Problem & Hypothesis
advertisement

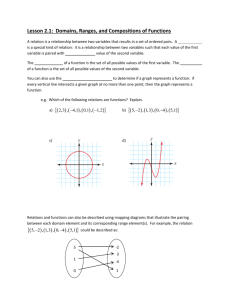
Problem & Hypothesis Jon Prueter Problem: When comparing plywood, composite, drywall, and spruce wood to block the most sound from the getting to opposite side of the piece of material, which will produce the quietest sound? Hypothesis: If you compare plywood, composite, drywall, and spruce wood to block the most sound, then composite will block the most sound. Materials: 1’ x 1’ sheet of plywood (1 inch thick) 1’ x 1’ sheet of drywall (1 inch thick) 1’ x 1’ sheet of spruce wood (1 inch thick) 1’ x 1’ sheet of composite (1 inch thick) 2 clamps that must extend past a foot 4, 1’ x 1’ sheets of clear plastic (1/2 inch thick) Decimeter Stereo Powered dill, with 1/8 thick bit and Phillips bit 10, 1 inch deep, by ¼ inch thick screws Power supply Paper and pencil for recording data Setup: 1’ x 1’ sheet of plywood, drywall, spruce, or composite. 4 clear pieces of platstic to form 3 sides and a top connected with screws. KEY Stereo Clamps (one on each side) Screws Decimeter placed on ground centered in the box Variables: Control: The level of sound without any type of material placed in front of the decimeter in the box. Independent: The different types of material (plywood, drywall, spruce, or composite) placed in front of the decimeter in the box. Dependent: The level of sound recorded from the different types of material used to block the sound. Constant: Distance from speaker to decimeter, distance from the material to the decimeter, where the decimeter is placed in the box, level of sound played out of the speaker (specify). Procedure: 1. Take the four pieces of 1’ x 1’ sheets of clear plastic and lay them out. 2. Take three of them and create a “C” shape using two screws to connect each side with screws by pre-drilling two holes on each side (see setup picture). 3. Place the fourth piece on the top of the already constructed shape and screw down by drilling three holes on each side and connect them with screws (when placed on the ground, only on side should not be covered). 4. Place the speaker of the stereo on foot away from the beginning of the plastic box. 5. Place the decimeter inside the box so that it is centered depending on the size of the decimeter. 6. Place your first type of material being tested on the side that is not already covered that should be facing the speaker. Using the two clamps, clamps the piece of material to the back of the plastic box, so the clamps are halfway up the side of the box. Do this for both sides and make sure the clamp is tight enough so that the material will not fall. 7. Play the sound out of the speaker (specify the sound level) that should be the same for each trial for twenty seconds. After every five seconds record the noise level indicated on the decimeter. Repeat this four times for every trial. Average all the readings for each different trial performed. 8. Repeat steps 6 and 7 for all four of the materials being tested, using 7 trials for each material. 9. Record data. Results: Type of material Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Trial 4 Trial 5 Trial 6 Trial 7 Average of 7 trials Plywood Drywall Spruce wood Composite Teacher Comments: This is looking very good. Nice set up diagram! Specify what level of sound you will be setting the stereo at. All you need now is the decimeter. I will be sending an email to all science teachers to see if we can get one. Once we have that you will be good to go.