Unit Teaching Resources Spatial Analysis
advertisement

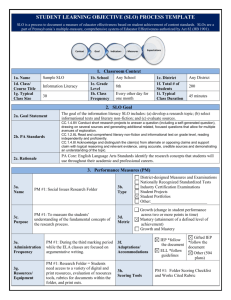
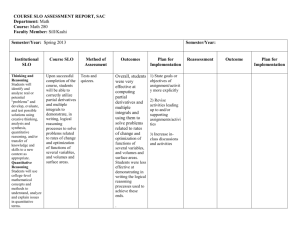
Teaching Resources: Spatial Analysis Unit 1: Reviewing the Basics of Geospatial Data - Students will review the basics of geospatial data including data organization in an appropriate format such as a geodatabase; the importance and role of coordinate system definition and projection between coordinate systems; the differences between vector and raster data formats; and basic cartographic and data presentation techniques. (optional primarily for background only, SLO 1) Resources: Unit 2: Introduction to Geospatial Analysis - Students will start to think about using geospatial data to explore data realtionships. Students will learn how to prepare a simple data set using a straightforward method such as a join. Students will classify quantitative data using a variety of statistical methods. Students will create a scatter plot of data and will present results of analysis in graph and cartographic format. (SLO 1, 5) Resources: Unit 3: Using Advanced Attribute and Spatial Queries for Data Exploration - Students will be given a data set that requires performing advanced queries to prepare the data for use in analysis. Students will use a data dictionary to decipher coded data in an attribute table. Students will determine how to use queries to address a question. Selection by location and bufferin is also introduced. (SLO 1, 2, 5) Resources: Unit 4: Vector Data Analysis: Overlay Techniques - Students will learn vector overlay analysis tools and concepts including union, intersect and identity, and how these tools can be used to analyze multiple geospatial data sets to answer a question. Students will convert from coverage format to modern GIS data fomat. Environment settings to enhance data organization will be introduced. (SLO 1, 3, 4, 5) Resources: Unit 5: Vector Data Analysis: Creating a Site Selection Model - Students will be learn proximity analysis including buffering lines and polygons. Students will be introduced to the concept of a geospatial data model by developing flow charts. Students will develop a model that satisfies multiple location criteria for a given project. (SLO 1, 3, 4, 5) Resources: Unit 6: Vector Data Analysis: Network Analysis - Students will prepare a vector data set for use in a network routing exercise including building topology. Students will use network techniques to create efficient routes including modeling of impedances. Students will generate service areas based on network analysis. (SLO 1, 3, 4) Resources: Unit 7: Building an Automated Model - Students will learn how to implement a multi-step model using automation tools. Students will learn to set appropriate environmental settings prior to running a model. They will set model parameters in order to alter model inputs. They will export their model to a script and edit the script. (SLO 3, 4) Resources: Unit 8: Raster Data Analysis: Working with Topographic Data - Students will learn how to use raw elevation data to create slope, aspect and hillshade surfaces. Students will use elevation and derived data sets to analyze an environmental issue. Students will reclassify raster data and use in a map algebra-based model, including weighting techniques. Students will use viewshed analysis to enhance site selection. Students will be introduced to TINs (SLO 1, 3, 4, 5) Resources: Unit 9: Raster Data Analysis: Working with Hydrographic Data - Students will obtain appropriate data sets and use them to do a surface hydrological analysis. Students will generate streams using flow direction and accumulation surfaces. Students will create watersheds based on topographic data. Students will use hydrographic data to analyze a scientific question. (SLO 1, 3, 4, 5) Resources: Unit 10: Raster Data Analysis: Density Surfaces - Students will interpolate data density surfaces from point data using appropriate methods. Students will convert between vector and raster format. Students will develop approach to a given question using density techniques. (SLO 1,2,3,4,5) Resources: Unit 11: Database Design and Schema Implementation – Students will build on the basics of Geodatabase design, learning how to implement subtypes, default values and other tools. Importing existing database schema will be introduced. Resources: Unit 12: Student Project – Solve a problem using geospatial technology from goals and data acquisition to analysis and processing to cartographic presentation and publishing. Students will create their own data using electronic methods (SLO 1, 2, 3, 4, 5) Resources: Funded by National Science Foundation Advanced Technological Education program [DUE #0801893]. Author’s opinions are not necessarily shared by NSF