Direct Formation of Acetate from the Partial Oxidation of Ethylene on
advertisement

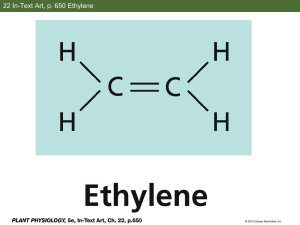
Supporting Information Direct Formation of Acetate from the Partial Oxidation of Ethylene on a Au/TiO2 Catalyst Isabel Xiaoye Green1, Monica McEntee1, Wenjie Tang2, Matthew Neurock1,2, and John T. Yates, Jr1,2. 1. Department of Chemistry, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA 22904 2. Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA 22904 1. Calibration for Gas Sample Analysis for Ethylene Oxide The samples were transferred to a Thermoquest CE Instruments Trace GC 2000 Series gas chromatography mass spectrometer (GC-MS) instrument with a 30 m GS-Q capillary column (Agilent Technologies, ID of 0.32 mm) for gas separation. Helium (Praxair, Ultralift) was filtered through a helium purifier and used as the carrier gas with a column flow rate set at 1.4 mL/min. The GC oven temperature program was set to 303 K for 10 minutes, and then heated at a rate of 5 K/min up to 373 K. Ions were detected in a Thermoquest Finnigan Voyager MS in electron impact positive ion (EI+) mode with a scan range from 10-250. The GC-MS was calibrated against standard ethylene oxide (C2H4O) solutions in dimethyl sulfoxide (10-3, 5x10-4, 10-4, 5x10-5, and 10-5 M solutions using a 0.5 μL sample volume) as shown in Figure S1(a). The number of C2H4O molecules detected for each concentration of the standard solution was acquired from the integrated area of the C2H4O elution peak for each gas chromatogram. One of the chromatograms, 5x10-4 M, is shown in Figure S1(b) with its corresponding mass spectrum averaged over 11.65-11.97 minutes of C2H4O elution in Figure S1(c). The limit of detection of the GC-MS was estimated to be ~3x1012 molecules, corresponding to 3x1015 molecules in the gas phase in the IR cell. Assuming an average Au particle size of ~3 nm and knowing the Au loading is ~8 wt%, we calculated the total amount of Au atoms at the perimeter to be ~1017 atoms in the 5 mg catalyst sample employed. If ~3x1015 ethylene oxide molecules were detected in our experiment in the ~2.3 L cell volume the detection limit would correspond to only ~3% of the total perimeter sites on the catalyst. 2. Measurement of Ethylene Oxide Production from Ethylene Oxidation on Au/TiO2 at 400K Gas samples were extracted from the vacuum cell using a 1 mL gas-tight syringe (Hamilton, Model 1001 SL SYR). The syringe enters through a PTFE rubber septum (Wilmad-LabGlass) which is screwed onto a homemade glass tube attached to the cell. A schematic of the tube and syringe is shown in Figure S2. The samples were extracted at 6, 20, 40, 60, 80 and 90 minutes during the ethylene partial oxidation experiment and transferred to the GC-MS for analysis. The GC oven temperature program is described above. 3. Adsorption of Ethylene The oxidation of ethylene proceeds by the initial adsorption of ethylene at potential sites at the Au/TiO 2 interface. Ethylene was examined at the Au, Ti5c and bridging oxygen sites at the interface. Ethylene was found to bind weakly in di-σ and π bound modes to the Au and and Ti5c sites, respectively (Figure S4). The adsorption energies for ethylene at Au (coordination number = 7) and Ti 5c were calculated to be -0.48 eV and -0.24 eV, respectively. # C2H4O molecules -1 Intensity (c s ) Calibration for C2H4O 14 1.5x10 14 1.0x10 13 5.0x10 0.0 0.5 L liquid samples -4 5x10 M 0.0 2.0x10 -4 4.0x10 -4 6.0x10 a -4 8.0x10 -4 1.0x10 -3 [C2H4O] (M) 6.0x10 6 4.0x10 6 -4 5x10 M C2H4O b 6 2.0x10 10.0 10.4 10.8 11.2 11.6 12.0 12.4 12.8 -1 Intensity (c s ) Elution Time (min) 1.5x10 6 1.0x10 6 29 Averaged Mass Spectrum from 11.65-11.97 min 15 5 5.0x10 0.0 44 25 50 c 75 100 125 m/z 150 175 200 225 250 Figure S1. Calibration of ethylene oxide in DMSO solution. (a). Calibration curve of ethylene oxide concentrations at 1x10-5 M, 5x10-5 M, 1x10-4M, 5x10-4 M and 1x10-3 M. (b). Gas chromatogram of 5x10-4 M ethylene oxide solution which was used for (a). (c). Mass spectrum averaged over 11.65-11.97 minutes of ethylene oxide elution, corresponding well to the literature cracking pattern for ethylene oxide (NIST Mass Spec Data Center SES, director "Mass Spectra" in NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg MD, 20899 http://webbook.nist.gov. Accessed 8 Jan 2013). To vacuum chamber Gas Extraction Setup Swaglok valve PTFE stop valve (Gas Tight) Glass Tube 1 mL Syringe Plunger with PTFE tip PTFE rubber septum w/plastic screw cap Figure S2. Schematic drawing of the gas extraction system for transfer of gas samples to the GC-MS. Figure S3. The model Au/TiO2 interface involving a 3x3 Au nano-rod covalently bonded to the bridging oxygen sites on the rutile TiO2 (110) surface support. A) top view, B) side view. Figure S4. Ethylene adsorption at a) Au site; b) perimeter Ti5c site.