6D Booklet 2011- 2012
advertisement

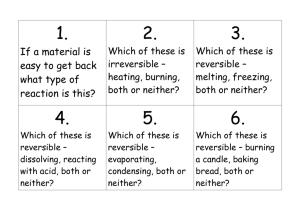
Glossary Burning When a fuel catches fire using oxygen from the air. It is an irreversible change Condensing When a gas changes into a liquid. It is a reversible change Dissolving When a solid mixes with a liquid and stays mixed. The mixture looks clear. It is a reversible change Evaporating When a liquid changes into a gas. It can happen over a range of temperatures. It is a reversible change. Freezing When a material changes from a liquid to a solid at a cold temperature such as in the freezer. It is a reversible change Hazard A danger Irreversible change A change in which new materials are made. It is very difficult to get back the original materials Mass The amount of material that is in an object Material A solid, liquid or a gas Melting When a material changes from a solid to a liquid. It is a reversible change Solidifying When a material changes from a liquid to a solid. It is a reversible change Reversible change A change where no new materials are made. It is possible to get back the original materials 1 What happens when we mix different materials? A change is reversible (physical) if you can get the original substances back. In reversible changes no new materials are made. Dissolving is a reversible change. A change is irreversible (chemical) if new materials are made. In irreversible changes new materials are made. A change is usually irreversible if a gas is made. Some materials dissolve when you put them into water, and some do not. Salt dissolves if you put it into water. You cannot see the salt any more, but you can tell it is still there because the water tastes salty. The dissolved salt and the water make a solution. If you let the water in the solution evaporate, the salt will be left behind. Some materials do not dissolve if you put them in water. A solid that does not dissolve can be separated from the mixture by filtering. Salt changes when you add it to water, but you can get the salt back again. The change is a reversible change. Some changes cannot be changes back again. They are called irreversible changes. Concrete is made by mixing cement with gravel and water. When the concrete dries it forms a new material, which sets and becomes hard. You cannot ‘unmix’ the concrete to get the cement, gravel and water back. This is an irreversible change. Another example of a substance that becomes hard after it is mixed with water is; Plaster of Paris. Some materials fizz when you put them into water or other liquids. The material changes, and part of it turns into a gas. The gas makes bubbles in the liquid. Changes like this are irreversible. Baking powder is used to make cakes rise. When baking powder is mixed with water it forms bubbles of gas. The bubbles make foam on top of the water. Other examples of substances which fizz (give out carbon dioxide gas) when we mix them with water are; Vitamin C tablets, indigestion tablets and liver salt. 2 What happens to materials when you change temperature? Heating and cooling some materials can cause them to change. Some changes caused by heating are irreversible. Changes caused by cooling are usually reversible Heat can make some materials change. If you heat ice, it melts and turns into liquid water. This change is reversible, because you can change the liquid water back into a solid again by cooling it down. Some changes caused by heating are not reversible. Heating changes cake mixture into a cake. You cannot ‘uncook’ a cake, so this change is irreversible. You can also change materials by cooling them down, but changes caused by cooling are usually reversible. You can freeze water to make ice, but the ice thaws and turns back into a liquid a liquid again when you let it warm up. The water Cycle: Melting Ice Evaporating Water Freezing Vapour Condensing 3 More irreversible changes Mixing acids with alkalis Rusting Burning When an acid is mixed with an alkali, a salt is produced. Sometimes carbon dioxide gas is also produced. This is an irreversible change. Acid + Alkali Salt + Carbon dioxide Examples of acids: vinegar and lemon juice Examples of alkalis: bicarbonate of soda, washing soda and marble. Rusting is also an irreversible change, where Iron (Steel) takes oxygen from the air and water and starts to make the yellow rust patches. The yellow rust is a substance called iron Oxide. Burning is an irreversible change, where carbon dioxide, water vapour are always produced. What happens when a candle burns? Flame Wax gas Wick Liquid wax Solid wax The wick is set alight. This makes the wax hot, so it starts to melt. The molten wax creeps up the wick. Now it gets so hot and changes into wax gas which burns using oxygen from the air, giving out carbon dioxide and water vapour. 4 Burning The Fire Triangle Fire Safety The Fire Triangle: Oxygen: From the air Heat: Source of ignition e.g. flame, matches, lighter or an electric spark. Fuel: material to be burned e.g. wood, paper, gas, benzene, etc. Fire safety: 1. All long hair has to be tied up. 2. Loose clothing must be tucked in. 3. Always use a sand tray. 4. Use a small candle and make sure it is standing securely in the sand tray. 5. Don’t hold the material to be burned with your hands. Use a forceps. 6. Only burn small pieces of materials. 7. Keep paper and all flammable substances away from the fire. 8. Work at a safe distance. 9. Keep your eyes on the burning candle. 10. Never sit beside a burning candle. 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26