unit 7 - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

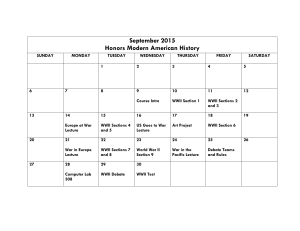
UNIT 7: POST WWII DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN POLICIES 1945-1989 FEBRUARY 11TH – MARCH 19TH 2009 Established Goals: All of you will be expected to: 11.8.2 Describe the significance of Mexican immigration and its relationship to the agricultural economy, especially in California. 11.8.5 Describe the increased powers of the presidency in response to the Great Depression, World War II, and the Cold War. 11.9.3 Trace the origins and geopolitical consequences (foreign and domestic) of the Cold War and containment policy, including the following: The era of McCarthyism, instances of domestic communism (e.g., Alger Hiss) and blacklisting The Truman Doctrine The Berlin Blockade The Korean War The Bay of Pigs invasion and the Cuban Missile Crisis Atomic testing in the American West, the “mutual assured destruction” doctrine, and disarmament policies The Vietnam War Latin American policy 11.9.4 List the effects of foreign policy on domestic policies and vice versa (e.g., protests during the war in Vietnam, the “Nuclear Freeze” movement). Understanding(s): Essential Question(s): Students will be able to understand that: - FDR expanded the powers of the executive (presidency) citing the need for decisive action in times - How did young people, of national emergency. These expanded powers were criticized, calling FDR’s terms the “imperial especially African presidency” and trying certain powers in court as unconstitutional. Americans and Latinos, - Smallpox was virtually eliminated through medical breakthroughs at the end of WWII. challenge the culture of - Truman decided to order an end to racial segregation in the military in 1948 in part because of the conformity following outstanding record of African Americans who served in the military during WWII. WWII? - The Cold War created paranoia about domestic communism that led to blacklisting of prominent people including the “Hollywood Ten.” Alger Hiss was accused of spying and perjury and imprisoned in 1950. - Should the President be - The federal government initiated the Bracero program during WWII in an effort to address the given extra power during urgent need for agricultural workers. periods of national - During the second half of the 20th century the largest source of labor in California agriculture was emergency? immigrants from Mexico. - The purpose of 1947 General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) was to expand international trade by reducing tariffs. - What threat did communism and socialism - President Truman dismissed Gen. MacArthur because of their disagreement over whether to invade Cuba. The Eisenhower doctrine of 1957 expanded the Truman doctrine in order to defend Israel. The Soviet Union escalated the “space race” by launching Sputnik in 1957. The Soviet Union did withdraw missiles from Cuba after the whole Bay of Pigs debacle in 1962. The Vietnam war was highly unpopular and created domestic discontent as well as international criticism (getting the Peace Corps kicked out of other countries as a form of protest). People who opposed the Vietnam War were called “doves” (as in the symbol of peace). Riots on college campuses such as Kent State and Jackson State happened after the U.S. invaded Cambodia during Cambodia during the Vietnam War. President Nixon tried to stop the criticism of the draft by creating a lottery system. President Nixon became known for his campaign slogans: “Appeal to the silent majority,” “law and order,” “less government,” and “peace with honor in Vietnam.” The U.N. statement of principles was based on the belief that an international peacekeeping organization could settle disputes without warfare. Eisenhower supported the establishment of the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization SEATO as an attempt to restrict communist aggression in Asia. A cause of the Korean War was North Korean forces, with Soviet approval, invading South Korea. The Truman Doctrine was a formal statement of intention of the U.S. to aid any country threatened by communism. The Cuban Missile Crises (1962) was the closest the U.S. and the Soviet Union actually came to fighting each other during the Cold War. The Truman Doctrine was a pledge on the part of the U.S. to help Turkey and Greece resist the spread of communism in the region. Changes in the balance of power among the three branches of government during the 20th century have resulted from the expansion of executive power during periods of crises. The 1964 joint resolution of Congress authorized the president to deploy troops into Vietnam. - - pose in the U.S.? How were the values of freedom and democracy proclaimed abroad betrayed at home? How has the U.S. role in the world shaped the idea of what it means to be “American” at home? All students will know the following key terms: McCarthyism, Alger Hiss, Blacklisting, Truman Doctrine, Berlin Blockade, Korean War, Bay of Pigs, Cuban missile crisis, atomic testing, Vietnam War, anti-war protests, Latin American policy, U.S. spending on defense and welfare, National debt, Federal and state spending on education, California Mater Plan, United Nations, International Declaration of Human Rights, International Monetary Fund, General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), NATO, SEATO, Reagan and the end of the Cold War, Middle East and Gulf War, Mexican-U.S. relations. Summative Assessments: - Origins of the Cold War debate 2/18 - Immigration debate 2/25 - Powers of the Presidency mock trial 2/26 - Communism debate ¾ - Latin American policies research paper 3/19 Other Evidence: - Cool War reading quiz. - Zinn: “A People’s War?” pp.407-442. - On-going teacher observations of student work and behavior - Entrance and exit tickets - Notebook checks 11TH GRADE U.S. HISTORY – FEBRUARY 2009 Sun Mon Wed Thu Fri Sat 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 WEEK ONE UNIT 7: Post WWII policies 11.8.2 Introductions to Unit 7 “WWII: A People’s War?” reading Pupil free day 15 WEEK THREE UNIT 7 11.8.5 16 23 Mexican immigration and CA economy The Cold War and the cool war. Reading Quiz 17 Cool War reading quiz No school 22 WEEK FOUR Unit 7 11.9.3 Tue 18 Origins of the Cold War debate 24 19 20 21 27 28 Mexican immigration Bracero program 25 Immigration / Guest Worker Debate Origins of the Cold War – U.S. and Russian perspectives. Nonconformity discussion. [Advisory trip] 26 Increased powers of the presidency. Mock trial 11th GRADE U.S. HISTORY – MARCH 2009 Sun Mon Tue 1 WEEK FIVE UNIT 7 11.9.3; 11.9.4 2 Wed Thu 3 Cold War containment policy at home 4 8 9 5 Sat 6 7 12 13 14 19 20 21 27 28 Korean war Truman doctrine Berlin blockade Cuban missile crises Communists were antiAmerican debate McCarthyism Alger Hiss Fri 10 11 WEEK SIX UNIT 7 Vietnam Cuban missile crises debate 15 WEEK SEVEN UNIT 7 22 16 17 Latin American Policy NAFTA GATT 23 Vietnam and student protest movement 18 Latin American Policy 24 25 Latin American Policy Research Paper Due 26