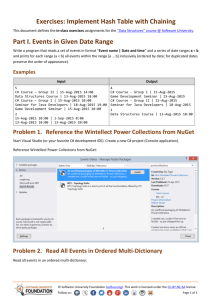
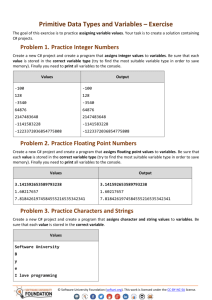
C# Advanced
advertisement
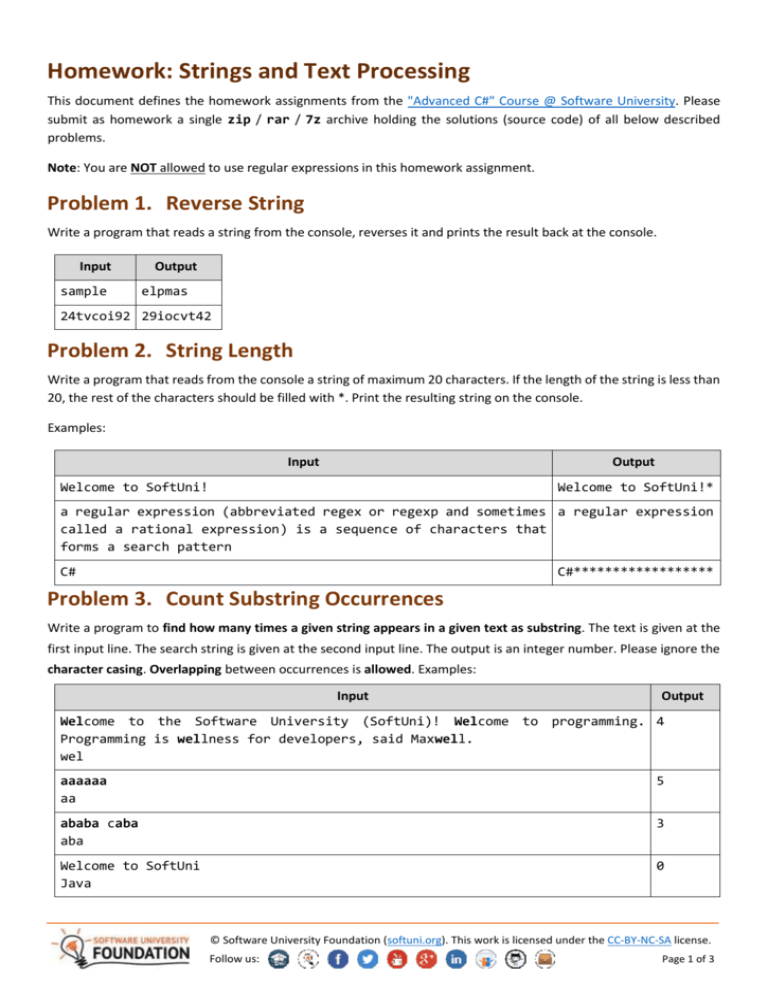
Homework: Strings and Text Processing This document defines the homework assignments from the "Advanced C#" Course @ Software University. Please submit as homework a single zip / rar / 7z archive holding the solutions (source code) of all below described problems. Note: You are NOT allowed to use regular expressions in this homework assignment. Problem 1. Reverse String Write a program that reads a string from the console, reverses it and prints the result back at the console. Input sample Output elpmas 24tvcoi92 29iocvt42 Problem 2. String Length Write a program that reads from the console a string of maximum 20 characters. If the length of the string is less than 20, the rest of the characters should be filled with *. Print the resulting string on the console. Examples: Input Output Welcome to SoftUni! Welcome to SoftUni!* a regular expression (abbreviated regex or regexp and sometimes a regular expression called a rational expression) is a sequence of characters that forms a search pattern C# C#****************** Problem 3. Count Substring Occurrences Write a program to find how many times a given string appears in a given text as substring. The text is given at the first input line. The search string is given at the second input line. The output is an integer number. Please ignore the character casing. Overlapping between occurrences is allowed. Examples: Input Output Welcome to the Software University (SoftUni)! Welcome to programming. 4 Programming is wellness for developers, said Maxwell. wel aaaaaa aa 5 ababa caba aba 3 Welcome to SoftUni Java 0 © Software University Foundation (softuni.org). This work is licensed under the CC-BY-NC-SA license. Follow us: Page 1 of 3 Problem 4. Text Filter Write a program that takes a text and a string of banned words. All words included in the ban list should be replaced with asterisks "*", equal to the word's length. The entries in the ban list will be separated by a comma and space ", ". The ban list should be entered on the first input line and the text on the second input line. Example: Input Output Linux, Windows It is not *****, it is GNU/*****. ***** It is not Linux, it is GNU/Linux. Linux is is merely the kernel, while GNU adds the merely the kernel, while GNU adds the functionality. Therefore we owe it to them functionality. Therefore we owe it to them by calling the OS GNU/*****! Sincerely, a by calling the OS GNU/Linux! Sincerely, a ******* client Windows client Problem 5. Unicode Characters Write a program that converts a string to a sequence of C# Unicode character literals. Examples: Input Output Hi! \u0048\u0069\u0021 What?!? \0057\0068\0061\0074\003f\0021\003f SoftUni \0053\006f\0066\0074\0055\006e\0069 Problem 6. Palindromes Write a program that extracts from a given text all palindromes, e.g. ABBA, lamal, exe and prints them on the console on a single line, separated by comma and space. Use spaces, commas, dots, question marks and exclamation marks as word delimiters. Print only unique palindromes, sorted lexicographically. Example: Input Output Hi,exe? ABBA! Hog fully a string. Bob a, ABBA, exe Problem 7. * Letters change Numbers This problem is from the Java Basics exam (8 February 2015). You may check your solution here. Nakov likes Math. But he also likes the English alphabet a lot. He invented a game with numbers and letters from the English alphabet. The game was simple. You get a string consisting of a number between two letters. Depending on whether the letter was in front of the number or after it you would perform different mathematical operations on the number to achieve the result. First you start with the letter before the number. If it's Uppercase you divide the number by the letter's position in the alphabet. If it's lowercase you multiply the number with the letter's position. Then you move to the letter after the number. If it's Uppercase you subtract its position from the resulted number. If it's lowercase you add its position to the resulted number. But the game became too easy for Nakov really quick. He decided to complicate it a bit by doing the same but with multiple strings keeping track of only the total sum of all results. Once he started to solve © Software University Foundation (softuni.org). This work is licensed under the CC-BY-NC-SA license. Follow us: Page 2 of 3 this with more strings and bigger numbers it became quite hard to do it only in his mind. So he kindly asks you to write a program that calculates the sum of all numbers after the operations on each number have been done. For example, you are given the sequence "A12b s17G". We have two strings – "A12b" and "s17G". We do the operations on each and sum them. We start with the letter before the number on the first string. A is Uppercase and its position in the alphabet is 1. So we divide the number 12 with the position 1 (12/1 = 12). Then we move to the letter after the number. b is lowercase and its position is 2. So we add 2 to the resulted number (12+2=14). Similarly for the second string s is lowercase and its position is 19 so we multiply it with the number (17*19 = 323). Then we have Uppercase G with position 7, so we subtract it from the resulted number (323 – 7 = 316). Finally we sum the 2 results and we get 14 + 316=330; Input The input comes from the console as a single line, holding the sequence of strings. Strings are separated by one or more white spaces. The input data will always be valid and in the format described. There is no need to check it explicitly. Output Print at the console a single number: the total sum of all processed numbers rounded up to two digits after the decimal separator. Constraints The count of the strings will be in the range [1 … 10]. The numbers between the letters will be integers in range [1 … 2 147 483 647]. Time limit: 0.3 sec. Memory limit: 16 MB. Examples Input Output A12b s17G P34562Z q2576f a1A 330.00 H456z Comment 12/1=12, 12+2=14, 17*19=323, 323–7=316, 14+316=330 46015.13 0.00 © Software University Foundation (softuni.org). This work is licensed under the CC-BY-NC-SA license. Follow us: Page 3 of 3