Sample questions
advertisement

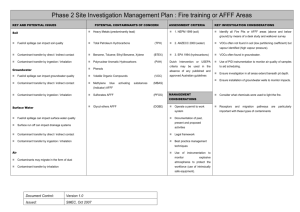
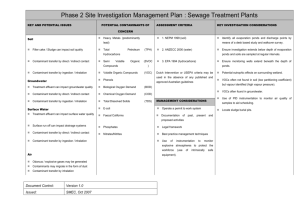
Using Environmental Molecular Diagnostics (EMD) – questions These questions may have more than one correct answer. There can be two or more correct answers. 1. What groups of analytical techniques can EMDs be classified into? A. chemical techniques B. physical techniques C. molecular biological techniques D. statistical techniques 2. CSIA measures the amounts of: A. radioactive isotopes (typically carbon, hydrogen, or chlorine) in contaminants B. stable isotopes (typically carbon, hydrogen, or chlorine) in contaminants C. stable ions (typically carbon, hydrogen, or chlorine) in contaminants 3. What can change the relative amount of each stable isotope in the contaminant? A. a contaminant is chemically degraded through natural or engineered processes B. dilution of the contaminant C. a contaminant moves through the environment D. a contaminant is biologically degraded through natural or engineered processes 4. What important questions can CSIA help answer about a chemical? A. source B. chemical formula C. degradation mechanisms D. rate of degradation 5. What can MBTs tells us about of microorganisms present in the environment? A. types of microorganisms B. shapes of microorganisms C. numbers of microorganisms D. biochemical capabilities of microorganisms 6. What are the three most commonly used MBTs? A. polymerase chain reaction (PCR), B. fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), C. quantitative PCR (qPCR) and reverse transcriptase-qPCR (RT-qPCR) D. DNA microarrays. E. enzyme activity probes (EAPs) F. stable isotope probing (SIP) 7. True or False. EMDs have application in each phase of environmental site management 7 8. What benefits can EMDs provide? A. Improve the management of contaminated sites B. Determine whether biotic or abiotic degradation is occurring at a site C. Identify specific contaminant sources or reveal whether multiple sources of contamination are present (for instance, isotopic fractionation) D. Improve evaluation and decision making for remediation strategies E. Identify degradation pathways and their degree of completion F. Identify the need for enhancements such as chemical amendments or bioaugmentation G. Estimate degradation rates. H. Aid in monitoring program decisions I. Provide complementary data to support site closure and other site management decisions 9. The genes of microbes (and other organisms) A. made of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA. B. DNA can be transcribed into RNA, C. translated into enzymes (and other proteins) D. some enzymes can degrade contaminants. 10. DNA-based analyses can tell us A. determine if microorganisms with the potential to biodegrade target contaminants are present at a site B. if biodegrading organisms are actively expressing biodegradation genes C. the abundance of the target microorganisms. 11. If we know the direct connection between the information provided by a DNA-based analysis, RNA analysis, and stable isotope-based analysis we can select appropriate EMD technologies. We must understand the difference between methods that find: A. biotic and abiotic attenuation mechanisms B. microbial presence (and enumeration in some cases) C. cellular activity (such as transcription) D. historic and potential biodegradation activity E. evidence of contaminant biodegradation 8