Graphing Reference Main Label for Graph Goes Here
advertisement

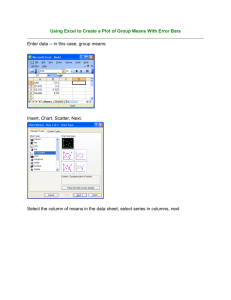
Graphing Reference Main Label for Graph Goes Here Key/Legend only if you need it = label = label Y-axis Label Goes Here This rectangle shows where you put the numbers for a graph. You must use equal and appropriate increments when numbering up. Be sure to use the entire graph Graph Checklist Have all 3 labels Properly number your y-axis Sub-labels for x-axis Do you need a key/legend Is it neat Is it easy to understand Spacing should be equally spread across the x-axis 0 Sub-labels for the bars Always start with zero at this point Sub-labels for the bars Sub-labels for the bars X-axis Label Goes Here Sub-labels for the bars Bar Graph Shows a comparison of data that has different categories. Typically graphs discontinuous data. The first bar CANNOT TOUCH THE Y-AXIS The bars should be equally spaced on the x-axis Use the same color for all bars The front page lays out what a bar graph should look like Double Bar Graph Are used for when each data group contains two different sets of data. The bars for both sets of data are next to each other (touching) for comparison. There are spaces between in the sets of data. The bars that are comparing data must be touching (leave space for the next set) The first set of bars CANNOT TOUCH THE Y-AXIS Use a key/legend to identify the different bars Line Graph For continuous data. Shows changes over time (time is on the x axis). Shows relationships between two variables or sets of data. Useful for showing trends in data and for making predictions. May have multiple lines to represent different variables The data table to the right is graphed below Time Spend Studying 0.5 hour 1 hour 1.5 hours 2 hours 2.5 hours Grade on Exam 1 63% 70% 83% 99% 100% “Comparison of Time Spent Studying To Grade Received on Exam” Percentage Scored on Exam = Exam 1 100 90 = Exam 2 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 .5 1 1.5 2 2.5 Time Spent Studying in Hours Grade on Exam 2 40% 47% 60% 77% 85% Stem and Leaf Plot Organizes large sets of numbers and classifies continuous data. Used to collect and organize data as it collected. Looks like a bar graph when turned on its side. o Examples: Graph students’ test scores out of 100. o The following are the test scores: 41, 55, 59, 62, 64, 75, 75, 75, 79, 82, 82, 82, 86, 88, 88, 89, 91, 91, 95, 96, and 99. Test Scores Out of 100 Stem Leaf 9 8 7 6 5 4 11569 2226889 5559 24 59 1 Histogram Number of Students Graphs frequency for a range of data and typically graphs continuous data. Bars have the same width and touch. Can touch the y-axis but you do not have to All bars should be the same color to help avoid confusion The graph below is for the stem and leaf information that is provided above Test Scores for Class 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 40’s 50’s 80’s 90’s Range of Test Scores 5’11 60’s 70’s