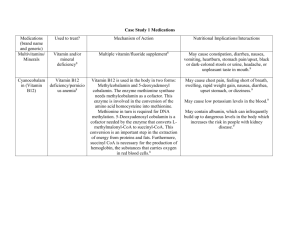
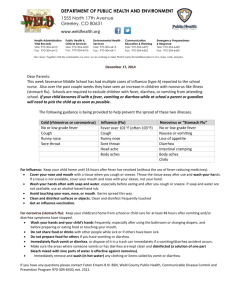
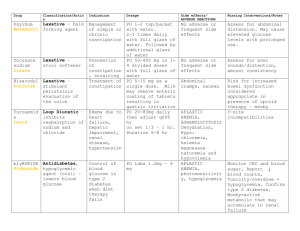
Food-related-illnesses
advertisement

SALMOMELLA ENTERITIS A gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria Lives in intestines & peri-reproductive tissue (ovaries, milk glands, etc.) Disease caused by infection with Salmonella Symptoms include diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramps Starts 12-2 hours after infection & last 4-7 days Severe cases can result in hospitalization & can infect the blood and lead to death Eggs identified as primary vehicle for SE infection Exterior of eggs contaminated by contact with feces Interior of eggs contaminated via tranovarian transmission In 1990’s it was estimated that 7% of egg farms had SE and 1 in 20,000 eggs were positive for SE STRAPHYLOCOCCAL AUREUS o A type of bacteria that is gram positive and is non-moving small round shaped or non-motile cocci. o Cocci or Coccus refers to the spherical shape o Commonly found on the skin, hair, nose, & throat o Thrives with warm temperatures on protein o Contamination from equipment, food prep surfaces, food handler not washing o Killed by cooking or pasteurization o Don’t prepare food in you have a nose or eye infection or wounds or skin infections on your hands or wrists o Symptoms are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, cramps, fever ESCHERICHIA COLI ENTERITIS (E. coli) Enteritis is inflammation or swelling of the intestines Most common cause of traveler’s diarrhea, a condition that is marked by loose stools, abdominal cramping, nausea, vomiting, and bloating Bacteria normally found in intestines of healthy people & amimals From contaminated water or food, especially raw vegetables & undercooked ground beef; unpasteurized milk, cheese or apple cidar Infection starts when you swallow a tiny amount of human or animal feces Caused by food preparer not washing hands after using the toilet CLOSTRIDIUM BOTULINUM (BOTULISM) Nerve toxin produced by the bacterium spores, a rod-shaped organisms grown best in low oxygen conditions Foodborne form often comes from improperly home-canned foods with low acid content, such as asparagus, green beans, beets and corn Found in improper handling during commercial manufacture of food Also found in fermented fish & other aquatic game foods Even potatoes wrapped in aluminum foil that are not properly kept hot or cold can develop this baterium Honey can contain this bacteria, therefore Honey should not be given with infant under 12 months old Bacteria can be found on floors, carpet, and countertops Toxin circulates in the blood & causes paralysis of the respiratory system and can cause respiratory failure; antitoxin is available Toxin is destroyed by high temperatures; boil food for 10 minutes Prevention: proper food processing; clean surfaces & equipment CAMPYLOBACTER JEJUNI Gram-negative slender, curved, and motile rod bacterium Causes illness called Campylobacteriosis aka gastroenteritis Symptoms: abdominal pain, nausea, headaches, muscle pain, diarrhea with blood & lasts 7-10 days Most common cause of diarrheal illness in US Found in raw chicken, raw milk, cows, flies, nonchlorinated water, feces Prevention: Cook poultry thoroughly, wash hands, clean equipment to prevent cross-contamination HEPATITIS A A virus (HAV) that causes liver disease Spread through food or water contaminated by feces Can be prevented by vaccination Source is also from raw or undercooked shellfish, or other foods that were prepared by an infected food handler Symptoms are diarrhea, jaundice, fever, abdominal pain, nausea, and loss of appetite Good personal hygiene and proper sanitation can help prevent the spread LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES Bacteria found in soil and water and some animals (poultry, cows) Sources-deli meats, hot dogs, raw milk, raw sprouts, cheese, seafood Grows even in cold temperatures Cooking and pasteurization will kill it Symptom: fever, stiff neck, confusion, weakness, vomiting, diarrhea Especially dangerous for pregnant women and infants Keep uncooked meats separate from fruits & vegetables Wash hand, keep surfaces clean Cook raw meats & fish thoroughly Can be treated with antibiotics CRYPTOSPORIDIUM o Waterborne microscopic parasite commonly known as “Crypto” o Very tolerant to chlorine disinfectants o Common in drinking water and recreational water o Can live in the intestine of humans and animal o Spread by contact with feces exposure, soil, water, or surfaces o Symptoms: stomach cramps, dehydration, nausea, vomiting, fever, weight loss o Treatment: Nitazoxanide given to treat diarrhea o It is very contagious! Don’t swim and children should be removed from day care until the diarrhea has stopped. o Wash your hands after using the toilet. NOROVIRUS Virus that is also called Norwalk Virus-the winter vomiting virus You can have this illness many times in your life and is the most common cause of acute gastroenteritis in the US Causes diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain Spread direct contact with infected person, contaminated food and drinks, and on surfaces Source: produce, shellfish, ready-to-eat foods, or any food contaminated with vomit or feces from an infected person Wash hands after using the toilet; avoid food preparation with bare hands; clean & disinfect surfaces No specific treatment; resolves within a few days Can be serious for young children or the elderly PREVENTION: WASH YOUR HANDS thoroughly after using the bathroom or changing diapers and before preparing or eating food. WASH YOUR HANDS after contact with animals or their environments (at farms, petting zoos, fairs, even your own backyard). COOK meats thoroughly. Ground beef and meat that has been needletenderized should be cooked to a temperature of at least 160°F/70˚C. It’s best to use a thermometer, as color is not a very reliable indicator of “doneness.” AVOID raw milk, unpasteurized dairy products, and unpasteurized juices (like fresh apple cider). AVOID swallowing water when swimming or playing in lakes, ponds, streams, swimming pools, and backyard “kiddie” pools. PREVENT cross contamination in food preparation areas by thoroughly washing hands, counters, cutting boards, and utensils after they touch raw meat. If food is prepared more than two hours before serving, keep hot foods hot (over 140° F) and cold foods cold (40° F or under). Store cooked food in a wide, shallow container and refrigerate as soon as possible. Keep HOT food HOT and COLD for COLD