What is the Ring of Fire?
advertisement

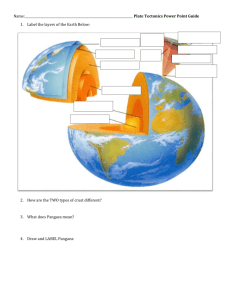
PLATE TECTONICS STUDY GUIDE: 1. What evidence did Alfred Wagner use to support his theory of continental drift? the shape of the continents, fossil evidence, matching rock types and geologic structures, and evidence of ancient climate patterns 2. Why do you think people didn't believe continental drift theory when Wagner first explained it? Wegener could not come up with an acceptable way to explain how the continents moved 3. Who were the two scientist that brought forth supporting evidence to Wagner's theroy, and what was their evidence? ARTHUR HOLMES AND HARRY HESS 4. What are the three different types of plate boundaries, describe each type? -- where new crust is generated as the plates pull away from each other. boundaries -- where crust is destroyed as one plate dives under another. -- where crust is neither produced nor destroyed as the plates slide horizontally past each other. 5. Give an example of a location on Earth where each type of plate boundary is present. Divergent boundary-The volcanic country of Iceland, which straddles the Mid-Atlantic Ridge Convergent-Off the coast of South America along the PeruChile trench, the oceanic Nazca Plate is pushing into and being subducted under the continental part of the South American Plate. Transform-example the San Andreas fault zone in California. 6. What are the three different types of convergent plate boundaries? Oceanic/continental; oceanic/oceanic; continental/continental 7. Give an example of a location on Earth where each type of convergent plate boundaries occur. South American plate-Andes Mtns.; The Himalayan mountain range 8. Explain what plate tectonics and ocean trenches have in common? Subduction zone where one plate goes under the other. 9. How old are the rocks off the east coast of North America relative to the rocks right along the mid atlantic ridge, why do you think this is the case? the age of the rocks increases as one moves away from the rift zone. The midoceanic ridge is the primary site for sea-floor spreading. 10. What is a convection current or cell, describe how it works (use a picture if you want)? the plate-driving force is the slow movement of hot, softened mantle that lies below the rigid plates. 11. What are the two main sources of heat inside the Earth? Just as a solid metal like steel, when exposed to heat and pressure, can be softened and take different shapes, so too can solid rock in the mantle when subjected to heat and pressure in the Earth's interior over millions of years. 12. What types of tectonic forces create mountains? Two plates pushing together, convergent boundaries 13. What are horsts and grabens, and where can they be found? horst and graben, elongate fault blocks of the Earth’s crust that have been raised and lowered, 14. Describe how the mountains across the Utah and Nevada were formed? The mountains of the Great basin were formed by plate spreading in that part of the North American Continent 15. What are two bad things that can happen as a result of plate tectonics, how did plate tectonics cause these events? Most earthquakes and volcanic eruptions do not strike randomly but occur in specific areas, such as along plate boundaries. 16. What are three good things that plate tectonics provide for humans, how do plate tectonics provide these things? Many of the Earth's natural resources of energy, minerals, and soil are concentrated near past or present plate boundaries. The utilization of these readily available resources have sustained human civilizations, both now and in the past. EXTRA CREDIT: What is the Ring of Fire? The Ring of Fire is the most seismically and volcanically active zone in the world.