Dr. Tuggle Exam Review 3
advertisement

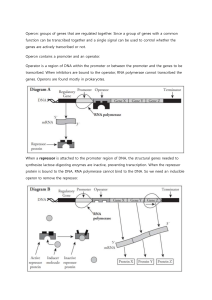
BIO 313 Exam 3 Review Ch. 16, 17, 21, 5-7 Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Laura Bio 313 Dr. Tuggle 10/25/15 1. Which of the following is not a level of gene regulation? a. Alteration of DNA structure b. mRNA processing c. Posttranslational modification d. Rate of replication 2. DNA binding motif that is characterized by two alpha helices is known as a. Leucine Zipper b. Zinc Finger c. Helix-turn-Helix d. Helix-loop-Helix 3. Draw the basic structure of an operon: 4. Continuously expressed genes under normal cellular conditions running the factory building is known as a. Positive control b. Constitutive expressed c. Negative control d. Inducibly regulated 5. Fill in the important characteristics of each Negative inducible Positive inducible Negative repressible Positive repressible 6. The lac operon is a ________ _________ operon a. Negative repressible b. Positive repressible c. Negative inducible d. Positive inducible 7. In the presence of allolactose, the lac repressor a. Binds the operator b. Binds the promoter c. Cannot bind the operator d. Binds to the regulatory gene 8. What is the effect of high levels of glucose on the lac operon a. Transcription is stimulated b. Little transcription takes place c. Transcription is not affected d. Transcription may be stimulated or inhibited, depending on the levels of lactose 9. In trp operon, what happens to the trp repressor in the absence of tryptophan? a. It binds to the operator and represses transcription b. It cannot bind to the operator and transcription takes place c. It binds to the regulator gene and represses transcription d. It cannot bind to the regulator gene and transcription takes place 10. Molecules that influence the formation of secondary structures in mRNA a. Ribozymes b. Riboswitches c. Antisense RNA d. Molecular chaperons 11. Chromatin structure is controlled by all of the following except a. DNase I hypersensitivity b. Histone modification c. DNA methylation d. DNA binding proteins 12. What is the function of an insulator? a. To enhance the effect of an enhancer b. To block all effects of the enhancer c. To block long range effects of the enhancer d. To enhance only a specific enhancer 13. Match the term to the definition Term Complete dominance Definition Phenptype of the heterozygote is intermediate (Falls within the range) between the phenotype of the two homozygotes Incomplete dominance The percentage of individuals having a particular genotype that express the expected phenotype Codominance Penetrance Expressivity The degree to which a character is expressed; strength of phenotype Phenotype of the heterozygote is the same as the phenotype of one of the homozygotes Phenotype of the heterozygote includes the phenotypes of both homozygotes 14. A child has type A blood. The genotypes of the parents could be any of the following except: a. IAIA x IBi b. IAIB x ii c. ii x IBii d. IAIB x IAIB 15. Match the term to the definition Term Sex-linked characteristic Definition Autosomal genes whose expression is limited to one sex Sex-influenced characteristic Genes whose expression is affected by the sex of the transmitting parent Sex-limited characteristic Cytoplasmic genes, which are usually inherited entirely from only one parent Genes located on the sex chromosome Genetic material maternal effect Nuclear genotype of the maternal parent Cytoplasmic inheritance Genomic imprinting Genes on autosomal chromosomes that are more readily expressed in one sex 16. Epigenetics effects all of the following except a. Stress levels b. Cognition c. Metabolism d. Likelihood of having twins 17. Which of the following is a disadvantages of humans of experimental subjects a. Enormous biological info b. Extensive genetic records c. Long generation time d. Large family size 18. What inheritance pattern is seen below? 19. Why do you have twin studies? What is their purpose? 20. What are Mendel’s 2 laws? Include the definitions! 21. What would be the gametes from the F1 generation? Indicate which ones would be recombinants.