Parasite Control
advertisement

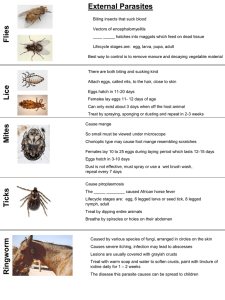
Life Cycle of Worms 1. General Signs of Worms a. Excellent appetite, but unable to gain weight b. Rough, dull hair coat c. Thin, unthrifty appearance d. Rapid tiring during hard work e. Tucked up flanks f. Digestive disturbances, such as diarrhea, constipation or colic g. Anemia h. Acute, heavy infestation may result in fever, depression and lack of appetite 2. Ascarids (roundworms) a. Appearance i. Yellowish/white in color ii. 9-12 in in length iii. Commonly found in foals and young horses b. Life course i. Adult female worm deposits eggs in small insects ii. Eggs passed on in feces and live in soil for long periods iii. Horse eats contaminated dirt, food, water or manure iv. Eggs pass to small intestines where they latch to larvae v. Larvae penetrate the intestine wall and enter bloodstream vi. Larvae travel to blood to the liver and lungs vii. Large are coughed up from lungs viii. Larvae are swallowed again ix. Larvae reach small intestine where they develop into manure adult roundworms. c. Damage i. To lungs and liver ii. Severe blockage of intestines and get colic iii. Lunge damage can result to pneumonia 3. Strongyles (bloodworms) a. Appearance i. Can get up to 2 inches ii. Horses of all ages get this iii. These are the most important and serious parasite b. Life course i. Worm eggs are passed out of feces ii. Eggs develop into larvae on the ground iii. Larvae crawl onto vegetation iv. Horse ingests larvae while grazing v. Larvae penetrate the wall of small intestine and enter bloodstream vi. Larvae travel through bloodstream to cecum and colon vii. Larvae penetrate wall of cecum and colon and develop into adults. c. Damage i. To lunge, heart, liver and intestines wall ii. Permanent damage to blood vessels causing blood clots 4. Pinworms (rectal worms) a. Appearance i. Female measure up to 6 inches, males measure up to 1 inch ii. White color and thread like b. Life course i. Female pinworms are passed out feces and deposit eggs in feces or around anal area ii. Horse ingests eggs by eating contaminate feed, water, manure or dirt iii. Adults live in dorsal colon. Mature female worms crawl out of rectum and deposit more eggs on surrounding skin. These eggs are rubbed off or passed out in feces and infest other horses. c. Damage i. Mild inflammation of the lower intestinal tract ii. Presence of eggs around anus causing itching 5. Large Stomach Worms a. Appearance i. White in color and slender in appearance ii. Measure ½ to 1 ¼ inch in length b. Life Course i. Adults in stomach. Females lay eggs in stomach ii. Eggs are passed out with feces iii. Flies lay eggs in feces iv. Worm eggs are eaten by fly maggots; young worms develop in the fly maggots and pupa v. Adult flies carrying infective larvae emerge vi. Horse ingest infective flies or larvae when flies feed on horse’s saliva vii. Larvae are ingested by horse and travel to stomach to mature and lay eggs again. c. Damage i. Inflammation of the stomach wall ii. Summer sores in eyes or moist wounds 6. Bots a. Appearance i. Not worms. Larvae of the bot fly ii. Bot flies are yellowish, hairy and bee-like flies iii. Bot eggs are white, yellow or black 1. Found on forelegs, around moth of under jaw 2. Size of pin head. b. Life Cycle i. Mature fly lay eggs on horse’s body ii. Horse licks or scratches eggs with tongue or teeth iii. Moisture from Tongue induces the eggs to hatch. Larvae invade the mucous membrane of horse’s mouth iv. Larvae migrate to stomach where they attach to stomach wall and mature. v. Mature bots are passed out in feces. vi. Larvae pupate in the ground vii. Adult flies emerge c. Damage i. Inflammation of stomach wall ii. Heavy infestation can cause rupture of stomach 7. Prevention a. Worm horses every 3 months or on schedule set by vet b. Take regular fecal samples to vet to to check for eggs. c. Foals wormed 6 seeks of age. d. Worm mare 30 days before foaling e. Proper sanitation measures i. Place horses on clean pastures ii. Dispose of manure properly iii. Keep stalls clean and paddocks clean f. Avoid putting a large number of horse on a single pasture g. Pasture rotation. h. Wash rectal or dock are to remove eggs. Don’t use clothes or brushes on any other areas of horse i. Take bot flies off by clipping, shaving or saturating them with vinegar or take off with bot knife. j. Eradicate flies in barn