ECELookForsandResourcesforCompetency3
advertisement

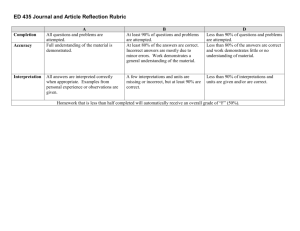
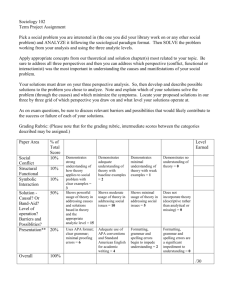
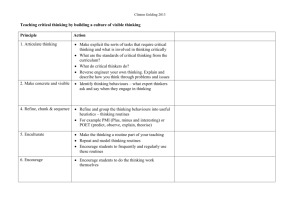
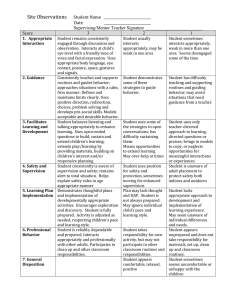
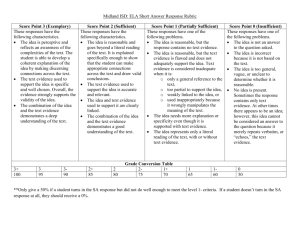
Pre-K Alignment Codes IC- Creative Curriculum Implementation Checklist CC-Creative Curriculum Guides G-GOLD Assessment E-ECERS ELL-SELLCA S-SELA PC-PCMI AP-Approaches to Learning Standards Framework For Effective Teaching Rubric 3. Culture of Achievement: A learning focused environment of shared high expectations promotes mastery. In one lesson…… Indicators Pre-K Alignments 3a. Enthusiasm for Learning Student shows eagerness to learn about a variety Students express satisfaction in solving problems of topics and ideas (G)Obj. 11.d and mastering new material. Student demonstrates confidence in meeting own needs (G- Obj.1.c) Student is able to articulate and demonstrate the steps necessary for problem solving. (Second Step –Unit 3) 3b. Persistence Students show persistence in confronting demanding concepts and tasks. Student plans and pursues own goal until it is reached (G-Obj. 11b ) Student sustains attention to tasks or projects over time (G-Obj. 11a) 3c. Community Classroom norms promote positive and productive teacher-student and student-student relationships. Student cooperates and share ideas and materials in socially acceptable ways (G-Obj. 3b) Student interacts cooperatively in groups-works on tasks with others. (G-Obj. 2c) Teacher shows appreciation for student’s interest needs and efforts. (IC III A-2) Student demonstrates prosocial behaviors when working in a group. (Second Step-Unit 1) Student demonstrates skills necessary for Look -fors (in teacher and student practice) Students can explain how they solved a problem or show what they did to fix it. Student uses their senses in investigating. They talk about how it feels smells, looks and links to their personal experiences. “It feels soft like my teddy bear” or, “it looks like an elephant with a horn”. Student may tell another child, “Put the big block on the bottom or it will fall down”, or “Turn the puzzle piece around so it can fit”. Student may investigate new materials to expand their interests: “I am looking in the Zoo book to find my animal”. Student might say, “look, I did it !” or, “I’m so excited, we’re going to the zoo today” Student attempts different strategies to get a desired result, like stacking the blocks differently for a taller building or continuing to try different positions to complete a puzzle. Student seeks answers to questions by exploring materials and/or asking questions of peers and adults. Student independently counts, orders objects, classifies or matches in their daily class activities like counting out the plates at lunch or using one to one representation in determining the number of children present. Student compares weight by persistently trying a variety of objects to balance the scale. Student plays with sounds until he/she finds a rhyming word to a given sample word. Manners and socially appropriate language are modeled by teacher and used by student, for example,” Please”,” Thank You”,” Can I help you?”, “ May I have a turn?” Conversations among students are frequently observed. Student shares ideas and works collaboratively on projects Student understands the schedule and independently follow the daily routine. Competency 3 Resources On Your Desk Creative Curriculum for Preschool Implementation Checklist pp. 23-30 Second Steps Curriculum Guide Framework For Effective Teaching Rubric sharing, trading and/or taking turns. (Second Step – Unit 3) 3d. Attention Teacher’s strategies and routines capture and maintain student attention on learning. Adapt instruction to include all children (eg. Offer challenging experiences, Use clear visual cues, use concrete objects and gestures) (IC-lll.C.1.4) Use transitions as an opportunity to teach concepts and skills (IC-ll.D.3) Draw children’s attention to the sounds of language through playful songs, stories, rhymes and chants to help develop phonological awareness. (IC-lll.C2.3) Provide a variety of materials for exploring and investigating the outdoors, the physical environment, number concepts, plants, our bodies, people and how they live. (IC-l. B.6,7,8,9,11, C.1,2,3,4) Display the daily schedule in words and pictures at children’s eye level. (IC. ll.A.2) Have consistent routines and procedures in place for children to follow (eg. Put belongings away at arrival, morning check in at attendance board, hand-washing procedures. (IC- llA.5) Teacher supports differentiated learning to auditory, visual and tactile/kinesthetic learners via a variety of strategies, for example: verbally modeling the sound/ symbol relationship, writing the letter in sand or foam, air writing, using a variety of materials like buttons, pop sticks, paint to provide visual and tactile feedback of letter formation. Teacher uses quick, simple two minute activities, songs, brainteasers, and phonological awareness games to productively use wait time before lunch, during transitions, hand washing, or standing in line to reduce/eliminate downtime for students. Teacher consistently introduces and rotates a variety of new materials and resources to maintain interest and sustain alignment of student attention to the instructional objective. Teacher establishes and follows a daily schedule and routines.