. 6. How was Hitler’s Nazi government different from the previous German government? a. The previous government was a monarchy; Hitler’s was a military. b. The previous government was Communist; Hitler was a Fascist. c. The previous government was democratic; Hitler was a dictator. d. The previous government mistreated its citizens; Hitler treated all citizens fairly. 7. In contrast to democracy, which form of government uses the military to maintain power against the people’s consent? a. monarchy c. theocracy b. dictatorship d. oligarchy 8. How would your life be different if you lived under the rule of a fascist dictatorship? a. Your civil rights, like freedom of speech, might be taken away. b. You would be separated from your family. c. Your property might be taken away by the Communist Party. d. You would no longer be allowed to go to school or play sports. 9. The hats on the hooks of the political cartoon to the right represent… a. the countries that have defeated the German army during World War II. b. the countries of the League of Nations. c. the countries Hitler has defeated in World War II. d. the representatives at the Munich Conference. 10. The Lend-Lease Act of 1941… a. supplied countries such as Great Britain and France with war materials and money. b. kept the United States out of war, but allowed them to help their allies. c. led to submarine attacks on American ships in the Atlantic Ocean. d. all of the above. 11. “We have no quarrel with the German people, except that they allow themselves to be governed by the Nazi Government. As long as that Government exists and pursues the methods it has so persistently followed during the last two years, there will be no peace in Europe. We shall merely pass from one crisis to another, and see one country after another attacked by methods which have now become familiar to us in their sickening technique.” Neville Chamberlain, Prime Minister of Great Britain, Speech to Parliament 1939 What event of World War II is being described by Neville Chamberlain in the quote above? a. b. c. d. The bombing of Pearl Harbor by the Japanese. The opening of the Auschwitz Death Camp by the Nazi government. The signing of the Lend-Lease Act by the United States of America. The invasion of Poland by the German military. 12. What cause of the bombing of Pearl Harbor is being illustrated to the right? a. The Lend-Lease Act b. The Iron Pact c. An oil embargo on the Japanese government d. The annexation of Manchuria by the Japanese. 13. A major cause of the internment of JapaneseAmericans during World War II was… a. because of immigration quotas established by the U.S. b. because the U.S. government was suspicious of spies and sabotage. c. due to the economic depression. d. due to racial prejudices. 14. The significance of the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan was that… a. atomic bombs/nuclear weapons were being used for the 1st time in world history. b. the Japanese military proved to be the strongest in the world. c. the United States of America became the 1st world super power. d. the Soviet Union and the Germans signed a treaty promising not to invade each other’s country. 15. After the defeat of Japan in World War II, the United States led the Allies in the occupation and rehabilitation of the Japanese state…the U.S….forces…enacted widespread military, political, economic, and social reforms…MacArthur also tried…to [change] the economy into a free market capitalist system…Allied advisors…dictated a new constitution. Source: U.S. Department of State The Allies helped Japan rebuild after World War II. Which describes how the Allies were involved in rebuilding Japan? a. The Allies sent military forces to rebuild Japan’s government and economic structures. b. The Allies sent military forces to help regulate Japan’s wealthy economy. c. The Allies sent military forces to take control of Japan’s military forces. d. The Allies sent military forces to rebuild Japan’s armed forces to protect the country. 16. After World War II, which two countries became the world’s super powers? a. China and Great Britain b. Great Britain and the United States of America c. The United States of America and the Soviet Union d. The Soviet Union and Japan 17. Due to the devastation of Britain’s economy after World War II, they were forced to declare independence to many of their colonies around the world, including… a. The United States of America. b. India. c. Australia. d. New Zealand. 18. At the Yalta Conference, the Big 3 (Roosevelt, Stalin, and Churchill) agreed to… a. sign a treaty to never go to war with each other again. b. demilitarize the Sudetenland. c. divide Germany into four zones of occupation. d. put surviving Nazis on trial in Nuremberg, Germany. 19. The “iron curtain” that separated Western and Eastern Europe represented the division between… a. independent, democratic countries versus countries under Soviet Union, communist influence. b. Great Britain versus the Soviet Union. c. absolute monarchial governments versus the democracies in Czechoslovakia and Austria. d. countries of the United Nations versus countries of NATO. 20. The map to the right represents… a. the division of India between the four super powers of the world. b. the division of Berlin, Germany into zones of occupation after World War II. c. the ethnic boundaries of German people living in Berlin after World War II. d. The fight over governmental control of Cuba.