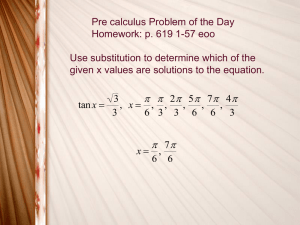
Steps to Solve 2 nd Degree Trigonometric
advertisement

TRIG EQUATIONS
Algebra 2 & Trigonometry Lab
Miss Kersting
Room 206
Period 1
Name:____________________________
Day 1 – Sum and Difference of Two Angles
Steps to Evaluate Sum and Difference of Two Angles When Given An Expansion:
sin A B sin A cos B cos A sin B
sin A B sin A cos B cos A sin B
cos A B cos A cos B sin A sin B
cos A B cos A cos B sin A sin B
tan A B
tan A tan B
1 tan A tan B
tan A B
tan A tan B
1 tan A tan B
1.) Match the equation to the corresponding formula on the formula sheet.
2.) Combine the expression into a single term.
3.) Perform the indicated operation and find the exact value from the special angles chart if
needed.
1.)
Write as a single expression:
cos300 cos30 sin300 sin30
2.)
Write as a single expression:
sin160 cos 20 cos160 sin 20
3.)
Find the exact value:
cos53 cos8 sin53 sin8
4.)
Find the exact value:
sin 70 cos 40 cos70 sin 40
5.)
Find the exact value:
cos160 cos10 sin160 sin10
6.)
Find the exact value:
sin150 cos30 cos150 sin30
7.)
Find the exact value of
tan 45 tan15
1 tan 45 tan15
p2
Steps to Evaluate Sum and Difference of Two Angles When Given Trig Ratios:
1. Match the equation to the corresponding formula on the formula sheet.
2. Draw the two triangles and find the missing side using SOHCAHTOA and the
Pythagorean Theorem.
3. Find the trigonometric fractions needed to fill in the equation, and find the resulting
value.
8.)
A and B are positive acute angles. If sin A
4
8
and cos B , find the value of sin A B .
17
5
9.)
A and B are positive acute angles. If tan A
3
12
and cos B , find the value of cos A B .
4
13
10.) A and B are positive acute angles. If sin A
3
8
and cos B , find the value of tan A B .
17
5
p3
Day 1 – Sum and Difference of Two Angles
HOMEWORK
Directions: Answer each question using the formulas from the Reference Sheet.
4
5
1.) If tan A and cos B , and A and B are positive acute angles, find cos A B .
3
13
2.)
Write as a single expression:
sin 240 cos60 cos 240 sin 60
3.)
Write as a single expression:
tan 25 tan15
1 tan 25 tan15
4.)
Find the exact value of
cos 26 cos154 sin 26 sin154
5.)
Find the exact value of
cos146 cos 26 sin146 sin 26
Answers to Day 1 Homework:
3.) tan 10°
33
1.)
4.) -1
65
2.) sin180
5.)
p4
1
2
Day 2 – Double and Half Angles
Do Now: Question 1.
5
7
1.) If tan A
and cos B
, and A and B are positive acute angles, find cos A B .
12
25
Steps to Evaluate Double Angles:
1.
sin 2 A 2sin A cos A
cos 2 A cos 2 A sin 2 A
cos 2 A 2 cos 2 A 1
Match the equation to the corresponding
formula on
the formula sheet.
2. Simplify the resulting equation.
cos 2 A 1 2sin A
2
tan 2 A
2 tan A
1 tan 2 A
Directions: Simplify each expression.
2 cos
2.)
sin 2
4.)
sin 2 A
sin 2 A
3.)
cos 2 A
sin A cos A
5.)
sec x sin 2x
p5
Directions: Solve each question for the desired value.
7.)
3
6.) If sin x , what is the value of cos 2x ?
5
8.)
Write as a single expression: 1 2sin 2 30
10.) The expression 2sin 2 cos 2 is
equivalent to:
(1) 2
(2) sin 2
9.)
If x is a positive acute angle and
5
sin x , what is the value of cos 2x ?
13
Write as a single expression:
2sin30 cos30
11.) The expression
(1) tan x
(2) cos x
(3) 1
(4) sin 2
p6
1 cos 2 x
is equivalent to:
sin 2 x
(3) sin x
(4) cot x
Steps to Evaluate Half Angles:
sin
1.
1
1 cos A
A
2
2
1
1 cos A
cos A
2
2
tan
Match the equation to the corresponding
formula on
the formula sheet.
2. Simplify the resulting equation.
1
1 cos A
A
2
1 cos A
12.) If cos y 0.28 , find the positive value of
y
cos .
2
13.) If cos x 0.02 , find the positive value of
x
sin .
2
p7
Day 2 – Double and Half Angles
HOMEWORK
Directions: Answer each question.
sin 2 A
sin A
1.) Simplify:
cos A
3.)
Write as a single expression: 1 2sin 2 45
5.)
If cos
7.)
If A is a positive acute angle and sin A
3
, find sin 2 .
2
Answers to Day 2 Homework:
1.) sin A
5.)
2.) tan A
3.) cos90
4.) sin 60
6.)
sin 2 A
2 cos 2 A
2.)
Simplify:
4.)
Write as a single expression:
2sin30 cos30
6.)
If x is a positive acute angle and
12
sin x , find cos 2x .
13
5
, find cos 2A .
3
3
2
119
169
7.)
p8
1
9
Day 3 – Pythagorean Identities
Do Now: Questions 1 & 2.
tan x
1.) What is
expressed in simplest form?
sec x
2.)
4
and lies in Quadrant II,
5
what is the value of tan ?
If cos
Pythagorean Identities
1.
Start with the Pythagorean Theorem: a 2 b 2 c 2 .
Convert the Pythagorean Theorem into its standard form on the unit circle below.
Two alternate forms of the Pythagorean Identity:
2. Divide by sin 2
3. Divide by cos 2
p9
Directions: Express in terms of sine, cosine, or both, then simplify.
2
5.) cot 2 1
4.) 1 cos
6.)
sin cot 2 1
8.)
1 sin
tan
cos
7.)
csc sin sin 2
9.)
1
cos
1
1
cos 2
p10
Directions: Express each problem in simplest terms.
sec
1.)
2.)
csc
3.)
5.)
1 cos 2 x
sin 2 x
4.)
Day 3 – Pythagorean Identities
HOMEWORK
tan
sec
1 cos x 1 cos x
2 2sin 2 x
cos x
Answers to Day 2 Homework:
1.) tan A
3.)
2.) sin A
4.)
1
sin2 x
5.)
p11
2 cos x
Day 4 – 1st Degree Trigonometric Equations
Do Now: Questions 1 & 2.
cos 2 x 1
1.) Simplify:
sin x
2.)
Solve for x to the nearest tenth: 7 x 3
HINT: use logs!
Steps to Solve 1st Degree Trigonometric Equations
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Solve for the trig function.
Use the inverse function to determine the reference angle.
Determine what quadrants will have the correct value based on ASTC.
Find all possible angle measures in the interval specified.
Convert to radians, if necessary.
Directions: Solve for , in the interval specified.
3.) Solve for , from 0 360
2cos 1 0
4.)
Solve for , from 0 2
cos 3cos 1
5.)
Solve for to the nearest degree,
0 360
5sin 15 sin 12
6.)
If x is a positive acute angle, solve for x to
the nearest degree:
4 tan x 1 1 tan x
6
3
7.)
Given 3 sin x 2 9 , solve for x, to the
8.)
Solve for all values of 2cos 3 0 when
0 .
nearest degree, in the interval 0 x 360
p13
Day 4 – 1st Degree Trigonometric Equations
HOMEWORK
Directions: Solve each equation in the range specified.
2.) If x is a positive acute angle, solve
1.) Solve for x in the interval 0 x :
1 cos x
2
4 to the nearest degree.
cos x
4sin x 7 3
3.)
Solve 2 tan x 3 3 to the nearest
degree in the interval 0 x 360 .
4.)
Solutions to Day 4 Homework:
1.)
6
2.) 71
3.)
4.)
p14
Find, to the nearest degree, the solution set
of 8cos x 2 0 over the domain
0 x 360 .
60, 240
104, 256
Day 5 – 2nd Degree Trigonometric Equations (1)
Do Now: Questions 1 & 2.
1.) Solve for y from 0 y 360 :
4 tan y 2 2 tan y 10
2.)
The roots of the equation 2 x 2 5 x 6 0
are
(1) Rational and unequal
(2) Rational and equal
(3) Irrational and unequal
(4) Imaginary
Steps to Solve 2nd Degree Trigonometric Equations
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Make sure you have only one trig function.
Factor if possible, or use the quadratic formula.
Find the reference angle for each factor.
Find all possible angle measures in the interval specified using ASTC.
Convert to radians, if necessary.
Directions: Solve for in the interval specified.
3.) Solve for x from 0 x 2 : tan 2 x tan x 0
4.)
Solve for x from 0 x 360 : 2sin 2 x 3sin x 2
5.)
Find, to the nearest degree, all values of in the interval 0 180 that satisfy the equation
3tan 1 2cot
p16
6.)
Solve for x to the nearest degree, from 0 x 360 : 2 cos2 x – 4 cos x + 1 = 0
p17
Day 5 – 2nd Degree Trigonometric Equations (1)
HOMEWORK
Directions: Solve each equation in the domain specified.
1.) Find all values of in the interval 0 360 : sin 2 sin 0
2.)
Find the measure of the smallest positive acute angle for which 2sin 2 3sin 1 0
p18
3.)
Find all values of in the interval 0 2 that satisfy the equation 2sin 1 csc
Solutions to Day 5 Homework:
1.) 0,90,180
2.)
30
3.)
5 3
, ,
6 6 2
p19
Day 6 – 2nd Degree Trigonometric Equations (2)
Do Now: Questions 1 & 2.
1.) Find all values of x, in the interval
2.)
0 x 360 , for which the equation is true:
2sin 2 x 1 sin x
If the measure of A 40 , a = 5, and b =
6, how many different triangles can be
constructed? (Ambiguous Case)
(1) 1
(2) 2
(3) 3
(4) 0
Steps to Solve 2nd Degree Trigonometric Equations with Two Functions
1.
Convert to only one trig function. Use either the Pythagorean Identity or the Double Angle
formulas to replace the squared value.
2. Solve like previous 2nd Degree Trigonometric Equations. (see p15)
Directions: Solve algebraically for all values of to the nearest degree in the interval 0 360
that satisfy the equation given.
3.) 4sin 2 x 4 cos x 5
p20
4.)
sin 2
1
1 cos
p21
5.)
3cos 2x 8sin x 5 0
p22
6.)
3cos 2 x 2sin x 1 0
p23
Day 6 – 2nd Degree Trigonometric Equations (2)
HOMEWORK
Directions: Solve algebraically for all values of to the nearest degree in the interval 0 360
that satisfy the equation given.
1.) 2 cos 2 x 3sin x 3 0
p24
2.)
cos 2 3sin 0
p25
3.)
2sin 2 x 3cos x 0
Answers to Day 6 Homework:
1. {30°, 90°, 150°}
2. {196°, 344°}
3. {120°, 240°}
p26
1.) Find the exact value of:
sin20cos40 + cos20sin40
3.) Simplify:
cotϴsecϴ
Day 7 – Review
2.) If A and B are positive acute angles, and
tan B = and cos A =
cos (A – B).
, find the value of
4.) Solve for x from 0 x 2 :
tan 2 x tan x 0
p27
5.)
Find the exact value of
6.) If x is a positive acute angle and sin x =
what is the value of cos 2x ?
7.) Find all degree measures of ϴ in the interval of 0 ≤ ϴ ≤ 360 to the nearest degree.
5sinϴ – 1 = 1 – 2sinϴ
p28
,
8.) Find all degree measures of ϴ in the interval of 0 ≤ ϴ ≤ 360 to the nearest degree.
9𝑠𝑖𝑛2 𝑥 − 9𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥 + 2 = 0
9.) Find all degree measures of ϴ in the interval of 0 ≤ ϴ ≤ 360 to the nearest degree.
3tanϴ = cotϴ
p29
11.) Find the exact value of
𝑠𝑖𝑛150𝑐𝑜𝑠30 − 𝑐𝑜𝑠150𝑠𝑖𝑛30.
p30