2 hours
advertisement
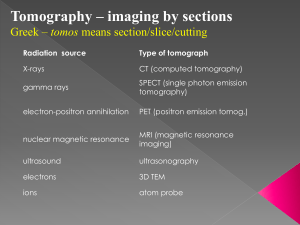
Technological card of lecture № 1 Theme: Modern beam diagnostics in pediatrics School hours: 2 hours Structure/plan of lecture 1. Value of a radiological method of research in diagnostics of various diseases of organ and systems. Indications, contraindications, features of carrying out at children. Radio protective protection. 2. A role and value of an ultrasonic method of research in diagnostics of various diseases of organ and systems. 3. A role and a place of a computer tomography in recognition of various diseases of organ and systems. Indications, contraindications, features of carrying out at children. Radio protective protection. 4. Value of a method of a magneticresonant tomography in recognition of various diseases of organ and systems. Indications, contra-indications, features of carrying out at children. 5. A role of a method radionuclide diagnostics in revealing various diseases of organ and systems. The purpose: To acquaint students with modern methods of radiologic diagnostics, their opportunities and prospects in pediatrics. Tasks: Results of educational activity: 1. To familiarize students with a Students list indications and contraradiological method of research. indications to radiologic methods of 2. To familiarize students with an research; ultrasonic method of research, its Classify methods of research (the cores, opportunities and prospects in pediatrics. additional, special) 3. To familiarize students with a method Name advantages and lacks of radiologic of a computer tomography. methods of research; 4. To familiarize students with a method List diagnostic opportunities of methods magnetic- resonant tomography. of research; 5. To familiarize students with a method Solve tests. radio nuclide diagnostics. Method of training: 1. Lecture 2. Discussion and analysis 3. Blitz -interrogation The form of the organization of Face-to-face-collective educational activity Means of training • schedules and tables, • visual materials • multimedia • videofilm Ways and means of a feedback The blitz-interrogation, test tasks beforeand after lecture. One of leading directions in modern pediatrics is radio diagnostics, which being a basis, really revolutionary changes in medicine, allows to study physiological processes proceeding in an organism, functional and morphological changes by means of an ionising radiation, ultrasonic and magnetic waves. Radio diagnostics in pediatrics includes as traditional radiological researches - radiology, roenthgenography, a linear tomography, etc., and also modern methods - x-ray heliocal and spiral computer tomography (XCТ) of the high permission and methods of radionuclide diagnostics. Simultaneously in group of techniques of radio diagnostics a magnetic-resonant tomography (МRТ), ultrasonic researches (US) and medical thermography are used. Each of the listed methods is characterized by a number of merits and lacks and, accordingly, differs certain limits of diagnostic possibilities. The advanced place in diagnostics has occupied a new complex direction - intervetion radiology. Methods of radio diagnostics, supplementing each other, differ with informatively, availability, simplicity of performance and "occupy one of leading places in system of clinical and preventive research of the population”. With their help about 80 % of all primary diagnoses are put. In a considerable part of diseases (up to 50 %) diagnostics in general is inconceivable without application, for example, roentgen radiologic methods in gastroenterology, pulmonology, traumatology, urology, etc. Thanks to introduction in practical public health services of the newest computerized technologies created on the basis of the modern electronic and microprocessor techniques, possibilities and a role of methods of beam diagnostics in medicine even more increases. Among of all methods of radiologic research most the wide circulation in practical public health services was received by methods of classical radio diagnosis. It is necessary to mean, that radiological and radio isotope methods of research, being sources of an ionizing radiation, have damaging influence on biological tissues, in communication, with what researches should be appointed under strict indications and with observance of certain protective actions. Roentgenoscopy represents transmission a thorax or an abdominal cavity of the patient directly behind the usual fluorescing X-ray screen or behind the screen of the television monitor at device equipment electron optic converter (EОC). Multiaxial and polypositional transmission allows to estimate anatomomorphological and functional (dynamic) features of organ as a whole or partially under the positive image. Radiography - X-ray pictures, including aim, on a film of standard formats in various projections, allow to reproduce the negative analogue image on which are estimated anatomic (the form, the sizes, position) and structural features of organs. At presence in modern radiodiagnostic apparatus of the device for digital processing of the image (transfer of the analogue image in digital) the last is displayed the display of the personal computer (personal computer). Use of the digital image creates a number of advantages in diagnostics: quality improves, resolution increases, and also radiologic loading on the patient (a little dose technology) essentially decreases. Versions of additional methods are: the linear tomography - a technique of level-by-level research, allows to reproduce the image of object (organ) on the set depth. It is carried out at synchronous movement in opposite directions of a x-ray tube and the cartridge with a film along motionless object under a corner 30-50 є. Distinguish a tomography longitudinal, cross-section and with a difficult motion cycle of a x-ray tube (circular, sinusoidal). The thickness of a revealed cut depends on the sizes of tomographic corner and is more often makes 2-3 mm, distance between cuts (tomographic step) is established voluntary, usually 0,5 - 1 sm. Methods of artificial contrastig. The density of internal organs and tissues of the person is approximately identical and during radiological research is not always sufficient for their accurate reproduction. With a view of visualisation of an internal structure of various organs, vessels and tissues, and a successful estimation of features of their internal structure resort to artificial contrast by means of contrast X-ray substances (RCS). In gastroenterology artificial contrast is widely used for research of various parts of the gastroenteric channel: radioscopy gullet, a stomach, a duodenum, a probe duodenography usual and in the conditions of a hypotonia with aeron, a large intestine - irrigoscopy, double contrast: research of biliar ducts – cholangiography. Operational, transdrainage, percutanous, transhepatic, retrograde, endoscopic, intravenous, laparoscopic. In pulmonology - bronchography, angiocardiography: in urology - excretory and ascending urography: in gynecology - gisterosalpingography: in osteology arthrography; fistulography, etc. Lecture equipment: 1. Tables: The device of the X-ray apparatus and X-ray tube; The device of a computer tomograph; The device of a magetic-resonant tomograph; The scanner device; The device of the ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus; 2. Resume on a theme; 3. The multimedia program; 4. Negatoscope; 5. Roentgenograms, echograms, scanograms, computer tomograms, magneticresonant tomograms on a theme.