sutures, needles, stapling devices terminology
advertisement

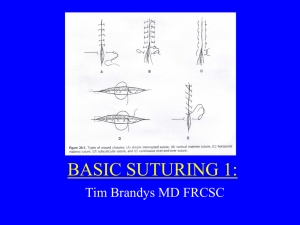
SUTURES, NEEDLESTERMINOLOGY TERM ABSORBABLE NONABSORBABLE RATE of ABSORPTION TYPES OF ABSORPTION ANASTOMOSIS APPROXIMATE PRIMARY SUTURE LINE SECOND SUTURE LINE SUTURE BOOK SUTURE ROUTINE BURIED SUTURE INTERRUPTED SUTURE CONTINUOUS SUTURE is also called “RUNNING -can be “locked” (blanket) “OVER AND OVER” HORIZONTAL/VERTICAL MATTRESS DEEP SUTURE SUBCUTICULAR SUTURE RETENTION OR STAY SUTURE Bridges/bolsters/rubber shods protect skin LIGATURE Free Tie – cut strand placed in surgeon’s open hand Reel Tie – continuous tie on spool Tie on passer – cut strand placed on clamp and handed to surgeon SYNTHETIC NATURAL gut – sheep submucosa Silk from silkworm Cotton – cotton plant Steel – carbon, iron metals Cotton – cotton plant NEEDLES – named by point Blunt – Rounded body tapers to blunt. Friable tissue use – liver, kidney, spleen DEFINITION Sutures absorbed by the body. The rate of absorption depends on suture type. Sutures that are NOT absorbed by the body. Time it takes to be dissolved by tissues Hydrolysis – suture breakdown by water in body tissues = only synthetics Phagocytosis – suture breakdown by enzymes in body tissues = only naturals To join lumen structures by suture/staples Bringing of edges together for better alignment of tissue for wound closure. Direct wound closure – 1st Intention Supporting suture line (see stay suture) Surgical towel containing multiple procedure sutures organized/ready for us Surgeon’s preference – same procedure = same sutures used (found on card) Stitch placed completely under surface Series of single stitches individually tied Series of stitches all tied at end of series. Suture placed in deep tissue layers Sutures placed under skin – knot seen only Second suture line to support and take pressure off primary line Used to tie off vessels or ducts. Secured by knotting. AKA = “ties” StickTie –swaged suture on needle holder AKA - Atraumatic Suture material man made from chemicals Suture material derived from nature. Cutting – 3 flat edges - skin, tendon, bone Taper – Rounded body tapers- Intestine, organs, muscle use. PRIMARY SUTURE LINE Sutures that directly hold wound together SECOND SUTURE LINE Supporting suture line – takes pressure off primary suture line (“stay” suture) Strand of material used to approximate tissue, ligate vessels or ducts Surgical towel containing multiple sutures to be used in procedure. Keeps different size ties organized and readily available Surgeon’s preference - Same routine = same suture Force of pull, measured in pounds, that knotted strand can withstand before it breaks. Determined by size and type of suture material. Ability of suture to move moisture along the length of its strand. Braided = wick Monofilament = no wick SUTURE SUTURE BOOK SUTURE ROUTINE TENSILE STRENGTH WICKING