Vocabulary Quiz Key Terms
advertisement

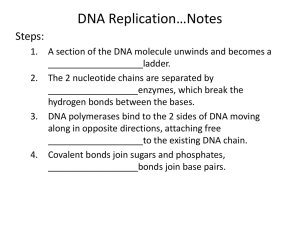
Vocabulary Key Terms Definitions Anticodon The branch of biology that studies heredity, the passing of traits (characteristics) from parents to offspring. Base Pair The five carbon sugar found in DNA. Central Dogma The three-based code in DNA or mRNA Chargaff’s Rule Smaller segments of RNA nucleotides that transport amino acids to the ribosome. Codon The synthesis of the mRNA from the template DNA. Deoxyribose The passing of traits from parents to offspring. DNA Helicase The processes in which parental strands of DNA separate, serve as templates, and produce DNA molecules that have one strand of parental DNA and one strand of new DNA. The basic mechanism or chain of events of reading and expressing genes that goes from DNA to RNA to Protein. DNA Polymerase Double Helix A genetically determined characteristic. Genetics Associates with proteins to form ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Heredity Ligase Any of a class of enzymes that catalyse the formation of covalent bonds and are important in the synthesis and repair of biological molecules, such as DNA. The site of protein synthesis. mRNA One of the following: Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine, Uracil. Nitrogenous Base The building blocks of DNA & RNA consisting of a five-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen-containing base. Nucleotides The shape of DNA that is often compared to a twisted ladder. Okazaki Fragments Replication Rule stating that the bases in a nucleic acid always pair up in the same way: A = T and G = C. Ribose The five carbon sugar found in RNA. (Ribosomal RNA) rRNA A process in which DNA has the unique ability to make an exact copy of itself Ribosome An enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the base pairs together as it unwinds and unzips the double helix, allowing new nucleotides to bind to the 2 single strands by base pairing. An enzyme that adds complementary nucleotides to the template strand of the unzipped double helix until the entire molecule has been replicated. The small segments of the lagging DNA strand. RNA Polymerase Semiconservation Replication Traits Long strands of RNA nucleotides that are formed complementary to one strand of DNA. Transcription After DNA is unzipped in the nucleus, this is the enzyme that binds to a specific section where an mRNA will be synthesized. tRNA The process through which the mRNA attaches to the ribosome and a protein is assembled. Translation A sequence of three nucleotides in a region of transfer RNA that recognizes a complementary coding triplet of nucleotides in messenger RNA during translation by the ribosomes in protein biosynthesis.