Monroe County Middle School Detailed Pacing Guide Grade Level
advertisement

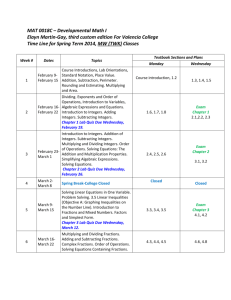
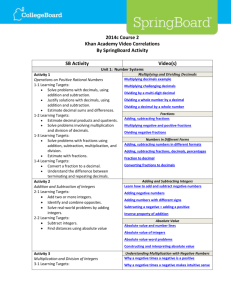
Monroe County Middle School Detailed Pacing Guide Grade Level: 7th Unit Title Content: Pre-Algebra / Mathematics Key Concepts Vocabulary Detailed by Unit Common Core Standards 7.NS.1 7.NS.3 Time Allotted Unit #1 The Number System Part 1 ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS Rational numbers can be represented in multiple ways and are useful when examining situations involving numbers that are not whole. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS In what ways can rational numbers be useful? KEY IDEAS reading/labeling a number line adding/subtracting integers modeling adding/subtracting integers balancing checkbook activity integer basketball activity using positive/negative chips adding/subtracting integers word problems modeling open responses absolute value additive inverse integer negative opposite positive rational number August Unit #2 The Number System Part 2 ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS Rational numbers can be represented in multiple ways and are useful when examining situations involving numbers that are not whole. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS In what ways can rational numbers be useful? KEY IDEAS multiplying integers dividing integers integer board game multiplying/dividing integers word problems using long division terminating/repeating decimals modeling open responses absolute value additive inverse complex fraction integer negative opposite positive rational number repeating decimal terminating decimal 7.NS.2 7.NS.3 September Unit #3 Fractions ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS Fractions are an important concept and very useful for discussions about measurement, probability, and data. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS In what ways can fractions be useful? KEY IDEAS changing improper fractions to mixed numbers changing mixed numbers to improper fractions adding/subtracting fractions adding/subtracting fractions word problems multiplying/dividing fractions multiplying/dividing fractions word problems open responses equivalent fractions greatest common factor improper fraction least common multiple mixed number rational number reciprocal 7.NS.3 October Unit #4 Decimals and Conversions ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS Believe it or not, fractions, decimals, and percents are all related. You will use these basic functions for the rest of your life. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS In what ways can decimals and conversions be useful? KEY IDEAS adding/subtracting decimals adding/subtracting decimals word problems multiplying/dividing decimals multiplying/dividing decimals word problems converting fractions to decimals/percents converting decimals to percents/fractions converting percents to fractions/decimals decimals percent 7.NS.2 7.NS.3 7.RP.3 October & November Unit #5 Ratios and Proportional Relationships ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS Ratios and proportional relationships are used to express how quantities are related and how quantities change in relation to each other. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How can ratios and proportional relationships be used to determine unknown quantities? KEY IDEAS definition of ratio/proportion writing a ratio setting up proportions definition of unit unit rate unit analysis apply knowledge to tables/graphs/similar figures constant of proportionality equivalent ratios origin proportional relationship rate ratio unit rate 7.RP.1 7.RP.2 7.RP.3 November & December Unit #6 Expressions and Equations ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS Algebraic expressions and equations are used to model real-life problems and represent quantitative relationships, so that the numbers and symbols can be mindfully manipulated to reach a solution or make sense of the quantitative relationships. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How can algebraic expressions and equations be used to model, analyze, and solve mathematical situations? KEY IDEAS variables coefficients constants difference between equations/expressions writing expressions verbally/algebraically writing equations verbally/algebraically solving for the variable using scales to model algebraic equations solving for the variable: one-step equations solving for the variable: two-step equations coefficient equation expression inequality like terms linear expression rational number variable 7.EE.1 7.EE.2 7.EE.3 7.EE.4 January & February working with inequalities graphing inequalities on a number line solving one-step inequalities solving two-step inequalities Unit #7 Using Probability ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS The rules of probability can lead to more valid and reliable predictions about the likelihood of an event occurring. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How is probability used to make informed decisions about uncertain events? KEY IDEAS finding probability “certain” events “impossible” events different between probability/chance event/complement theoretical probability experimental probability coin activity sample space counting principle compound events dependent/independent events permutations/combinations chance combination complement compound event counting principle dependent events event experimental probability factorial independent events likely outcome permutation sample space theoretical probability tree diagram unlikely 7.SP.5 7.SP.6 7.SP.7 7.SP.8 February & March Unit #8 Geometry Part 1 ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS Geometric attributes (such as shapes, lines, angles, figures, and planes) provide descriptive information about an object’s properties and position in space and support visualization and problem solving. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How does geometry better describe objects? KEY IDEAS identifying rays/segments/lines right/acute/obtuse angles angles that are complementary/supplementary adjacent/vertical/congruent angles scalene/isosceles/equilateral triangles right/acute/obtuse triangles classifying polygons regular/irregular polygons special quadrilaterals difference between square/rectangle trapezoid/parallelogram/rhombus congruent polygons identifying parts of a circle constructing circle graphs constructing perpendicular lines finding bisector/section bisector/midpoint acute triangle circle graph complementary equilateral triangle isosceles triangle obtuse triangle parallel lines parallelogram rectangle regular polygon rhombus right triangle scalene triangle square supplementary trapezoid 7.G.1 7.G.2 7.G.3 7.G.5 March compass activity Unit #9 Part 2 ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS Geometric attributes (such as shapes, lines, angles, figures, and planes) provide descriptive information about an object’s properties and position in space and support visualization and problem solving. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How does geometry better describe objects? KEY IDEAS estimating perimeter area finding height/base of parallelograms finding perimeter/area of parallelograms finding perimeter/area of triangles finding area of trapezoids finding area of irregular shapes finding circumference/area of circles perfect square/square root the Pythagorean Theorem classifying 3-dimensional figures drawing 3-dimensional figures finding surface area/volume of prisms finding surface area/volume of cylinders using nets activity finding geometry in the real world activity area circumference cone cylinder hypotenuse irrational number net perimeter prism pyramid Pythagorean Theorem sphere square root surface area three-dimensional figure volume 7.G.1 7.G.3 7.G.4 7.G.6 March & April Unit #10 Displaying and Analyzing Data ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS The rules of probability can lead to more valid and reliable predictions about the likelihood of an event occurring. ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How is probability used to make informed decisions about uncertain events? KEY IDEAS displaying data using frequency tables/line plots/histograms interpreting data using spreadsheets using double bar graphs/double line graphs working with stem-and-leaf plots identifying random samples writing survey questions survey activity identifying populations identifying misleading graphs/statistics drawing/interpreting scatter plots biased question cell double bar graph double line graph frequency table histogram legend line plot negative trend no trend population positive trend random sample sample scatter plot spreadsheet stem-and-leaf plot 7.SP.1 7.SP.2 7.SP.3 7.SP.4 April & May