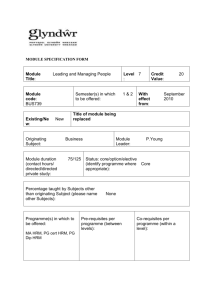
MODULE SPECIFICATION TEMPLATE MODULE DETAILS Module
advertisement
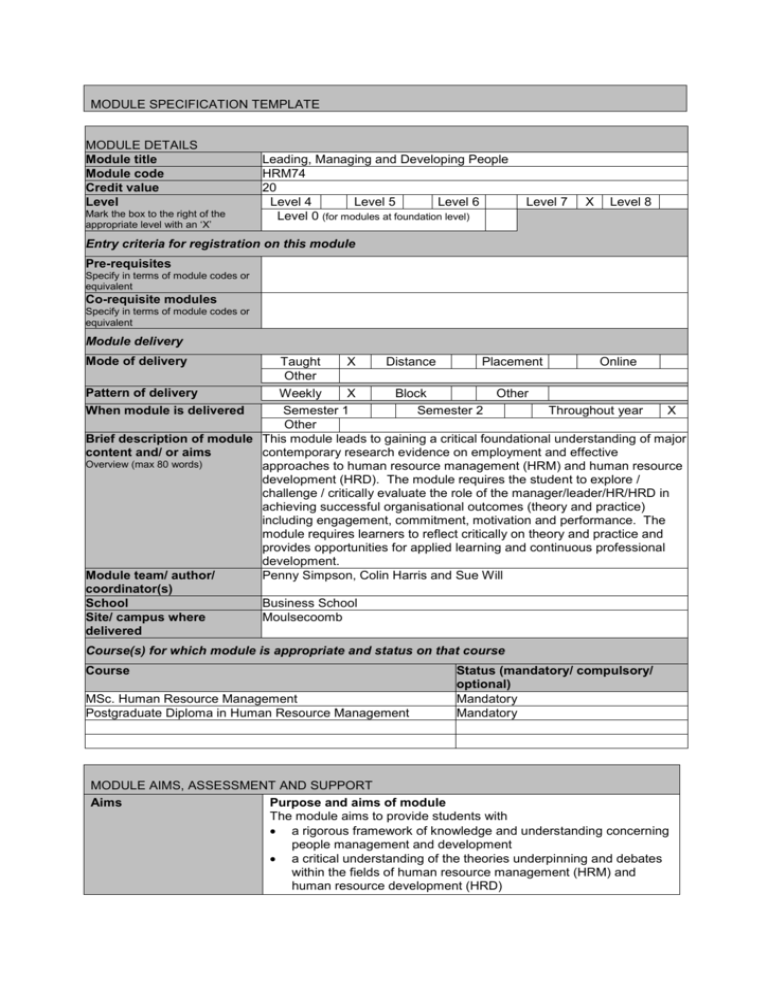
MODULE SPECIFICATION TEMPLATE MODULE DETAILS Module title Module code Credit value Level Mark the box to the right of the appropriate level with an ‘X’ Leading, Managing and Developing People HRM74 20 Level 4 Level 5 Level 6 Level 0 (for modules at foundation level) Level 7 X Level 8 Entry criteria for registration on this module Pre-requisites Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Co-requisite modules Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Module delivery Mode of delivery Taught X Distance Placement Online Other Pattern of delivery Weekly X Block Other When module is delivered Semester 1 Semester 2 Throughout year X Other Brief description of module This module leads to gaining a critical foundational understanding of major content and/ or aims contemporary research evidence on employment and effective Overview (max 80 words) approaches to human resource management (HRM) and human resource development (HRD). The module requires the student to explore / challenge / critically evaluate the role of the manager/leader/HR/HRD in achieving successful organisational outcomes (theory and practice) including engagement, commitment, motivation and performance. The module requires learners to reflect critically on theory and practice and provides opportunities for applied learning and continuous professional development. Module team/ author/ Penny Simpson, Colin Harris and Sue Will coordinator(s) School Business School Site/ campus where Moulsecoomb delivered Course(s) for which module is appropriate and status on that course Course MSc. Human Resource Management Postgraduate Diploma in Human Resource Management Status (mandatory/ compulsory/ optional) Mandatory Mandatory MODULE AIMS, ASSESSMENT AND SUPPORT Aims Purpose and aims of module The module aims to provide students with a rigorous framework of knowledge and understanding concerning people management and development a critical understanding of the theories underpinning and debates within the fields of human resource management (HRM) and human resource development (HRD) Learning outcomes On completion of this module learners will be able to demonstrate their knowledge, understanding and ability to: Subject specific 1. Review and critically evaluate major contemporary research and debates in the fields of human resource management (HRM) and human resource development (HRD) 2. Understand, analyse and critically evaluate the internal managerial and business environment within which HR professionals work. 3. Debate and critically evaluate the characteristics of effective leadership and the methods used to develop leaders in organisations. 4. Evaluate major theories relating to motivation, commitment and engagement at work and how these are put into practice by organisations. 5. Critically examine the effectiveness of change management in organisations. 6. Critically discuss the aims and objectives of the HRM and HRD function in organisations and how these are met in practice. 7. Assess the contribution made by HRM and HRD specialists in different types of organisation. 8. Promote professionalism and an ethical approach to HRM and HRD practice in organisations. Cognitive 1. Critically evaluate and synthesise current research and established theories in the literature 2. Critically apply theory to organisational practice Content Indicative module content Indicative content is provided for each learning outcome. This is neither prescriptive nor exhaustive 1. HRM and HRD. Major research studies on contemporary developments in the HRM and HRD fields (UK and overseas including CIPD), links between HR practice and business outcomes, measuring the value of the HR function; HRM and HRD practices in successful organisations, effective interface between HR and line management through partnership working. 2. Internal managerial and business environment within which HR professionals work. Management, managing and managerial functions within organisations; nature of management and leadership power, authority and influence. 3. Effective leadership and leadership development. Leadership and management styles and their impact, characteristics of successful and unsuccessful leaders, significance of effective leadership, developing effective leaders in organisations. 4. Motivation, commitment and engagement Major theories relating to motivation, commitment, and engagement at work (theory and practice), the HR equation – work, reward, job satisfaction and the psychological contract, flexibility and flexible working, reward and recognition, performance management and career development. 5. Change management The politics of management and the change agenda; effective approaches to change management and major theories in the field, the central role played by people management practices in the effective management of change. 6. The HRM and HRD functions Models and roles of the HR function; organisation and job design, attracting and retaining people, motivating and managing performance, efficient administration of the employment relationship, managing employee relations, learning, training and developing people, rewarding people. 7. Contribution made by HRM and HRD specialists in different types of organisation. Major contemporary developments in HRM and HRD practice in larger private sector companies, small and medium-sized enterprises, public sector organisations, voluntary sector organisations and international corporations. Learning support 8. HRM and HRD practice: professionalism and ethics Major debates about professionalism and ethics in organisations, common ethical dilemmas faced by managers and ways of resolving these, equity and fair-dealing, managing within the expectations of the law. Students are supported by tutors, Studentcentral (or equivalent VLE), Student Support (as needed) and the resources of the library. Indicative reading – most recent editions of: Core text(s) Rees, G. and French R. Leading, Managing and Developing People. London: CIPD. Other recommended reading Armstrong, M. A Handbook of Human Resource Practice. London: Kogan Page. Beardwell, J and Claydon, T. Human Resource Management: a contemporary approach. Harlow: Financial Times Prentice Hall. Boxall P., Purcell, J. and Wright, P. (eds). The Oxford Handbook of Human Resource Management. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Bratton, J and Gold, J. Human Resource Management: Theory and Practice. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. Buchanan D & Huczynski A, Organizational Behaviour: An Introductory Text. Harlow: Financial Times Prentice Hall. Cornelius N, Human Resource Management: a managerial perspective. London: Thomson Business Press. Gibb, S. Human Resource Development: Processes, Practices and Perspectives. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. Marchington, M. & Wilkinson, A. Human Resource Management at Work, People Management and Development. London: CIPD. Mullins, L.J. Management & Organisational Behaviour. Harlow: Financial Times Prentice Hall. Pinnington, A., Macklin, R. and Campbell, T. (eds). Human Resource Management: ethics and employment. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Redman, T. & Wilkinson, A. Contemporary Human Resource Management: Text and Cases. Harlow: Financial Times Prentice Hall. Storey, J., (ed), Human Resource Management: A Critical text. London: Thomson Learning. Taylor, S. People Resourcing. London: CIPD. Torrington, D., Hall, L. and Taylor, S., Human Resources Management. Harlow: FT Prentice Hall. Recommended journals include: British Journal of Industrial Relations Human Resource Development International Human Resource Management Journal Journal of Human Resource Management Personnel Review Recommended websites include: Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development http://www.cipd.co.uk/ Chartered Management Institute http://www.managers.org.uk/ Institute for Employment Studies (IES) http:// www.employmentstudies.co.uk Online library: Xpert HR People Management http://www.peoplemanagement.co.uk/pm/ Teaching and learning activities Details of teaching and learning activities The teaching incorporates a variety of methods including lectures, workshops, student presentations, seminars, guest speakers, group work, podcasts, quizzes and support from the available resources. Allocation of study hours (indicative) Study hours Where 10 credits = 100 learning hours SCHEDULED This is an indication of the number of hours students can expect to spend in scheduled teaching activities including lectures, seminars, tutorials, project supervision, demonstrations, practical classes and workshops, supervised time in workshops/ studios, fieldwork, external visits, and work-based learning. 40 GUIDED INDEPENDENT STUDY All students are expected to undertake guided independent study which includes wider reading/ practice, follow-up work, the completion of assessment tasks, and revisions. 160 PLACEMENT The placement is a specific type of learning away from the University that is not work-based learning or a year abroad. TOTAL STUDY HOURS 200 Assessment tasks Details of assessment for this module The module will be assessed by two elements each with a weighting of 50%: 1. an unseen examination of 2 hours. 2. individual written coursework of up to 2500 words. Types of assessment task1 % weighting Indicative list of summative assessment tasks which lead to the award of credit or which are required for progression. (or indicate if component is pass/fail) WRITTEN 50% COURSEWORK Written exam Written assignment/ essay, report, dissertation, portfolio, project output, set exercise 50% PRACTICAL Oral assessment and presentation, practical skills assessment, set exercise EXAMINATION INFORMATION Area examination board MSc Human Resource Management Refer to Faculty Office for guidance in completing the following sections External examiners Name Position and institution Date appointed Date tenure ends Refer to Studentcentral (or equivalent VLE) QUALITY ASSURANCE Date of first approval 2010 Only complete where this is not the first version Date of last revision December 2012 Only complete where this is not the first version Date of approval for this July 2014 version Version number 3 Modules replaced Specify codes of modules for which this is a replacement Available as free-standing module? Yes No X