Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI
advertisement
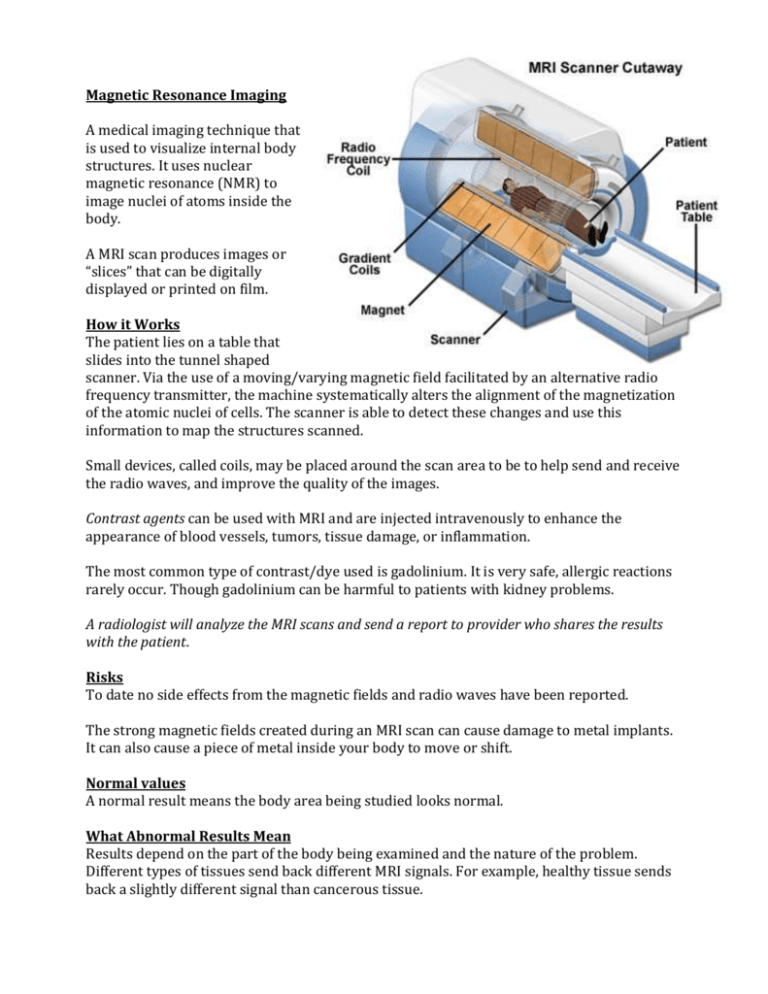
Magnetic Resonance Imaging A medical imaging technique that is used to visualize internal body structures. It uses nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to image nuclei of atoms inside the body. A MRI scan produces images or “slices” that can be digitally displayed or printed on film. How it Works The patient lies on a table that slides into the tunnel shaped scanner. Via the use of a moving/varying magnetic field facilitated by an alternative radio frequency transmitter, the machine systematically alters the alignment of the magnetization of the atomic nuclei of cells. The scanner is able to detect these changes and use this information to map the structures scanned. Small devices, called coils, may be placed around the scan area to be to help send and receive the radio waves, and improve the quality of the images. Contrast agents can be used with MRI and are injected intravenously to enhance the appearance of blood vessels, tumors, tissue damage, or inflammation. The most common type of contrast/dye used is gadolinium. It is very safe, allergic reactions rarely occur. Though gadolinium can be harmful to patients with kidney problems. A radiologist will analyze the MRI scans and send a report to provider who shares the results with the patient. Risks To date no side effects from the magnetic fields and radio waves have been reported. The strong magnetic fields created during an MRI scan can cause damage to metal implants. It can also cause a piece of metal inside your body to move or shift. Normal values A normal result means the body area being studied looks normal. What Abnormal Results Mean Results depend on the part of the body being examined and the nature of the problem. Different types of tissues send back different MRI signals. For example, healthy tissue sends back a slightly different signal than cancerous tissue. PROS/ Benefits It provides good contrast between soft tissues. It is used to determine pathological tissues (ie brain tumor) from normal tissues. It’s non invasive and harmless to patient. It’s safe to use during pregnancy, no fetal harm caused. There is no ionizing radiation like CT and X-Ray scans which cause biological damage. CONS/ Considerations It is very expensive You cannot scan a patient if they have irremovable metal implants, objects, etc. o Aneurism coils/clips, cochlear implant, pace maker, heart valve, shrapnel, etc. The MRI machine is very loud! The scan process can take from 30 minutes to 2 hours depending on type. Most MRI machines enclose the patient in a small space and can cause claustrophobia. The patient must remain still during the scan and remaining immobile and in a position ideal for the scan may cause patient discomfort. Precautions/Safety Have pt wear hospital gown or clothing without metal fasteners Ear protection headphones should be worn by patient during scan. Metal objects in the room will fly toward the opening of the machine where the patient is at high speeds and cause injury when scan is being done. MRI scans provide the ability to distinguish separate structures a small distance apart from each other (spatial resolution) similarly to a CT scan however the MRI scan provides the ability to distinguish the differences between two similar but not identical tissues (contrast resolution). X-ray does not clearly distinguish soft tissue. MRI CT Scan X- Ray References http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003335.htm www.mayoclinic.com/health/mri/MY00227