Special Education and Nursing Definitions (new
advertisement

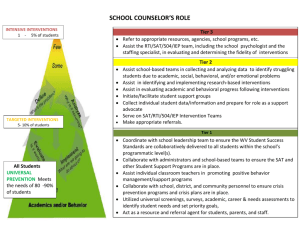
Special Education and Nursing Definitions RTI (Response to Intervention) The purpose of RTI is to ensure success of all students, and provide early assistance to students who are experiencing academic and/or behavioral challenges. RTI guides the SAT in developing a plan to support students in becoming successful in the general education setting. It supports the teachers to develop successful strategies and interventions to use with all students. Tier IA All students are Tier IA students-they are enrolled in classes at the appropriate level and have teachers that use best practices and core curricula. Teachers fill our classroom profiles at the beginning of the year. Teachers document how each of their students is progressing and communicates with parents. If a student appears to not be making adequate progress, the teacher is challenged to determine what factors may be barriers to learning. Tier IB indicates the teacher’s development of a classroom intervention plan (CIP) and a student academic improvement plan (AIP)-progress is measured over the next 4-6 weeks and the process is shared with the parents. If the issues are behavioral or health-related in nature, the student is referred to the Health and Wellness team for consideration and recommendations. For behaviors, a functional behavioral assessment (FBA) may be completed and a behavioral intervention plan (BIP) can be developed and implemented. For health related issues, an individualized health plan (IHP) is developed and implemented. In both situations, if the student is showing growth and achievement he/she can remain in Tier IB indefinitely. However, if interventions are not showing improvement, a request to go to SAT is submitted. SAT Team (Student Assistance Team)-Each school site has a SAT whereby concerned teachers and/or parents may request a meeting regarding a student’s academic progress issues. The team is usually chaired by an appointed staff member and is comprised of the student’s teacher, counselor, nurse*, assistant principal, etc. SAT Process-The teacher or parent may request a SAT meeting when there are concerns regarding a student’s progress after implementation of Tier I interventions have been made. The SAT chairperson convenes a meeting with the concerned parties and reviews the student’s progress, the interventions implemented and responses to those interventions. (See below SAT Meeting) SAT-Health Record Review-As part of the SAT process, the sponsor teacher requests the school nurse to review the student’s health record which includes the latest results of hearing and vision, any pertinent known health concerns and medications currently taken. Tier II – SAT Meeting-An initial meeting includes discussion of the concerns, interventions attempted and response, and then discussion regarding ideas to support student success. A plan of action is designed and documented-this is called the SAT Intervention Plan. Two additional review meetings are held at designated intervals. Following the second meeting, the determination to return the student to Tier IB, retain the student in Tier II with continued interventions or refer to the Diagnostician is made. Once the diagnostician determines that the student should be tested for special education and the parents have been notified, the School Nurse is asked to complete the Initial Health History and Assessment. 504 Accommodation Plan-Section 504 is a federal civil rights law under the Rehabilitation Act of 1973. The law protects individuals with disabilities from discrimination. In the school setting, the law prohibits discrimination on the basis of disability from all school programs and activities in both public and private schools that receive direct or indirect federal funding. Students may qualify if they have a mental or physical disability that substantially limits one or more major life activities and significantly affects the student’s education. SAT and 504-The SAT team serves as the starting point for consideration for a 504 plan. Decisions are made according to eligibility criteria by the SAT/504 team at the school site. Special Education Diagnostician/Evaluation Specialist-Specially trained teacher who administers a battery of tests to the student to determine/evaluate Special Education eligibility. Diagnosticians test and analyze test results making recommendations for a student plan of action for academic success. Initial Evaluation-For Nursing, the Initial Evaluation relates to the initial testing of a student for diagnostic evaluation. The School Nurse completes the Initial Health History with the parent/guardian, performs a limited physical assessment and determines the need for medical referral or additional medical information that would aid in the educational diagnostic process. The school nurse completes the Nursing Summary Form for Special Education and submits to the requesting Diagnostician with recommendations for referral if needed. Re-Evaluation-For Nursing, the Re-evaluation relates to the 3-year re-evaluation of the student in Special Education. The School Nurse completes the Nursing Assessment and Health History Review. The Nursing Summary Form for Special Education is completed with current information/findings or referrals and submitted to the requesting Head Special Education Teacher or Sponsor Teacher. IEP-The Individualized Education Plan is the formal plan developed for the student based on findings of the diagnostician and teacher and parent recommendation. The IEP determines which subjects require additional support through the Special Education program, inclusion in regular classroom education as well as the need for related services such as Speech and Language, OT, PT, Adaptive PE, and School Health. When the student has significant health issues that impacts his education or that require nursing services at school, the School Nurse should be present for the IEP meeting to make recommendations for school health services time needed on the IEP, to explain the health issues and how they impact education, and to serve as a resource to nonhealth staff in determining the student’s needs in the educational setting. Sponsor Teacher-Special Education classroom teacher or regular education teacher for a student. IEP Specialist –staff person designated to complete the IEP on the TIENET software; act as a knowledgeable resource for the components of the IEP. Head Special Education Teacher- school site teacher responsible for the coordination of the school’s special education program and student evaluations and/ or reevaluations. PSS (Program Site Specialist)- administrator-in some cases an assistant principalwho coordinates the Special Education Programs for a selected group of schools. Multi-DisciplinaryTeam (MDT) /Eligibility Determination Team (EDT)- The team comprised of diagnosticians that reviews and determines the outcome for Special Education Testing. School Health Services/Time on IEP- The amount of time the IEP team at the site determines to be appropriate for the provision of health care of a student. Service time may be direct face-to-face services (i.e. med administration, g-tube feedings, assessment/monitoring, student education, suctioning, etc.) or indirect (i.e. creating the IHP, communication with parent/physician, coordination of services, referrals, staff education, etc.) Service time is measured in minutes or hours per day, week, month or semester. *Only direct (face-to-face) service time is billable* Intensive Support Program (ISP)-Special classrooms designed to meet the challenges of students with multiple developmental delays and special health needs. Typically, these students are mentally challenged and require assistance in the activities of daily living. Some of these students will require g-tube feedings and meds, tracheal suctioning, toileting, feeding, etc. Additionally, some of these students will come from group homes due to the high level of care required. Behavioral Intervention Program (BIP) (including behavior intervention plan; functional behavior assessment)- BIP is a term used by the district for the overall programs housed at specific school sites and/or for the behavior intervention plan designed to help the student control their behaviors while focusing on academic success. The programs are designed to work with those students experiencing severe emotional disorders and mental illness manifesting difficult behaviors. Schools that are not designated BIP’s do have classrooms devoted to those students who have difficulty controlling behavior but are not to the point of extreme concern and can be managed with individual behavioral intervention plans and trained staff. Medically Fragile- This term typically defines those students who have been identified by the Center for Developmentally Delayed/Disabled who are considered high risk and require nursing care in the home and/or in the schools. These students require advanced technology to sustain life, are at high risk for infection and hospitalization and are developmentally delayed. Medically Complex- The medically fragile student is considered medically complex, but there are those students who have chronic health conditions but do not benefit from the Medically Fragile Program such as students with spina bifida and requiring nursing interventions such as catheterization or perhaps the student with endstage cancer who might require flushing of their ports or surveillance for infection etc. or the newly diagnosed student with Type I diabetes who requires constant intervention. Chronic Conditions- Those students with long term health issues that require medication or treatments to keep their condition under control but could easily have exacerbation and require additional intervention at school-asthma, diabetes, seizures, etc. Emotionally Disturbed- as it relates, to education, is an eligibility for Special Education and not made on a psychiatric diagnosis. School psychologists determine the eligibility based on specific characteristics that are exhibited over a long period of time and to a marked degree that it adversely affects a child’s educational performance. While a psychiatric diagnosis is not imperative, it helps to support the eligibility. For more in depth explanation, go to http://cecp/air.org/resources/2oth/eligchar.asp