Name Date Grade 8 Science Group ____ D21. Explain how the
advertisement

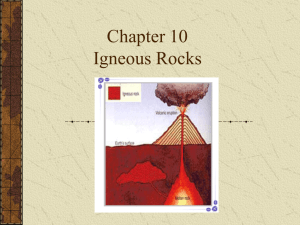
Name __________________________ Date __________________ Grade 8 Science Group ____ D21. Explain how the internal energy of the Earth causes matter to cycle through the magma and the solid earth IGNEOUS ROCKS Read the information below on “Igneous Rocks”. Then answer the questions which follow by writing the letter of the correct answer on the space to the left. Igneous rocks (from the Greek word for fire) form from when hot, molten rock (magma) crystallizes and solidifies. The melt originates deep within the Earth near active plate boundaries or hot spots, then rises toward the surface. Igneous rocks are divided into two groups, intrusive or extrusive, depending upon where the molten rock solidifies. Intrusive (or plutonic) igneous rock forms when magma is trapped deep inside the Earth. Great globs of molten rock rise toward the surface. Some of the magma may feed volcanoes on the Earth's surface, but most remains trapped below, where it cools very slowly over many thousands or millions of years until it solidifies. Slow cooling means the individual mineral grains have a very long time to grow, so they grow to a relatively large size. Intrusive rocks have a coarse grained texture. Granite is an igneous rock that is composed of four minerals. These minerals are quartz, feldspar, mica, and usually hornblende. Granite forms as magma cools far under the earth's surface. Because it hardens deep underground it cools very slowly. This allows crystals of the four minerals to grow large enough to be easily seen by the naked eye. Extrusive (or volcanic) igneous rock is produced when magma exits and cools outside of, or very near the Earth's surface. These are the rocks that form at erupting volcanoes and oozing fissures. The magma, called lava when molten rock erupts on the surface, cools and solidifies almost instantly when it is exposed to the relatively cool temperature of the atmosphere. Quick cooling means that mineral crystals don't have much time to grow, so these rocks have a very fine-grained or even glassy texture. Hot gas bubbles are often trapped in the quenched lava, forming a bubbly, vesicular texture. Obsidian is a very shiny natural volcanic glass. When obsidian breaks it fractures with a distinct conchoidal fracture. Obsidian is produced when lava cools very quickly. The lava cools so quickly that no crystals can form. When people make glass they melt silica rocks like sand and quartz then cool it rapidly by placing it in water. Obsidian is produced in nature in a similar way. Pumice is a light, porous volcanic rock that forms during explosive eruptions. It resembles a sponge because it consists of a network of gas bubbles frozen amidst fragile volcanic glass and minerals. _____1. The word, Igneous, means __(1)__ in Greek. a. fire b. rock c. crust d. pebble _____ 2. Igneous rocks are grouped according to where the __(2)__ rock becomes solid. a. minerals b. igneous c. trapped d. melted _____3. Another name for Intrusive rock is __(3)__ rock. a. sedimentary b. plutonic c. volcanic d. metamorphic _____4. Intrusive rock results from __(4)__ cooling. a. fast b. speedy c. slow d. no _____5. Due to this rate of cooling, intrusive rocks have __(5)__ sized crystals. a. large b. no c. small d. tiny c. obsidian d. pumice _____6. An example of an intrusive igneous rock is a. granite b. basalt ____7. Another name for Extrusive rock is __(7)__ rock. a. sedimentary b. plutonic c. volcanic d. metamorphic _____8. Extrusive rock results from __(8)__ cooling which produces very small crystals. a. fast b. slow c. mediocre d. exhaustive _____9. An example of an extrusive igneous rock which has a glassy texture is a. granite b. basalt c. obsidian d. pumice ____10. __(10)__ becomes trapped in cooling lava to give pumice its sponge-like look. a. gas b. lava c. grains d. minerals