4-5 ch5
advertisement

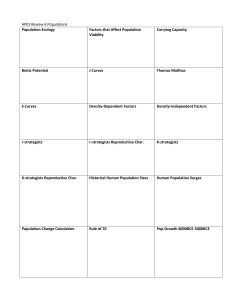
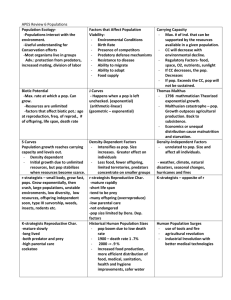
Warm-up: (10-19-15) *ch.5 CW/CG and rubric out for stamp! Read the article on Parachuting Cats. Answer the questions in your warm-up Do not copy the questions No complete sentences Remember to answer the questions on Task 5 of Turkey trouble Be sure to label your graphs (x and y axis) or you wont get a stamp. Chapter 5-5 Population Ecology Goals for today: Contrast biotic potential and environmental resistance Contrast exponential and logistic growth curves Contrast density dependent and independent factors Describe stable, irruptive, cyclic, and irregular population curves Community or Population Ecology? Eastern screech owls bring live blind snakes to their nests to live with them. Babies grow faster and stronger with the snake present. Biotic Potential Biotic potential and environmental resistance determine carrying capacity. Biotic potential: pop.’s capacity for growth intrinsic rate of increase (r): rate of growth with unlimited resources. High intrinsic rate of increase means: Many offspring Reproduce early in life Reproduce often Short generation time What are some examples of organisms that have a high intrinsic rate of increase? Can a population increase its size indefinitely? No! there are limits… Limiting factors: limit pop. growth What are some limiting factors? Environmental Resistance Environmental Resistance: factors that limit pop. growth. Ex. Competition This is like (+,-) feedback Both the biotic potential and environmental resistance determine the carrying capacity. Carrying capacity (K): the max. pop. an area can sustain without being degraded What two factors determine carrying capacity? Exponential model Doesn’t take into account limiting factors: food, space, waste removal. Only accurate prediction for short period of time. What is the shape of a graph showing exponential growth? Why are the turkeys in trouble in Task 1? Exponential model Exponential model: describes a population that increases rapidly after only a few generations. Ex. Bacteria. # of indiv. time Logistic model Accounts for limiting factors. Birth and death rates are not constant. Moves closer to carrying capacity (K) Logistic model # of indiv. time Region A: pop. growing exponentially Region B: death rate inc./birth rate dec. Region C:stabilizing; death rate/birth rate equal. Exceeding Carrying Capacity: If you exceed carrying capacity, what are your options? 1. Move 2. Switch Habits 3. Decline in Size The population crash will not happen right away. What is this called? In 1911, 25 reindeer (4 males and 21 females) were introduced onto St. Paul island. At that time there were no predators of the deer on the island and hunting of the reindeer was not permitted. By 1938, there were about 2,000 reindeer on St. Paul Island. Guess what happened next???? By 1950, only ____ deer were left. Population Density and Population Change A population’s density can affect how rapidly it can grow or decline. Density dependent factors Density independent factors Density dependent Ex. Food shortage, disease Density independent factors: pop. reduced by a factor that doesn’t depend on pop. size. Ex. Natural disasters Competition is a density-_____ factor Hurricane? Ebola? Flood? Mudslide? Types of Population Curves in Nature Stable Irruptive Cyclic (boom-and-bust) Irregular Stable: fluctuates slightly above and below carrying capacity. Irruptive: explodes and then crashes to a more stable level. What type of feedback is seen in the crash part of this curve? Cyclic: fluctuates regularly a.k.a. boom-and-bust Irregular: erratic changes (possibly due to drastic changes to the habitat) Ex. Insect populations in severe winters Check for Understanding: 1. List 2 examples of density independent factors. 2. The logistic growth curve looks like the letter ____. 3. Describe a stable population curve. 4. Describe an irruptive population curve.