Chapter 6 sedimentary rock review sheet
advertisement

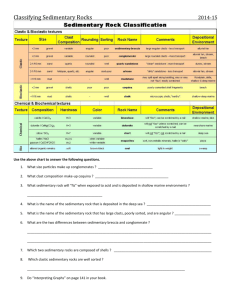
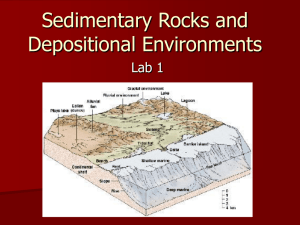
Earth Systems 3209 Review Sheet Chapter 6 - Sedimentary Rocks Terms Sediment Compaction Detrital Sedimentary Rocks Siltstone Breccia Precipitates Dolostone (dolomite) Chert Lignite Fossil Imprint Diagenesis Cementation Chemical Sedimentary Rocks Sandstone Mudstone Sorting Coquina Coal Bituminous Petrifaction Trace Fossil Litification Clastic Shale Conglomerate Evaporites Limestone Chaulk Peat Anthracite Carbonization Mould fossil Topics p. 158 – 159: Describe sedimentary rocks and explain in basic terms how they form. (Diagenesis and Lithification) p. 159 and 165: Understand that there are 3 basic groups of sedimentary rocks based on how they are formed: 1. Detrital (aka. Clastic) 2. Chemical 3. Biochemical p. 160 – 165: Identify the major clastic sedimentary rock groups: shale, siltstone, sandstone, conglomerate, breccias p. 161: Understand how sorting is a measurement of how similar are the particle sizes in a sample of sedimentary rock (ex. well sorted vs. poorly sorted) The degree of sorting and particle size relates to the speed at which water once moved sediments across the surface of the land. NOTE: chemical sedimentary rocks are not considered to be sorted. p. 174: Know how different sedimentary environments produce specific types of sedimentary rocks: A. fluvial - breccia, conglomerate, sandstone, siltstone, shale, and mudstone B. lagoonal - siltstone, shale, and mudstone C. beaches - conglomerate, sandstone D. deep ocean/marine - includes turbidites (conglomerate, sandstone, siltstone, shale), but is E. dominated by chemical sedimentary rocks E. shallow marine - various types of clastic sedimentary rocks p. 165 – 170: Explain how some sedimentary rocks are formed through chemical processes: A. Evaporites (halite, gypsum, sylvite) B. Precipitates (limestone, dolomite, travertine) p. 165 – 170: Explain how some sedimentary rocks are formed through Biochemical processes: Coquina, chaulk, chert, limestone (coral), coal p. 173: See table 6.2 for a good summary of the key information from this chapter. p. 171: Describe the key stages in the formation of coal: Peat – Lignite – Bituminous - Anthracite p. 183: Explain the basic process of fossilization. p. 184: Describe the three conditions necessary for fossilization A. Remains are rapidly covered up by soil, mud, rocks, etc. B. Low oxygen levels C. Find grained sediments surround the remains p. 183 – 186: Describe how each of the following processes produces a fossil: A. Petrifaction by replacement B. Carbonization C. Mould and Cast D. Preserved Intact (ex. frozen or in amber) E. Imprints F. Trace Fossils (ex. dinosaur eggs or coprolites (poop) )