Fin 335 Summer 10 Test 2
advertisement

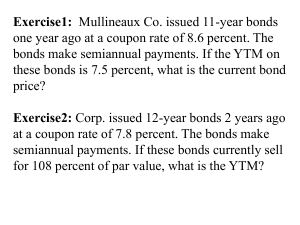
FIN 335 Test II – Chp 5-8 Name:________________________________________________ Summer 2010 Dr. Clay M. Moffett 1. The principal amount of a bond that is repaid at the end of the loan term is called the: A. face value. B. premium value. C. clean price. D. dirty price. E. compounded price. 2. The coupon rate for a bond is best defined as the: A. annual interest divided by the current market price. B. annual coupon divided by the dirty market price. C. annual interest divided by the clean market price. D. semi-annual interest divided by the par value. E. annual interest divided by the face value. 3. The annual interest on a bond divided by the bond's market price is called the: A. yield to maturity. B. yield to call. C. total yield. D. current yield. E. required yield. 4. Amy found a bond lying in a street. She picked it up, detached the appropriate bond coupon, and collected the current interest payment. Which type of bond did Amy find? A. bearer B. coupon C. street D. registered E. secure 5. A debenture is: A. long-term debt secured by fixed assets of the borrower. B. long-term debt secured by real estate. C. unsecured debt that generally matures in ten years or more. D. unsecured debt that generally matures in less than ten years. E. any type of debt that is short-term in nature. 6. A call provision in a bond agreement grants the issuer the right to: A. call the bondholder to determine if he or she would like to extend the term of the bond agreement. B. replace the bonds with equity securities. C. change the coupon rate provided the bondholders are notified in advance. D. buy back the bonds on the open market prior to maturity. E. repurchase the bonds prior to maturity at a pre-specified price. 7. A bond that pays no interest payments and sells at a deep discount is called a(n) _____ bond. A. callable B. income C. zero coupon D. convertible E. tax-free 8. The Fisher effect expresses the relationship between: A. the yield to call and the yield to maturity. B. the current yield and the yield to call. C. coupon and real rates. D. real and nominal rates. E. nominal and coupon rates. 9. A $1,000 face value bond is currently quoted at 93.7. The bond pays semiannual payments of $32.50 and matures in 8 years. What is the coupon rate? A. 3.25 percent B. 4.89 percent C. 5.00 percent D. 6.50 percent E. 7.56 percent 10. The 8.5 percent annual coupon bonds of Eberly, Inc. are selling for $930.12. The bonds have a face value of $1,000 and mature in 9 years. What is the yield to maturity? A. 4.84 percent B. 5.24 percent C. 8.12 percent D. 9.31 percent E. 9.70 percent 11. The Trading Depot has $1,000 face value bonds outstanding with a market price of $980. The bonds pay interest annually, mature in 8 years, and have a yield to maturity of 7.339 percent. What is the current yield? A. 7.00 percent B. 7.14 percent C. 7.34 percent D. 7.59 percent E. 7.88 percent 12. The Bailey Brothers want to issue 20-year, zero coupon bonds that yield 9 percent. What price should it charge for these bonds if the face value is $1,000? A. $157.25 B. $163.70 C. $178.43 D. $194.49 E. $202.64 13. The voting system whereby a shareholder can cast all of his or her votes for a single candidate for the board of directors is called _____ voting. A. proxy B. aggregate C. cumulative D. straight E. condensed 14. If I grant another individual the right to vote on my behalf for the directors of a corporation, I am voting by: A. the straight method. B. the cumulative method. C. consent. D. proxy. E. preference. 15. A broker is an agent who: A. trades on the floor of an exchange for himself or herself. B. buys and sells from inventory. C. offers new securities for sale to dealers only. D. mediates sales between dealers. E. arranges transactions among investors. 16. The price of a stock at year 5 can be expressed as: A. P0 g5. B. D0 (1 + R)5. C. P1 (1 + R)5. D. D6 / (R g). E. D5 / (R g). 17. NASDAQ is a(n): A. electronic dealer market. B. electronic broker market. C. market based on specialists. D. dealer market with a single market maker. E. electronic ECN. 18. Sid's Video Store will pay an annual dividend of $2.15 next month. The company just announced that future dividends will be increasing by 1.5 percent annually. How much are you willing to pay for one share of this stock if your required return is 14 percent? A. $15.36 B. $16.13 C. $17.20 D. $18.06 E. $19.42 19. B&T, Inc. is expected to pay its first annual dividend five years from now. That payment will be $3.10 a share. Starting in year six, the company will increase the dividend by 2 percent per year. The required return is 15 percent. What is the value of this stock today? A. $11.86 B. $12.09 C. $13.63 D. $14.66 E. $15.71 20. Anthony's Appliances pays a constant quarterly dividend of $.35 per share. How much are you willing to pay for one share if you require a 9 percent rate of return? A. $3.89 B. $7.78 C. $11.67 D. $15.56 E. $19.44 21. A series of equal cash flows that occur at the beginning of each time period for a limited number of time periods is called a(n): A. ordinary annuity. B. beginning annuity. C. annuity due. D. perpetuity. E. perpetuity due. 22. Which one of the following is an annuity, but not a perpetuity? A. unequal payments each month for 18 months B. payments of equal amount each quarter forever C. unequal payments each year forever D. equal payments every six months for 48 months E. unending equal payments every other month 23. Roger just financed some new furniture through his credit union. His loan requires payments of $185 a month for 3 years. Assuming that all payments are paid timely, his last payment will pay off the loan in full. What type of loan does Roger have? A. amortized B. perpetual C. pure discount D. lump sum E. interest-only 24. CNP, Inc. is considering a project that will produce cash inflows of $12,000 in year one, $27,600 in year two, and $48,100 in year three. What is the present value of these cash inflows if the company assigns the project a discount rate of 10.5 percent? A. $58,372.13 B. $64,999.91 C. $69,113.58 D. $71,824.90 E. $76,370.51 25. Steven can afford car payments of $250 a month for 60 months. The bank will lend him this money at 6.2 percent interest. How much can Steven borrow? A. $12,568.63 B. $12,869.39 C. $13,672.38 D. $14,104.91 E. $14,770.27 26. A loan disclosure, as required by law, states that a credit card has an interest rate of 18.2 percent. Interest is compounded on a quarterly basis. What is the effective annual rate? A. 16.84 percent B. 16.96 percent C. 17.08 percent D. 19.48 percent E. 19.64 percent 27. The discount rate that causes the net present value of a project to equal zero is called the: A. yield to maturity. B. required return. C. market rate. D. internal rate of return. E. average accounting return. 28. Which one of the following is the preferred method of analyzing a proposed investment? A. payback B. profitability index C. accounting rate of return D. internal rate of return E. net present value 29. Which one of the following statements is correct? A. The payback period is computed based on the present value of each of a project's cash flows. B. The payback rule states that you should accept a project if the payback period is less than one year. C. The payback rule works best when applied to mutually exclusive decisions. D. The payback rule is biased in favor of short-term investments. E. The payback period considers the timing and amount of all of a project's cash flows. 30. Which one of the following methods of analysis has the least value from a financial point of view? A. profitability index B. net present value C. average accounting return D. modified internal rate of return E. internal rate of return 31. Chance, Inc. is considering a project with an initial cost of $1 million. The project will not produce any cash flows for the first two years. Starting in year 3, the project will produce cash inflows of $625,000 a year for four years. This project is risky, so the firm has assigned it a discount rate of 20 percent. What is the net present value? A. -$243,117.95 B. -$63,681.07 C. $123,582.71 D. $348,299.25 E. $617,959.10 32. Sue and Tina are both considering the same project with the cash flows shown below. Sue is content earning 10 percent on the project but Tina wants to earn at least 14 percent. Who, if either, should accept this project? A. Sue, but not Tina B. Tina, but not Sue C. Sue, Tina can go either accept or reject as her NPV is zero D. neither Sue nor Tina E. both Sue and Tina 33. A project has the following cash flows. What is the internal rate of return? A. 12.46 percent B. 13.97 percent C. 14.08 percent D. 15.39 percent E. 16.20 percent 34. What is the payback period for a $37,000 investment with the following cash flows? A. 3.51 years B. 3.89 years C. 4.22 years D. 4.73 years E. This project never pays back Fin 335 Summer 10 Test 2 Key 1. The principal amount of a bond that is repaid at the end of the loan term is called the: A. face value. b. premium value. c. clean price. d. dirty price. e. compounded price. 2. The coupon rate for a bond is best defined as the: a. annual interest divided by the current market price. b. annual coupon divided by the dirty market price. c. annual interest divided by the clean market price. d. semi-annual interest divided by the par value. E. annual interest divided by the face value. 3. The annual interest on a bond divided by the bond's market price is called the: a. yield to maturity. b. yield to call. c. total yield. D. current yield. e. required yield. 4. Amy found a bond lying in a street. She picked it up, detached the appropriate bond coupon, and collected the current interest payment. Which type of bond did Amy find? A. bearer b. coupon c. street d. registered e. secure 5. A debenture is: a. long-term debt secured by fixed assets of the borrower. b. long-term debt secured by real estate. C. unsecured debt that generally matures in ten years or more. d. unsecured debt that generally matures in less than ten years. e. any type of debt that is short-term in nature. 6. A call provision in a bond agreement grants the issuer the right to: a. call the bondholder to determine if he or she would like to extend the term of the bond agreement. b. replace the bonds with equity securities. c. change the coupon rate provided the bondholders are notified in advance. d. buy back the bonds on the open market prior to maturity. E. repurchase the bonds prior to maturity at a pre-specified price. 7. A bond that pays no interest payments and sells at a deep discount is called a(n) _____ bond. a. callable b. income C. zero coupon d. convertible e. tax-free 8. The Fisher effect expresses the relationship between: a. the yield to call and the yield to maturity. b. the current yield and the yield to call. c. coupon and real rates. D. real and nominal rates. e. nominal and coupon rates. 9. A $1,000 face value bond is currently quoted at 93.7. The bond pays semiannual payments of $32.50 and matures in 8 years. What is the coupon rate? a. 3.25 percent b. 4.89 percent c. 5.00 percent D. 6.50 percent e. 7.56 percent 10. The 8.5 percent annual coupon bonds of Eberly, Inc. are selling for $930.12. The bonds have a face value of $1,000 and mature in 9 years. What is the yield to maturity? a. 4.84 percent b. 5.24 percent c. 8.12 percent d. 9.31 percent E. 9.70 percent 11. The Trading Depot has $1,000 face value bonds outstanding with a market price of $980. The bonds pay interest annually, mature in 8 years, and have a yield to maturity of 7.339 percent. What is the current yield? a. 7.00 percent B. 7.14 percent c. 7.34 percent d. 7.59 percent e. 7.88 percent 12. The Bailey Brothers want to issue 20-year, zero coupon bonds that yield 9 percent. What price should it charge for these bonds if the face value is $1,000? a. $157.25 b. $163.70 C. $178.43 d. $194.49 e. $202.64 13. The voting system whereby a shareholder can cast all of his or her votes for a single candidate for the board of directors is called _____ voting. a. proxy b. aggregate C. cumulative d. straight e. condensed 14. If I grant another individual the right to vote on my behalf for the directors of a corporation, I am voting by: a. the straight method. b. the cumulative method. c. consent. D. proxy. e. preference. 15. A broker is an agent who: a. trades on the floor of an exchange for himself or herself. b. buys and sells from inventory. c. offers new securities for sale to dealers only. d. mediates sales between dealers. E. arranges transactions among investors. 16. The price of a stock at year 5 can be expressed as: a. P0 g5. b. D0 (1 + R)5. c. P1 (1 + R)5. D. D6 / (R g). e. D5 / (R g). 17. NASDAQ is a(n): A. electronic dealer market. b. electronic broker market. c. market based on specialists. d. dealer market with a single market maker. e. electronic ECN. 18. Sid's Video Store will pay an annual dividend of $2.15 next month. The company just announced that future dividends will be increasing by 1.5 percent annually. How much are you willing to pay for one share of this stock if your required return is 14 percent? a. $15.36 b. $16.13 C. $17.20 d. $18.06 e. $19.42 19. B&T, Inc. is expected to pay its first annual dividend five years from now. That payment will be $3.10 a share. Starting in year six, the company will increase the dividend by 2 percent per year. The required return is 15 percent. What is the value of this stock today? a. $11.86 b. $12.09 C. $13.63 d. $14.66 e. $15.71 20. Anthony's Appliances pays a constant quarterly dividend of $.35 per share. How much are you willing to pay for one share if you require a 9 percent rate of return? a. $3.89 b. $7.78 c. $11.67 D. $15.56 e. $19.44 21. A series of equal cash flows that occur at the beginning of each time period for a limited number of time periods is called a(n): a. ordinary annuity. b. beginning annuity. C. annuity due. d. perpetuity. e. perpetuity due. 22. Which one of the following is an annuity, but not a perpetuity? a. unequal payments each month for 18 months b. payments of equal amount each quarter forever c. unequal payments each year forever D. equal payments every six months for 48 months e. unending equal payments every other month 23. Roger just financed some new furniture through his credit union. His loan requires payments of $185 a month for 3 years. Assuming that all payments are paid timely, his last payment will pay off the loan in full. What type of loan does Roger have? A. amortized b. perpetual c. pure discount d. lump sum e. interest-only 24. CNP, Inc. is considering a project that will produce cash inflows of $12,000 in year one, $27,600 in year two, and $48,100 in year three. What is the present value of these cash inflows if the company assigns the project a discount rate of 10.5 percent? a. $58,372.13 b. $64,999.91 C. $69,113.58 d. $71,824.90 e. $76,370.51 25. Steven can afford car payments of $250 a month for 60 months. The bank will lend him this money at 6.2 percent interest. How much can Steven borrow? a. $12,568.63 B. $12,869.39 c. $13,672.38 d. $14,104.91 e. $14,770.27 26. A loan disclosure, as required by law, states that a credit card has an interest rate of 18.2 percent. Interest is compounded on a quarterly basis. What is the effective annual rate? a. 16.84 percent b. 16.96 percent c. 17.08 percent D. 19.48 percent e. 19.64 percent 27. The discount rate that causes the net present value of a project to equal zero is called the: a. yield to maturity. b. required return. c. market rate. D. internal rate of return. e. average accounting return. 28. Which one of the following is the preferred method of analyzing a proposed investment? a. payback b. profitability index c. accounting rate of return d. internal rate of return E. net present value 29. Which one of the following statements is correct? a. The payback period is computed based on the present value of each of a project's cash flows. b. The payback rule states that you should accept a project if the payback period is less than one year. c. The payback rule works best when applied to mutually exclusive decisions. D. The payback rule is biased in favor of short-term investments. e. The payback period considers the timing and amount of all of a project's cash flows. 30. Which one of the following methods of analysis has the least value from a financial point of view? a. profitability index b. net present value C. average accounting return d. modified internal rate of return e. internal rate of return 31. Chance, Inc. is considering a project with an initial cost of $1 million. The project will not produce any cash flows for the first two years. Starting in year 3, the project will produce cash inflows of $625,000 a year for four years. This project is risky, so the firm has assigned it a discount rate of 20 percent. What is the net present value? a. -$243,117.95 b. -$63,681.07 C. $123,582.71 d. $348,299.25 e. $617,959.10 32. Sue and Tina are both considering the same project with the cash flows shown below. Sue is content earning 10 percent on the project but Tina wants to earn at least 14 percent. Who, if either, should accept this project? a. Sue, but not Tina b. Tina, but not Sue c. Sue, Tina can go either accept or reject as her NPV is zero d. neither Sue nor Tina E. both Sue and Tina 33. A project has the following cash flows. What is the internal rate of return? a. 12.46 percent B. 13.97 percent c. 14.08 percent d. 15.39 percent e. 16.20 percent 34. What is the payback period for a $37,000 investment with the following cash flows? a. 3.51 years b. 3.89 years c. 4.22 years d. 4.73 years E. This project never pays back