Assessment
advertisement

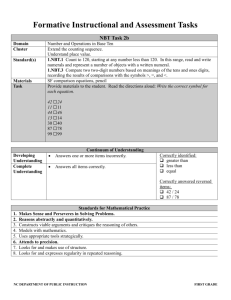
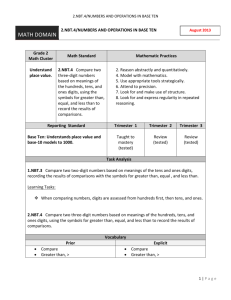
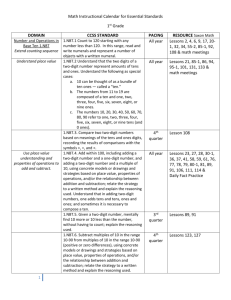
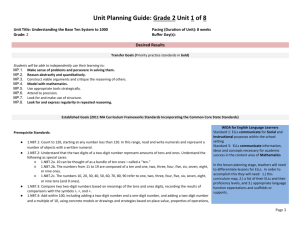
Student Name: Standard Code: EL1-MA-NBT.03.00.0 Teacher Name: Total # possible: Date: 12 Mastery #: 10 Score: Name_____________________________________ EL1-MA-NBT.03.00.0 Task 3a Find the value of each base ten blocks and write the total on the line. 3) Draw the following numbers in base ten blocks. Draw a ten as a long skinny rectangle and a one as a small square. 53 81 17 Name_____________________________________ EL1-MA-NBT.03.00.0 Task 3b Name_____________________________________ EL1-MA-NBT.03.00.0 Task 3c Write the correct symbol for each equation. < = > 1) 42 24 2) 11 11 3) 44 46 4) 87 78 5) 99 99 NBT Task 3a Domain Cluster Standard(s) Materials Task Developing Understanding Complete Understanding 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Number and Operations in Base Ten Understand place value. 1.NBT.03.00.0 Understand that the two digits of a two-digit number represent amounts of tens and ones. Understand the following as special cases: 1.NBT.03.A.0 10 can be thought of as a bundle of ten ones — called a “ten.” 1.NBT.03.B.0 The numbers from 11 to 19 are composed of a ten and one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine ones. 1.NBT.03.C.0 The numbers 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 refer to one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine tens (and 0 ones). BLM and pencil Direct students to count the number of base ten blocks and write the total in expanded form. Continuum of Understanding Incorrectly represents two-digit numbers in groups of ones and tens. Incorrectly writes two-digit numbers in groups of ones and tens. Correctly represents two-digit numbers in groups of ones and tens. Correctly writes two-digit numbers in groups of ones and tens. Standards for Mathematical Practice Makes Sense and Perseveres in Solving Problems. Reasons abstractly and quantitatively. Constructs viable arguments and critiques the reasoning of others. Models with mathematics. Uses appropriate tools strategically. Attends to precision. Looks for and makes use of structure. Looks for and expresses regularity in repeated reasoning. Strategy(ies) Used: Counts groups of tens Count groups of ones NBT Task 3b Domain Cluster Standard(s) Materials Task Number and Operations in Base Ten Extend the counting sequence. Understand place value. 1.NBT.03.00.0 Understand that the two digits of a two-digit number represent amounts of tens and ones. Understand the following as special cases: 1.NBT.03.E.0 Compare two two-digit numbers based on meanings of the tens and ones digits, recording the results of comparisons with the symbols >, =, and <. BLM comparison cards, pencil Cut out the comparison cards and the symbol cards. Show the student card #1 (42 ☐ 51). Then show the student the symbol cards (>, =, <). Say: Which symbol do you need to use to make this sentence true? After the student selects and places the symbol card, say: read your sentence to me. Repeat with cards #2-4. Developing Understanding Complete Understanding 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Continuum of Understanding Uses an incorrect symbol for one or more items. Uses symbols correctly but reads one or more equations incorrectly. Uses incorrect symbol but reads the sentence as a true equation (e.g., 42 > 51 and reads “42 is less than 51”). Uses the correct symbol for all items. Reads all equations correctly. Standards for Mathematical Practice Makes sense and perseveres in solving problems. Reasons abstractly and quantitatively. Constructs viable arguments and critiques the reasoning of others. Models with mathematics. Uses appropriate tools strategically. Attends to precision. Looks for and makes use of structure. Looks for and expresses regularity in repeated reasoning. Correctly uses symbols: > < = Correctly reads symbols: >: greater than <: less than =: equals, the same amount as, the same as NBT Task 3c Domain Cluster Standard(s) Materials Task Number and Operations in Base Ten Extend the counting sequence. Understand place value. 1.NBT.03.00.0 Understand that the two digits of a two-digit number represent amounts of tens and ones. Understand the following as special cases: 1.NBT.03.E.0 Compare two two-digit numbers based on meanings of the tens and ones digits, recording the results of comparisons with the symbols >, =, and <. SF comparison equations, pencil Provide materials to the student. Read the directions aloud: Write the correct symbol for each equation. 42 ☐ 24 11 ☐ 11 44 ☐ 46 13 ☐ 14 30 ☐ 40 87 ☐ 78 99 ☐ 99 Developing Understanding Complete Understanding Continuum of Understanding Answers one or more items incorrectly. Answers all items correctly. Correctly identified: greater than less than equal Correctly answered reversed items: 42 / 24 87 / 78 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Standards for Mathematical Practice Makes Sense and Perseveres in Solving Problems. Reasons abstractly and quantitatively. Constructs viable arguments and critiques the reasoning of others. Models with mathematics. Uses appropriate tools strategically. Attends to precision. Looks for and makes use of structure. Looks for and expresses regularity in repeated reasoning.