INTRODUCTION. Apixaban(ELIQUIS) is an oral anticoagulant for
advertisement

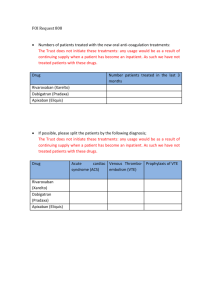
INTRODUCTION. Apixaban(ELIQUIS) is an oral anticoagulant for the treatment of venous thromboembolic events. It is a direct factor Xa inhibitor. BIOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES It is chemically described as 1-(4methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-[4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl]-4,5,6,7tetrahydro-1H-pyrazolo[3,4c]pyridine-3-carboxamide. Its molecular formula is C25H25N5O4, which corresponds to a molecular weight of 459.5. Apixaban is a white to pale-yellow powder. At physiological pH (1.2–6.8), apixaban does not ionize; its aqueous solubility across the physiological pH range is ~0.04 mg/mL. MECHANISM OF ACTION. It is an anticoagulant that works by blocking the action of factor Xa. Factor Xa is an important protein in the coagulation cascade that causes blood to clot. Reducing the action of factor Xa reduces the ability of blood to clot. DOSING AND ADMINISTRATION Apixaban (eliquis) tablets are available for oral administration in strengths of 2.5 mg and 5 mg of apixaban with the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, sodium lauryl sulfate, and magnesium stearate. The film coating contains lactose monohydrate, hypromellose, titanium dioxide, triacetin, and yellow iron oxide (2.5 mg tablets) or red iron oxide (5 mg tablets). The usually recommended dose is 5 mg by mouth twice daily. The dose for individuals 80 years or older, weighing less than or equal to 60 kg, or with reduced kidney function is 2.5 mg twice daily. INDICATIONS. 1. Reduction Of Risk Of Stroke And Systemic Embolism In Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation: The recommended dose of ELIQUIS for most patients is 5 mg taken orally twice daily. 2. Prophylaxis Of Deep Vein Thrombosis Following Hip Or Knee Replacement Surgery: The recommended dose of ELIQUIS is 2.5 mg taken orally twice daily. The initial dose should be taken 12 to 24 hours after surgery. In patients undergoing hip replacement surgery, the recommended duration of treatment is 35 days. In patients undergoing knee replacement surgery, the recommended duration of treatment is 12 days. CONTRAINDICATIONS. ELIQUIS is contraindicated in patients with the following conditions: 1.Active pathological bleeding 2.Severe hypersensitivity reaction to ELIQUIS (e.g., anaphylactic reactions) PRECAUTIONS Increased Risk Of Stroke With Discontinuation Of ELIQUIS In Patients With Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation Spinal/Epidural Anesthesia Or Puncture Patients with Prosthetic Heart Valves Pregnancy, (category B),labour and delivery Nursing mothers Pediatric age group Geriatric age group End stage renal disease patients maintained with haemodialysis SIDE EFFECTS: (though rare) Blood in the eyes blood in the urine bloody or black, tarry stools bruising or purple areas on the skin confusion constipation coughing up blood decreased alertness difficulty swallowing dizziness fainting fast heartbeat headache hives itching joint pain or swelling nausea and vomiting nosebleeds puffiness or swelling of the eyelids or around the eyes, face, lips, or tongue redness of the eye severe stomach pain shortness of breath skin rash tightness in the chest unusual tiredness or weakness vomiting of blood or material that looks like coffee grounds DRUG INTERACTIONS. Blood levels of apixaban are increased by drugs that reduce the activity of the liver enzymes that break down apixaban. The dose of apixaban should be reduced to 2.5 mg twice daily if combined with drugs that reduce the activity of these enzymes. Examples include ketoconazole (Nizoral, Extina, Xolegel, Kuric), itraconazole (Sporanox), ritonavir (Norvir), and clarithromycin (Biaxin, Biaxin XL) Drugs that increase the breakdown of apixaban reduce its blood levels and its effectiveness. Examples include carbamazepine (Tegretol, Tegretol XR, Equetro, Carbatrol), rifampin, St. John's Wort, and phenytoin (Diantin, Dilantin-125. They should not be combined with apixaban. Administration of other drugs that also can prevent clotting will increase the risk of bleeding during treatment with apixaban. Examples include aspirin, heparin, chronic use of NSAIDs, and drugs that breakdown blood clots (fibrinolytics). CONCLUSION Apixaban is a relatively new oral anticoagulant, which is still being studied for use in various clinical scenarios, but it has however been shown to be superior to warfarin in preventing stroke or systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation. It also causes less bleeding and lower mortality.